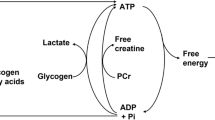
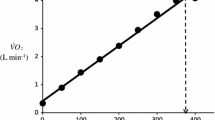
Abstract
We present a new model of the underlying dynamics of the oxygen uptake \(\dot VO_2 (\upsilon , t)\) kinetics for various exercise intensities. This model is in the form of a set of nonlinear coupled vector fields for the \(\ddot VO_2 (\upsilon , t)\) and \(\dot \upsilon \), the derivative of the exercise intensity with respect to time. We also present a new and novel means for calculating the oxygen demand, D(v, t), and hence also the oxygen deficit and debt, given the time series of the \(\dot VO_2 (\upsilon , t)\). This enables us to give better predictions for these values especially for when exercising at or close to maximal exercise intensities. Our model also allows us to predict the oxygen uptake time series given the time series for the exercise intensity as well as to investigate the oxygen uptake response to nonlinear exercise intensities. Neither of these features is possible using the currently used three-phase model. We also present a review of both the underlying physiology and the three-phase model. This includes for the first time a complete set of the analytical solutions of the three-phase model for the oxygen deficit and debt.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Astrand, P.O., Saltin, B., 1961. Oxygen uptake during the first minutes of heavy muscular exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 16(6), 971–976.
Astrand, P.O., Rodahl, K., Dahl, H.A., Stromme, S.B., 2003. Textbook of Work Physiology: Physiological Bases of Exercise. Human Kinetics, Champaign, IL.
Bangsbo, J., 1996a. Physiological factors associated with efficiency in high intensity exercise. Sports Med. 22(5), 299–305.
Bangsbo, J., 1996b. Oxygen deficit: A measure of the anaerobic energy production during intense exercise? Can. J. Appl. Physiol. 21(5), 350–363.
Bangsbo, J., 1998. Quantification of anaerobic energy production during intense exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 30(1), 47–52.
Bangsbo, J., Krustrup, P., Gonzalez-Alonso, J., Bonshel, R., Saltin, B., 2000. Muscle oxygen kinetics at onset of intense dynamic exercise in humans. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 279, R899–R906.
Barstow, T.J., 1994. Characterization of \(\dot VO_2 \) kinetics during heavy exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 26(11), 1327–1334.
Barstow, T.J., Mole, P.A., 1987. Simulation of pulmonary oxygen uptake during exercise in humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 63, 2253–2261.
Barstow, T.J., Mole, P.A., 1991. Linear and nonlinear characteristics of oxygen uptake kinetics during heavy exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 71(6), 2099–2106.
Barstow, T.J., Casaburi, R., Wasserman, K., 1993. O2 uptake kinetics and the O2 deficit as related to exercise intensity and blood lactate. J. Appl. Physiol. 75, 755–762.
Bearden, S.E., Moffatt, R.J., 2000. \(\dot VO_2 \) kinetics and the O2 deficit in heavy exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 88, 1407–1412.
Bernard, O., Maddio, F., Ouattara, S., Jimenez, C., Charpenet, A., Melin, B., Bittel, J., 1998. Influence of the oxygen uptake slow component on the energy cost of high-intensity submaximal treadmill running in humans. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 78, 578–585.
Billat, V.L., 2000. \(\dot VO_2 \) slow component and performance in endurance sports. Brit. J. Sports Med. 34(2), 83–85.
Billat, V.L., 2001a. Interval training for performance: A scientific and empirical practice. Special recommendations for middle and long distance running. Part I: Aerobic interval training. Sports Med. 31(1), 13–31.
Billat, V.L., 2001b. Interval training for performance: A scientific and empirical practice. Special recommendations for middle and long distance running. Part II: Anaerobic interval training. Sports Med. 31(12), 75–90.
Billat, V.L., Mille-Hamard, L., Demarle, A., Koralsztein, J., 2002. Effect of training in humans on off-and on-transient oxygen uptake kinetics after severe exhausting intensity runs. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 87, 496–505.
Billat, V.L., Bocquet, V., Slawinski, J., Laffitte, L., Demarle, A., Chassaing, P., Koralsztein, J.P., 2000. Effect of prior intermittent runs at vVO2max on oxygen kinetics during an all-out severe run in humans. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fitness 40, 185–194.
Borrani, F., Canadau, R., Millet, G.Y., Perrey, S., Fuchslocher, J., Bouillon, 2001. Is the \(\dot VO_2 \) slow component dependent upon progressive recruitment of fast-twitch fibres in trained runners. J. Appl. Physiol. 90, 2212–2220.
