Abstract
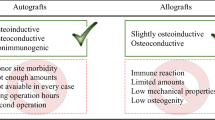
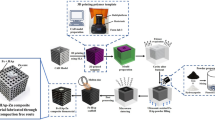
Multifunctional porous biological hydroxyapatite (b-Hap) tablets prepared from fine bone powder (FBP) are predicted to be useful as a calcium supplement and at the same time as low-dose drug carriers. FBP was hydrothermally extracted, then mechanically compressed and sintered without using chemical additives to prepare the porous b-Hap tablets. The properties of FBP and b-Hap tablets were characterized by XRD, FTIR, SEM, mechanical, and porosity tests. Moreover, an aqueous drug solution of atenolol was used to evaluate release behavior from porous b-Hap tablets. The prepared FBP exhibited microstructures with grain sizes of about 50 to 100 μm while b-Hap tablets sintered at 800 °C exhibited high porosity (55%) and compression strength of 8.5 MPa. When the atenolol-loaded b-Hap tablets were immersed in the acidic medium, the release of atenolol from the tablets continued for 120 min with complete dissolution of the b-Hap tablets. These results indicate that the porous b-Hap tablets are promised as an economic calcium supplement and as low-dose drug carriers.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xie, L., Yu, H., Deng, Y., Yang, W., Liao, L., Long, Q.: Preparation, characterization and in vitro dissolution behavior of porous biphasic α/β-tricalcium phosphatebioceramics. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 59, 1007–1015 (2016)
Tao, Z.-S., Zhou, W.-S., Tu, K., Huang, Z.-L., Zhou, Q., Sun, T., Lv, Y.-X., Cui, W., Yang, L.: Effect exerted by teriparatide upon repair function of β-tricalcium phosphate to ovariectomised rat's femoral metaphysis defect caused by osteoporosis. Injury. 46, 2134–2141 (2015)
Morsy, R.: Development and evaluation of degradable hydroxyapatite/sodium silicate composite for low-dose drug delivery systems. Bull. Mater. Sci. 39, 1273–1278 (2016)
Laffargue, P., Fialdes, P., Frayssinet, P., Rtaimate, M., Hildebrand, H.F., Marchandise, X.: Adsorption and release of insulin-like growth factor-I on porous tricalcium phosphate implant. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 49, 415–421 (2000)
Paul, W., Sharma, C.P.: Tricalcium phosphate delayed release formulation for oral delivery of insulin: a proof-of-concept study. J. Pharm. Sci. 97, 875–882 (2008)
Baradari, H., Damia, C., Dutreih-Colas, M., Laborde, E., Pécout, N., Champion, E., Chulia, D., Viana, M.: Calcium phosphate porous pellets as drug delivery systems: effect of drug carrier composition on drug loading and in vitro release. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 32, 2679–2690 (2012)
Gervaso, F., Padmanabhan, S.K., Scalera, F., Sannino, A., Licciulli, A.: Mechanical stability of highly porous hydroxyapatite scaffolds during different stages of in vitro studies. Mater. Lett. 185, 239–242 (2016)
Morsy, R.: Multifunctional antibacterial biocomposite rich of trace elements based on biological hydroxyapatite and ZnO nanoparticles. Rom. J. Biophys. 25, 291–300 (2015)
Miyasaka, R., Kikukawa, K., Sakuma, S.: Enhanced solubility and intestinal absorption of cisplatin by coating with nano-hydroxyapatite. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 35, 294–302 (2016)
Roy, A., Jhunjhunwala, S., Bayer, E., Fedorchak, M., Little, S.R., Kumta, P.N.: Porous calcium phosphate-poly (lactic-co-glycolic) acid composite bone cement: a viable tunable drug delivery system. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 59, 92–101 (2016)
Fereshteh, Z., Fathi, M., Bagri, A., Boccaccini, A.R.: Preparation and characterization of aligned porous PCL/zein scaffolds as drug delivery systems via improved unidirectional freeze-drying method. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 68, 613–622 (2016)
Ahnfelt, E., Sjögren, E., Hansson, P., Lennernäs, H.: In vitro release mechanisms of doxorubicin from a clinical bead drug-delivery system. J. Pharm. Sci. 105, 3387–3398 (2016)
Terukina, T., Saito, H., Tomita, Y., Hattori, Y., Otsuka, M.: Development and effect of a sustainable and controllable simvastatin-releasing device based on PLGA microspheres/carbonate apatite cement composite: in vitro evaluation for use as a drug delivery system from bone-like biomaterial. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 37, 74–80 (2017)
Ma, Y., Ge, Y., Li, L.: Advancement of multifunctional hybrid nanogel systems: construction and application in drug co-delivery and imaging technique. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 71, 1281–1292 (2017)
Taratula, O., Kuzmov, A., Shah, M., Garbuzenko, O.B., Minko, T.: Nanostructured lipid carriers as multifunctional nanomedicine platform for pulmonary co-delivery of anticancerdrugs and siRNA. J. Control. Release. 171, 349–357 (2013)
Waheed, S., Rahman, S., Siddique, N.: Calcium supplements as source of trace elements: adequacy and safety of supplements with vitamin C, vitamin D and phosphate formulations. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 89, 134–140 (2014)
Li, M., Zhang, T., Yang, H., Zhao, G., Xu, C.: A novel calcium supplement prepared by phytoferritin nanocages protects against absorption inhibitors through a unique pathway. Bone. 64, 115–123 (2014)
Cosijns, A., Vervaet, C., Luyten, J., Mullens, S., Siepmann, F., Van Hoorebeke, L., Masschaele, B., Cnudde, V., Remon, J.P.: Porous hydroxyapatite tablets as carriers for low-dosed drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 67, 498–506 (2007)
Morsy, R.: Developing a multifunctional bio-ceramics composite based on b-tricalcium phosphate working as a single carrier for calcium supplement and low-dose drugs. Int. J. Mater. Res. 107, 1062–1064 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morsy, R., Al Qahtani, F.N. & Elnimr, T. Development and characterization of porous bioceramic tablets based on bone powder for medical applications. J Aust Ceram Soc 54, 331–335 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-017-0157-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-017-0157-0