Abstract
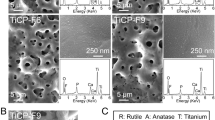
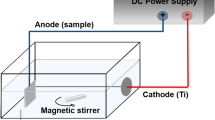
A pine cone-shaped tungsten−molybdenum−titanium oxides combinatorial coating was successfully grown on Ti–6Al–7Nb implant (Ti67) by a combined approach of RF/DC physical vapor deposition (PVD) and one-pot anodization. The results indicated that the surface morphology and the phase composition were significantly changed as a function of sputtering target and anodization period. Prior to anodization, PVD coating process resulted in the formation of crystalline mono- and multi-layer Mo and Mo/W thin films. After anodization for 60 min, a crystalline mixed oxide structure was formed as a result of oncoming electrochemical reactions. Compared to a single bare substrate and as-sputtered Mo/W multi-layer coating, the 60-min-anodized specimen had the highest hydrophilicity as well as Vickers hardness and showed adhesion strength of around 397 ± 1 MPa. Remarkably, the proposed modification is not only limited to Mo/W multi-layer coating, but can also be employed to a wide range of other transition metals to form a mixed oxide mono-layer on the surface of medical-grade titanium alloys for potential biomedical applications.

Pine cone-like WO3 /MoO3 /TiO2 nanoflakes biofilm modified Ti6Al7Nb implant.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fathi, M.H., Mortazavi, V.: Tantalum, niobium and titanium coatings for biocompatibility improvement of dental implants. Dent Res J. 4, 74–82 (2007)
Cremasco, A., Osório, W.R., Freire, C.M.A., et al.: Electrochemical corrosion behavior of a Ti–35Nb alloy for medical prostheses. Electrochim Acta. 53, 4867–4874 (2008)
Niinomi, M.: Fatigue performance and cyto-toxicity of low rigidity titanium alloy, Ti–29Nb–13Ta–4.6Zr. Biomaterials. 24, 2673–2683 (2003)
Abdel-Hady, M., Hinoshita, K., Morinaga, M.: General approach to phase stability and elastic properties of β-type Ti-alloys using electronic parameters. Scr Mater. 55, 477–480 (2006)
Correa, D.R.N., Kuroda, P.A.B., Grandini, C.R., et al.: Tribocorrosion behavior of β-type Ti-15Zr-based alloys. Mater Lett. 179, 118–121 (2006)
Stoica, E.D., Fedorov, F., Nicolae, M., et al.: Ti6Al7Nb surface modification by anodization in electrolytes containing HF. UPB Sci Bull Series B. 74, 277–288 (2012)
Rafieerad, A.R., Bushroa, A.R., Nasiri-Tabrizi, B., et al.: Toward improved mechanical, tribological, corrosion and in-vitro bioactivity properties of mixed oxide nanotubes on Ti–6Al–7Nb implant using multi-objective PSO. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 69, 1–18 (2017)
Rafieerad, A.R., Bushroa, A.R., Nasiri-Tabrizi, B., et al.: GEP-based method to formulate adhesion strength and hardness of Nb PVD coated on Ti–6Al–7Nb aimed at developing mixed oxide nanotubular arrays. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 61, 182–196 (2016)
Rafieerad, A.R., Bushroa, A.R., Nasiri-Tabrizi, B., et al.: Mechanical properties, corrosion behavior and in-vitro bioactivity of nanostructured Pd/PdO coating on Ti–6Al–7Nb implant. Mater Des. 103, 10–24 (2016)
Daudt, N.F., Bram, M., Cysne Barbosa, A.P., et al.: Surface modification of highly porous titanium by plasma treatment. Mater Lett. 141, 194–197 (2015)
Marx, B., Marx, C., Marx, R., Reisgen, U., Wirtz, D.C.: Bone cement adhesion on ceramic surfaces—surface activation of retention surfaces of knee endoprostheses by atmospheric pressure plasma vs. thermal surface treatment. J Adv Ceram. 5, 137–144 (2016)
