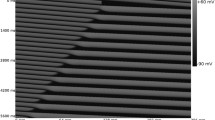
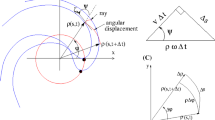
Abstract
Cardiac waves can fail to propagate when the membrane potential of the cells in the wavefront rises too slowly. The sodium channel inactivation gates play an important role in this process of propagation block. Simple models including inactivation gates can have travelling waves of constant form with two possible velocities. A stability analysis demonstrates that the slower velocity is always unstable, and in limited parameter regimes the faster velocity can also be unstable. Waves with the lower velocity propagate a finite distance before they dissipate due to this instability and this distance is calculated. The distance can be large suggesting that they might be seen in certain pathological conditions. The analytical results are compared with numerical simulations of the simplified model and a detailed cardiac ionic model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beeler, G. W. and H. Reuter (1977). Reconstruction of the action potential of ventricular myocardial fibres. J. Physiol. 268, 177–210.
Biktashev, V. N. (2002). Dissipation of the excitation wavefronts. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 168102.
Brugada, P. and J. Brugada (1992). Right bundle branch block, persistent st segment elevation and sudden cardiac death: a distinct clinical and electrocardiographic syndrome: a multicenter report. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 20, 1391–1396.
Carpenter, G. A. (1977). Periodic solutions of nerve impulse equations. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 58, 152–173.
Chen, Q. et al. (1998). Genetic basis and molecular mechanism for idiopathic ventricular fibrillation. Nature 392, 293–296.
Dockery, J. D. and J. P. Keener (1989). Diffusive effects of dispersion in excitable media. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 49, 539–566.
FitzHugh, R. A. (1960). Thresholds and plateaus in the Hodgkin-Huxley nerve equations. J. Gen. Physiol. 43, 867–896.
Hastings, S. P. (1975). On travelling wave solutions of the Hodgkin-Huxley equations. Arch. Rational Mech. Anal. 60, 229–257.
Hinch, R. (2002a). An analytical study of the physiology and pathology of the propagation of cardiac action potentials. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 78, 45–81.
Hinch, R., (2002b). Mathematical models of the heart. PhD thesis, Oxford University.
Hodgkin, A. L. and A. F. Huxley (1952a). The dual effect of membrane potential on sodium conductance in the giant axon of loligo. J. Physiol. 117, 497–506.
Hodgkin, A. L. and A. F. Huxley (1952b). A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerves. J. Physiol. 117, 507–544.
Kagiyama, Y., J. L. Hill and L. S. Gettes (1982). Interaction of acidosis and increased extracellular potassium on action potential characteristics and conduction in guinea pig ventricular muscle. Circ. Res. 51, 614–623.
Lapidus, L. and G. F. Pinder (1999). Numerical Solutions of Partial Differential Equations in Science and Engineering, Wiley.
Luo, C. H. and Y. Rudy (1994). A dynamicmodel of cardiac ventricular action potentials, i: simulations of ionic currents and concentration changes. Circ. Res. 74, 1071–1096.
Maginu, K. (1985). Geometrical characteristics associated with stability and bifurcations of periodic travelling waves in reaction-diffusion systems. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 45, 750–773.
McKean, H. P. (1970). Nagumo’s equation. Adv. Math. 4, 209.
Miller, R. N. and J. Rinzel (1981). The dependence of impulse propagation speed on firing frequency, dispersion, for the Hodgkin-Huxley model. Biophys. J. 34, 227–259.
Nagumo, J., S. Arimoto and S. Yoshizawa (1962). An active pulse transmission line simulating nerve axon. Proc. IRE 50, 2061.
Noble, D. (1960). Cardiac action and pacemaker potentials based on the Hodgkin-Huxley equations. Nature 188, 495–497.
Noble, D., A. Varghese, P. Kohl and P. Noble (1998). Improved guinea-pig ventricular cell model incorporating a diadic space, i K r and i K s, and length-and tension-dependent processes. Can. J. Cardiol. 14, 123–134.
Ockendon, J., S. Howison, A. Lacy and A. Movchan (1999). Applied Partial Differential Equations, Oxford University Press.
Rinzel, J. and J. B. Keller (1973). Traveling wave solutions of a nerve conduction equation. Biophys. J. 13, 1313–1337.
Shaw, R. M. and Y. R. Rudy (1997). Electrophysiological effects of acute myocardial ischaemia: a mechanistic investigation of action potential conduction and conduction failure. Circ. Res. 80, 124–138.
Tan, H. L., M. T. E. Bink-Boelkens, C. R. Bezzina, P. C. Viswanathan, G. C. M. BeaufortKrol, P. J. van Tintelen, M. P van den Berg, A. A. M. Wilde and J. R. Balser (2001). A sodium-channel mutation causes isolated cardiac conduction disease. Nature 409, 1043–1047.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hinch, R. Stability of cardiac waves. Bull. Math. Biol. 66, 1887–1908 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bulm.2004.05.004
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bulm.2004.05.004