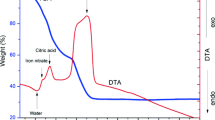
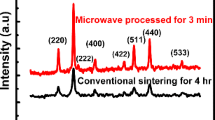
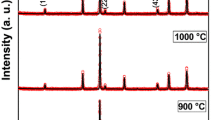
Abstract
In this study, MFe2O4 nanoparticle materials (M = Mn, Ni, Zn) were synthesized by sol–gel combustion using polyvinyl alcohol blend sago starch as the chelating agent. To achieve the highest percentage yield, the concentration of PVA and of sago starch solution for coating the synthesized materials is 1.0 g and 30 mL (35% sago starch solution). The samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction and transmission electron microscopy techniques: the crystallite size was observed to be 8–27 nm. The magnetic properties of all three samples were studied, and the measurements were carried out using a vibrating sample magnetometer; the samples exhibit ferromagnetic properties. NiFe2O4 nanoparticle gave the highest saturation magnetization value of 109.32 emu/g and the lowest coercivity value of 83.20 Oe. Moreover, the samples showed no difference in thermal properties. The synthesized MFe2O4 nanoparticle can be applied as a density magnetic recording media material.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Sakthipandia, N. Lenina, R. Rajesh Kannaa, A. Sabah Afrozeb, M. Sivabharathya, PVA-doped NiNdxFe2−xO4 nanoferrites: tuning of dielectric and magnetic properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 485, 105–111 (2019)
Y. Liu, Y. Yang, Y. Zhang, Y. Wang, X. Zhang, Y. Jiang, M. Wei, Y. Liu, X. Liu, J. Yang, A facile route to synthesis of CoPt magnetic nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 48, 721–724 (2013)
M.K. Shobana, S. Sankar, Characterization of sol–gel-prepared nanoferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 599–601 (2009)
M.H. Sousa, E. Hasmonay, J. Depeyrot, F.A. Tourinho, J.C. Bacri, E. Dubois, R. Perzynski, YuL Raikher, NiFe2O4 nanoparticles in ferrofluids: evidence of spin disorder in the surface layer. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 242, 572–574 (2002)
C.G. Ramankutty, S. Sugunan, Surface properties and catalytic activity of ferrospinels of nickel, cobalt and copper, prepared by soft chemical methods. Appl. Catal. A 218, 39–51 (2001)
H. Yang, C. Zhang, X. Shi, H. Hu, X. Du, Y. Fang, Y. Ma, H. Wu, S. Yang, Water-soluble superparamagnetic manganese ferrite nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging. Bio Mater. 31, 3667–3673 (2010)
C. Sun, S. Jerry, H. Lee, M. Zhang, Magnetic nanoparticles in MR imaging and drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 60, 1252–1265 (2008)
R. Bhosale, R. Shende, J. Puszynski, H2 generation fromthermochemical water-splitting using sol–gel synthesized Zn/Sn/Mn-doped Ni-ferrite. Int. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2, 852–862 (2010)
P.S. Hedaoo, D.S. Badwaik, S.M. Suryawanshi, K.G. Rewatkar, Structural and magnetic studies of Zn doped nickel nanoferrites synthesize by sol-gel auto combustion method. Mater. Today Proc. 15, 416–423 (2019)
M. Arifuzzaman, M.B. Hossen, J.D. Afroze, M.J. Abden, Structural and electrical properties of Cu substituted Ni–Cd nanoferrites for microwave applications. Phys. B 588, 412170 (2020)
S. Asiri, M. Sertkol, S. Guner, H. Gungunes, K.M. Batoo, T.A. Saleh, H. Sozeri, M.A. Almessiere, A. Manikandan, A. Baykal, Hydrothermal synthesis of CoyZnyMn1−2yFe2O4 nanoferrites: magneto-optical investigation. Ceram. Int. 44, 5751–5759 (2018)
W. Wu, Q.G. He, C.Z. Jiang, Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis and surface functionalization strategies. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 3, 397–415 (2008)
F. Cavalieri, E. Chiessi, R. Villa, L. Vigano, N. Zaffaroni, M.F. Telling, G. Paradossi, Novel PVA-based hydrogel microparticles for doxorubicin delivery. Biomacromol 9, 1967–1974 (2008)
M.T. Ramesan, M. Varghese, P. Jayakrishnan, P. Periyat, Silver-doped zinc oxide as a nanofiller for development of poly (vinyl alcohol)/poly (vinyl pyrrolidone) blend nanocomposites. Adv. Polym. Technol. 37, 21650 (2018)
M. Sairam, B.V.K. Naidu, S.K. Nataraj, B. Sreedhar, T.M. Aminabhavi, Poly (vinyl alcohol)-iron oxide nanocomposite membranes for pervaporation dehydration of isopropanol, 1, 4-dioxane and tetrahydrofuran. J. Memb. Sci. 283, 65–75 (2006)
M. Okamoto, B. John, Synthetic biopolymer nanocomposites for tissue engineering Scaffolds. Prog. Polym. Sci. 38, 1487–1503 (2013)
B. Fauzi, M.G. Mohd Nawawi, R. Fauzi, S.N. Liyana Mamauod, Physicochemical characteristics of sago starch-chitosan nanofillers film. BioRes. 14, 8324–8330 (2019)
N.H. Arshad, S.A. Zaman, M.H. Rawi, S.R. Sarbini, Resistant starch evaluation and in vitro fermentation of lemantak (native sago starch), for prebiotic assessment. Int. Food. Res. J. 25, 951–957 (2018)
E.Y. Purwani, T. Purwadaria, M.T. Suhartono, Fermentation RS3 derived from sago and rice starch with Clostridium butyricum BCC B2571 or Eubacterium rectale DSM 17629. Anaerobe 18, 55–61 (2012)
