Abstract
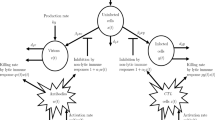
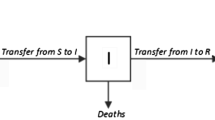
This paper introduces a model for the evolution of positive HIV population and manifestation of AIDS (acquired immunideficiency syndrome). The focus is on the nature of the transference rate of HIV to AIDS. Expert knowledge indicates that the transference rate is uncertain and depends strongly on the viral load and the CD4+ level of the infected individuals. Here, we suggest to view the transference rate as a fuzzy set of the viral load and CD4+ level values. In this case the dynamic model results in a fuzzy model that preserves the biological meaning and nature of the transference rate λ. Its behavior fits the natural history of HIV infection reported in the medical science domain. The paper also includes a comparison between the fuzzy model and a classic Anderson’s model using data reported in the literature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barros, L., R. C. Bassanezi and M. B. Leite (2003). The epidemiological models SI with fuzzy parameter of transmission. Comput. Math. Appl. 45, 1619–1628.
Brazilian Ministry of Health (2004). http://www.aids.gov.br.
Caetano, M. and T. Yoneyama (1999). A comparative evaluation of open loop and closed loop drug administration strategies in the treatment of AIDS. Acad. Brasil. Ciên. 71, 589–597.
Coutinho, F., L. F. Lopez, M. N. Burattini and E. Massad (2001). Modelling the natural history of HIV infection in individuals and its epidemiological implications. Bull. Math. Biol. 63, 1041–1062.
Jafelice, R., L. C. Barros, R. C. Bassanezi and F. Gomide (2002a). Fuzzy rules in asymptomatic HIV virus infected individuals model, in Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence and Applications Vol. 85, Ohmsha: IOS Press, pp. 208–215.
Jafelice, R., L. C. Barros, R. C. Bassanezi and F. Gomide (2002b). Modelos epidemiológicos com parâmetros subjetivos. Technical report, Department of Computer Engineering and Industrial Automation, FEEC, State University of Campinas (in Portuguese).
Jafelice, R., L. C. Barros, R. C. Bassanezi and F. Gomide (2003). Methodology to determine the evolution of asymptomatic HIV population using fuzzy set theory (submitted for publication).
Kandel, A. (1986). Fuzzy Mathematical Techniques with Applications, Addison-Wesley.
Krivan, V. and G. Colombo (1998). A non-stochastic approach for modeling uncertainty in population dynamics. Bull. Math. Biol. 60.
Murray, J. (1990). Mathematical Biology, Berlin: Springer.
Nguyen, H. and E. A. Walker (2000). A First Course in Fuzzy Logic, Chapman and Hall/CRC.
Novak, M. (1999). The mathematical biology of human infections. Conservation Ecol. 3.
Novak, M. and C. R. M. Bangham (1996). Population dynamics of immune responses to persistene viruses. Science 272.
Ortega, N., L. C. Barros and E. Massad (2003). Fuzzy gradual rules in epidemiology. Kybernetes: Int. J. Syst. Cybernetics 32, 460–477.
Pedrycz, W. and F. Gomide (1998). An Introduction to Fuzzy Sets: Analysis and Design, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Perelson, A. and P. W. Nelson (1999). Mathematical analysis of HIV-1 dynamics in vivo. SIAM Rev. 41, 3–44.
Peterman, T., D. P. Drotman and J. W. Curran (1985). Epidemiology of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome AIDS. Epidemiol. Rev. 7, 7–21.
Ralescu, D., Y. Ogura and S. Li (2001). Set defuzzification e choquet integral. Int. J. Uncertain. Fuzziness Knowl.-Based Syst. 9, 1–12.
Saag, M. (1995). Diagnóstico laboratorial da AIDS presente e futuro, in Tratamento Clínico da AIDS, 3rd edn., M. Sande and P. A. Volberding (Eds), Revinter, pp. 27–43. (in Portuguese).
Sugeno M. (1974). Theory of Fuzzy integrals and its applications, PhD thesis, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan.
Zadeh, L. (1965). Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control 8, 338–353.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jafelice, R.M., de Barros, L.C., Bassanezi, R.C. et al. Fuzzy modeling in symptomatic HIV virus infected population. Bull. Math. Biol. 66, 1597–1620 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bulm.2004.03.002
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bulm.2004.03.002