Brooks, G.A., Gaesser, G.A., 1980. End points of lactate and glucose metabolism after exhausting exercise. J. Appl. Physiol.: Respirat. Environ. Exerc. Physiol. 49, 1057–1069.
Brooks, G.A., Hittelman, K.J., Faulkner, J.A., Beyer, R.E., 1971. Temperature, skeletal muscle mitochondrial functions, and oxygen debt. Am. J. Physiol. 220, 1053–1059.
Casaburi, R., Barstow, T.J., Robinson, T., Wasserman, K., 1989a. Influence of work rate on ventilatory and gas exchange kinetics. J. Appl. Physiol. 67, 547–555.
Casaburi, R., Daly, J., Hansen, J.E., Effros, R.M., 1989b. Abrupt changes in mixed venous blood gas composition after the onset of exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 67, 1106–1112.
Costill, D., Kovaleski, J., Porter, D., Kirwan, J., Fielding, R., King, D., 1985. Energy expenditure during front crawl swimming: Predicting success in middle distance events. Int. J. Sports Med. 6(4), 266–270.
Coyle, E.F., Hamilton, M.T., Alonso, J.G., Montain, S.J., Ivy, J.L., 1991. Carbohydrate metabolism during intense exercise when hyperglycemic. J. Appl. Physiol. 70, 834–840.
Davies, C.T., Di Prampero, P.E., Cerretelli, P., 1972. Kinetics of the cardiac output and respiratory gas exchange during exercise and recovery. J. Appl. Physiol. 32, 618–625.
Engelen, M., Porszasz, J., Riley, M., Wasserman, K., Maehara, K., Barstow, T.J., 1996. Effects of hypoxic hypoxia on O2 uptake and heart rate kinetics during severe exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 81(6), 2500–2508.
Gaesser, G.A., Brooks, G.A., 1984. Metabolic bases of excess post-exercise oxygen consumption: A review. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 16, 29–43.
Gaesser, G.A., Poole, D.C., 1996. The slow component of oxygen uptake in humans. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 24, 35–70.
Guckenheimer, J., Holmes, P., 1983. Nonlinear Oscillations, Dynamical Systems and Bifurcations of Vector Fields. Springer-Verlag.
Hamilton, M.T., Alonso, J.G., Montain, S.J., Coyle, E.F., 1991. Fluid replacement and glucose infusion during exercise prevents cardiovascular drift. J. Appl. Physiol. 71, 871–877.
Harris, P., 1969. Lactic acid and the phlogiston debt. Cardiovasc. Res. 3, 381–390.
Hill, D.W., Ferguson, C.S., 1999. A physiological description of critical speed. Eur. J. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 79(3), 290–293.
Hill, A.V., Lupton, L., 1923. Muscular exercise, lactic acid and the supply and utilization of oxygen. Q. J. Med. 16, 135–171.
Hill, D.W., Stevens, E.C., 2001. The \(\dot VO_2 \) response to the onset of severe intensity exercise. Can. J. Appl. Physiol. 26(4), 350–355.
Hill, D.W., Poole, D.C., Smith, J.C., 2002. The relationship between power and time to achieve \(\dot VO_{2_{max} } \). Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 34(4), 709–714.
Kalis, J.K., Freund, B.J., Joyner, M.J., Jilka, S.M., Nitolo, J., Wilmore, J.H., 1988. Effect of B-blockade on the drift in O2 consumption during prolonged exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 64, 753–758.
Kantz, H., Schreiber, T., 1999. Nonlinear Time Series Analysis. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Karlsson, J., Saltin, B., 1970. Lactate, ATP and CrP in working muscles during exhausting exercise in man. J. Appl. Physiol. 29, 598–602.
Kindig, C.A., McDonough, P., Erickson, H.H., Poole, D.C., 2001. Effect of L-NAME on oxygen uptake kinetics during heavy-intensity exercise in the horse. J. Appl. Physiol. 91, 891–896.
Koga, S., 1990. Breath-by-breath gas exchange kinetics during constant load work. Ann. Physiol. Anthropol. 9(2), 163–166.
Krogh, A., Lindhard, J., 1913. The regulation of respiration and circulation during the initial stages of muscular work. J. Physiol. (Lond) 47, 112–136.
Krogh, A., Lindhard, J., 1919–1920. The changes in respiration at the transition from work to rest. J. Physiol. (Lond) 53, 431–437.
Lamarra, I., Whipp, B.J., Ward, S.A., Wasserman, K., 1987. Effect of interbreath fluctuations on characterizing exercise gas exchange kinetics. J. Appl. Physiol. 62, 2003–2012.
Langsetmo, I., Poole, D.C., 1999. \(\dot VO_2 \) recovery kinetics in the horse following moderate, heavy and severe exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 86, 1170–1177.