Z.N. Tan, A. Rosma, H. Napisah, A.A. Karim, M.T. Liong, Characteristics of Metroxylon sagu resistant starch type III as prebiotic substance. J. Food Sci. 80, H872–H882 (2015)
M.M. Afiq, A.R. Azura, Effect of sago starch loadings on soil decomposition of Natural Rubber Latex (NRL) composite films mechanical properties. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 85, 139–149 (2013)
M.D.H. Beg, S. Kormin, M. Bijarimi, H.U. Zaman, Preparation and characterization of low-density polyethylene/thermoplastic starch composites. Adv. Polym. Technol. 35, 21521 (2016)
R. Mohamed, N.W.A. Mutalib, M.N. Norizan, R.S.N. Hirzin, S.A.M. Isa, Effect of different plasticizers on tensile properties of PVA/sago starch system before and after weathering exposure. AIP Conf. Proc. 1985, 030005 (2018)
H.L. Tan, Y.Y. Wong, S. Muniyandy, K. Hashim, J. Pushpamalar, Carboxymethyl sago pulp/carboxymethyl sago starch hydrogel: effect of polymer mixing ratio and study of controlled drug release. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 133, 43652 (2016)
N. Oladzadabbasabadi, S. Ebadi, A.M. Nafchi, A.A. Karim, S.R. Kiahosseini, Functional properties of dually modified sago starch/κ-carrageenan films: an alternative to gelatin in pharmaceutical capsules. Carbohydr. Polym. 160, 43–51 (2017)
R.T. Widodo, A. Hassan, Compression and mechanical properties of directly compressible pregelatinized sago starches. Powder Technol. 269, 15–21 (2015)
S.C. Pang, C.L. Tay, S.F. Chin, Starch-based gel electrolyte thin films derived from native sago (Metroxylon sagu) starch. Ionics 20, 1455–1462 (2014)
A.B. Kousaalya, R. Kumar, B.T.N. Sridhar, Thermal conductivity of precursor derived Si–B–C–N ceramic foams using Metroxylon sagu as sacrificial template. Ceram. Int. 41, 1163–1170 (2015)
P. Nuengmatcha, A. Noypha, W. Tangwatanakul, T. Charoensuk, P. Porrawatkul, S. Chanthai, Effect of boron addition on the phase–transition temperature of CoPt–B nanoparticles synthesized by sol–gel autocombustion using sago starch as a chelating agent. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 57, 385–391 (2020)
S.F. Chin, S.N.A.M. Yazid, S.C. Pang, S.M. Ng, Facile synthesis of fluorescent carbon nanodots from starch nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 85, 50–52 (2012)
A. Hunyek, C. Sirisathitkul, C. Mahaphap, U. Boonyang, W. Tangwatanakul, Sago starch: chelating agent in Sol-gel synthesis of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. 53, 173–176 (2017)
M. Zhang, Z. Zi, Q. Liu, P. Zhang, X. Tang, J. Yang, X. Zhu, Y. Sun, J. Dai, Size effects on magnetic properties of Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 prepared by sol-gel method. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, 609819 (2013)
M. George, A.M. John, S.S. Nair, P.A. Joy, M.R. Anantharaman, Finite size effects on the structural and magnetic properties of sol–gel synthesized NiFe2O4 powders. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 302, 190–195 (2006)
S. Shafiu, R. Topkaya, A. Baykal, M.S. Toprak, Facile synthesis of PVA–MnFe2O4 nanocomposite: its magnetic Investigation. Mater. Res. Bull. 48, 4066–4071 (2013)
K. Sakthivel, G. Mani, C. Shen-Ming, L. Shih-Hao, A. Muthumariappan, M. Veerappan, A novel synthesis of non-aggregated spinel nickel ferrite nanosheets for developing non-enzymatic reactive oxygen species sensor in biological samples. J. Electroanal. Chem. 820, 161–167 (2018)
O. Bin-Dahman, J. Jose, M. Al-Harthi, Studies on compatibility of biodegradable starch/polyvinyl alcohol blends. Polym. Eng. Sci. 52, 2167–2172 (2012)
P. Sivakumar, R. Ramesh, A. Ramanand, S. Ponnusamy, C. Muthamizhchelvan, Synthesis, studies and growth mechanism of ferromagnetic NiFe2O4 nanosheet. J. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258, 6648–6652 (2012)
S. Noppakun, J. Wang, B.C. Christopher, Influence of chelating agents on the microstructure and antibacterial property of cobalt ferrite nanopowders. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. 49, 84–91 (2013)
M.G. Naseri, E.B. Saion, M. Hashim, A.H. Shaari, H.A. Ahangar, Synthesis and characterization of zinc ferrite nanoparticles by a thermal treatment method. Solid State Commun. 151, 1031–1035 (2011)
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by Nanomaterials Chemistry Research Unit, Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science and Technology, and Nakhon Si Thammarat Rajabhat University Research Fund (NSTRU 019/2561), Nakhon Si Thammarat, Thailand.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Porrawatkul, P., Nuengmatcha, P., Tangwatanakul, W. et al. Effect of Zn, Ni, and Mn doping ions on magnetic properties of MFe2O4 (M = Mn, Zn, and Ni) nanoparticles synthesized via sol–gel autocombustion using PVA/sago starch blend as a chelating agent. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 57, 676–683 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43207-020-00069-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43207-020-00069-2