Langsetmo, I., Weigle, G.E., Fedde, M.R., Erickson, H.H., Barstow, T.J., Poole, D.C., 1997. \(\dot VO_2 \) kinetics in the horse during moderate and heavy exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 83, 1235–1241.
Linnarsson, D., 1974. Dynamics of pulmonary gas exchange and heart rate changes at start and end of exercise. Acta Physiol. Scand. Suppl. 415, 1–68.
MacDonald, M., Pedersen, P.K., Hughuson, R.L., 1997. Acceleration of \(\dot VO_2 \) kinetics in heavy submaximal exercise by hyperoxia and prior high-intensity exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 83(4), 1318–1325.
Mader, A., 2003. Glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation as a function of cytosolic phosphorylation state and power output of the muscle cell. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 88(4–5), 317–338.
Margaria, R., Mangili, F., Cuttica, F., Cerretelli, P., 1965. The kinetics of the oxygen consumption at the onset of muscular exercise in man. Ergonomics 8, 49–54.
Martin, D.E., Coe, P.N., 1997. Better Training for Distance Runners. Human Kinetics, Champaign, IL.
Medbo, J.I., Mohn, A.C., Tabata, I., 1988. Anaerobic capacity determined by maximal accumulated O2 deficit. J. Appl. Physiol. 64, 50–60.
Meyerhof, O., 1920. Die Energieumwandlungen im Muskel. II. Das Schicksal der Milchsäure in der Erholungsperiode des Muskels. Arch. Ges. Physiol. 182, 284–317.
Montpetit, R.R., Leger, L.A., Lavoie, J.M., Cazorla, G., 1981. \(\dot VO_2 \) peak during free swimming using the backward extrapolation of the O2 recovery curve. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 47(4), 385–391.
Noakes, T., 2003. Lore of Running. Discover the Science and Spirit of Running, 4th edition. Human Kinetics, Champaign, IL.
Obert, P., Cleuziou, C., Candau, R., Courteix, D., Lecoq, A.M., Guenon, P., 2000. The slow component of O2 uptake kinetics during high-intensity exercise in trained and untrained prepubertal children. Int. J. Sports Med. 21, 31–36.
Ozyener, F., Rossiter, H.B., Ward, S.A., Whipp, B.J., 2001. Influence of exercise intensity on the on-and off-transient kinetics of pulmonary oxygen uptake in humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 53(3), 891–902.
Paterson, D.H., Whipp, B.J., 1991. Asymmetries of oxygen uptake transients at the on-and offset of heavy exercise in humans. J. Physiol. (Lond) 443, 575–586.
Poole, D.C., 1994. Role of exercising muscle in slow component of \(\dot VO_2 \). Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 26(11), 1335–1340.
Poole, D.C., Barstow, T.J., Gaesser, G.A., Willis, W.T., Whipp, B.J., 1994. \(\dot VO_2 \) slow component: Physiological and functional significance. Med. Sci. Sport Exerc. 26(11), 1354–1358.
Potter, C.R., Childs, D.J., Houghton, W., Armstrong, N., 1999. Breath-to-breath noise in the ventilatory and gas exchange responses of children to exercise. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 80(2), 118–124.
Press, W.H., Teukolsky, S.A., Vetterling, W.T., Flannery, B.P., 1993. Numerical Recipes in C: The Art of Scientific Computing, 2nd edition. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Puente-Maestu, L., Abad, J.B., Godoy, R., Pérez-Parra, J.M., Gubillo, J.M., Whipp, B.J., 2002. Breath-by-breath fluctuations of pulmonary gas exchange and ventilation in COPD patients. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 87, 535–541.
Ren, J.M., Broderg, S., Sahlin, K., 1989. Oxygen deficit is not affected by the rate of transition from rest to submaximal exercise. Acta Physiol. Scand. 135, 545–548.
Rodriguez, F.A., 2000. Maximal oxygen uptake and cardiorespiratory response to maximal 400 m free swimming, running and cycling tests in competitive swimmers. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fitness. 40(2), 87–95.
Rodriguez, F.A., Mader, A., 2003. Energy metabolism during 400 m and 100 m crawl swimming: Computer simulation based on free swimming measurement. In: Chatard, J.C. (Ed.), Biomechanics and Medicine in Swimming IX. Publications de l’Universite de Saint-Etienne, Saint-Etienne, pp. 373–378.
Rodriguez, F.A., Keskinen, K.L., Keskinen, O.P., Malvela, M., 2003. Oxygen uptake kinetics during free swimming: A pilot study. In: Chatard, J.C. (Ed.), Biomechanics and Medicine in Swimming IX. Publications de l’Universite de Saint-Etienne, Saint-Etienne, pp. 379–384.
Rossiter, H.B., Howe, F.A., Ward, S.A., Kowalchuk, J.M., Griffiths, J.R., Whipp, B.J., 2000. Intersample fluctuations in phosphocreatine concentration determined by 31P-magnetic resonance spectroscopy and parameter estimation of metabolic responses to exercise in humans. J. Physiol. 528(2), 359–369.
Saltin, B., 1987. The physiological and biochemical basis of aerobic and anaerobic capacities in man; effect of training and range of adaption. In: Maehlum, S., Nilsson, S., Renstrom, P., (Eds.), An Update in Sports Medicine: Proceedings from the Second Scandinavian Conference in Sports Medicine. pp. 16–59.
Saltin, B., 1990. Anaerobic capacity: Past, present and prospective. In: Taylor, A., Gollmack, P.D. (Eds.), Biochemistry of Exercise VII. Human Kinetics, Champaign, IL, pp. 387–412.
Saltin, B., Gagge, A.P., Bergh, U., Stolwigk, J.A.J., 1972. Body temperatures and sweating during exhaustive exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 32(2), 635–643.
Saltin, B., Kim, C.K., Terrados, N., Larsen, H., Svendenhag, J., Rolf, C.J., 1995a. Morphology, enzyme activities and buffer capacity in leg muscles of Kenyan and Scandinavian runners. Scand. J. Med. Sports 5, 222–230.
Saltin, B., Larsen, H., Terrados, W., Bangsbo, J., Bak, T., Kim, C.K., Svedenhag, J., Rolf, C.J., 1995b. Aerobic exercise capacity at sea level and at altitude in Kenyan boys, junior and senior runners compared with Scandinavian runners. Scand. J. Med. Sports 5, 209–221.
Stainsby, W.N., Barclay, J.K., 1970. Exercise metabolism: O2 deficit, steady level O2 uptake and O2 uptake for recovery. Med. Sci. Sports 2, 177–186.
Stirling, J.R., 2000. Transport and bifurcation in a non-area preserving 2 dimensional map with applications to the discharge of pollution in an estuarine flow. Physica D 144, 169–193.
Stirling, J.R., 2003. Nonlinear dynamics, transport and the patchiness of clouds of pollution in an estuarine fluid flow. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst., Ser. B 3(2), 263–284.
Stirling, J.R., Zakynthinaki, M.S., 2004. Mathematical modelling of the physiological response to exercise (translated into Polish). Sport Wyczynowy bimonthly periodical (submitted for publication).
Stirling, J.R., Zakynthinaki, M.S., 2004. Stability and the maintenance of balance following a perturbation from quiet stance. Chaos 14(1), 96–105.
Wasserman, K., Whipp, B.J., Castagna, J., 1974. Cadriodynamic hyperpnea: Hyperpnea secondary to cardiac output increase. J. Appl. Physiol. 36, 457–464.
Wasserman, K., Hansen, J.E., Sue, D.Y., Casaburi, R., Whipp, B.J., 1999. Principles of Exercise Testing and Interpretation, Including Pathophysiology and Clinical Applications, third ed. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins.
Weissman, M.L., Jones, P.W., Oren, A., Lammarra, N., Whipp, B.J., Wasserman, K., 1982. Cardiac output increase and gas exchange at the start of exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 52, 236–244.
Weltman, A., 1995. The Blood Lactate Response to Exercise (Current Issues in Exercise Science). Human Kinetics, Champaign, IL.
Whipp, B.J., 1994. The slow component of O2 uptake kinetics during heavy exercise. Medi. Sci. Sports Exerc. 26(11), 1319–1326.
Whipp, B.J., Wasserman, K., 1972. Oxygen uptake kinetics for various intensities of constant load work. J. Appl. Physiol. 33, 351–356.
Whipp, B.J., Rossiter, H.B., Ward, S.A., 2002. Exertional oxygen uptake kinetics: A stamen or stamina? Biochem. Soc. Trans. 237–247.
Xing, H.C., Cochrane, J.E., Yamamoto, Y., Hughson, R.L., 1991. Frequency domain analysis of ventilation and gas exchange kinetics in hypoxic exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 71(6), 2394–2401.
Zakynthinaki, M.S., Stirling, J.R., 2004. Smoothing of physiological time series data using Fourier filtering: Application to the heart rate response to exercise (submitted for publication).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stirling, J.R., Zakynthinaki, M.S. & Saltin, B. A model of oxygen uptake kinetics in response to exercise: Including a means of calculating oxygen demand/deficit/debt. Bull. Math. Biol. 67, 989–1015 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bulm.2004.12.005
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bulm.2004.12.005