Jelikić-Stankov, M., Uskoković-Marković, S., Holclajtner-Antunović, I., et al.: Compounds of Mo, V and W in biochemistry and their biomedical activity. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 21, 8–16 (2007)
Ribeiro, A.M., Flores-Sahagun, T.H., Paredes, R.C.: A perspective on molybdenum biocompatibility and antimicrobial activity for applications in implants. J Mater Sci. 51, 2806–2816 (2016)
Qureshi, N., Patil, R., Shinde, M., et al.: Innovative biofilm inhibition and anti-microbial behavior of molybdenum sulfide nanostructures generated by microwave-assisted solvothermal route. Appl Nanosci. 5, 331–341 (2015)
Mardare, C.C., Hassel, A.W.: Investigations on bactericidal properties of molybdenum−tungsten oxides combinatorial thin film material libraries. ACS Comb Sci. 16, 631–639 (2014)
Saiae, E.: The orthorhombic phase of WO3. Acta Cryst. B33, 574–577 (1977)
He, T., Yao, J.: Photochromism of molybdenum oxide. J Photochem Photobiol C. 4, 125–143 (2003)
Hanaor, D.A.H., Sorrell, C.C.: Review of the anatase to rutile phase transformation. J Mater Sci. 46, 855–874 (2011)
Nasiri-Tabrizi, B., Pingguan-Murphy, B., Basirun, W.J., Baradaran, S.: Crystallization behavior of tantalum and chlorine co-substituted hydroxyapatite nanopowders. J Ind Eng Chem. 33, 316–325 (2016)
Rafieerad, A.R., Bushroa, A.R., Nasiri-Tabrizi, B., et al.: Vertically oriented ZrO2-TiO2-Nb2O5-Al2O3 mixed nanopatterned bioceramics on Ti6Al7Nb implant assessed by laser spallation technique. J Alloys Compd. 721, 456–475 (2017)
Liang, W., Zhu, L., Li, W., Liu, H.: Facile fabrication of a flower-like CuO/Cu(OH)2 nanorod film with tunable wetting transition and excellent stability. RSC Adv. 5, 38100–38110 (2015)
Ng, C., Ye, C., Ng, Y.H., Amal, R.: Flower-shaped tungsten oxide with inorganic fullerene-like structure: synthesis and characterization. Cryst Growth Des. 10, 3794–3801 (2010)
Wang, C., Wang, M., Xie, K., et al.: Room temperature one-step synthesis of microarrays of N-doped flower-like anatase TiO2 composed of well-defined multilayer nanoflakes by Ti anodization. Nanotechnology. 22, 305607 (2011)
Shirdar, M.R., Izman, S., Taheri, M.M., et al.: Effect of post-treatment techniques on corrosion and wettability of hydroxyapatite-coated Co–Cr–Mo alloy. Arab J Sci Eng. 40, 1197–1203 (2015)
Rupp, F., Gittens, R.A., Scheideler, L., Marmur, A., Boyan, B.D., Schwartz, Z., Geis-Gerstorfer, J.: A review on the wettability of dental implant surfaces I: theoretical and experimental aspects. Acta Biomater. 10, 2894–2906 (2014)
Schwarz, F., Ferrari, D., Herten, M., Mihatovic, I., Wieland, M., Sager, M., Becker, J.: Effects of surface hydrophilicity and microtopography on early stages of soft and hard tissue integration at nonsubmerged titanium implants: an immunohistochemical study in dogs. J Periodontol. 78, 2171–2184 (2007)
Junker, R., Dimakis, A., Thoneick, M., Jansen, J.A.: Effects of implant surface coatings and composition on bone integration: a systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res. 20, 185–206 (2009)
Sandhyarani, M., Rameshbabu, N., Venkateswarlu, K., Rama, K.L.: Fabrication, characterization and in-vitro evaluation of nanostructured zirconia/hydroxyapatite composite film on zirconium. Surf Coat Technol. 238, 58–67 (2014)
Sharifahmadian, O., Salimijazi, H.R., Fathi, M.H., et al.: Relationship between surface properties and antibacterial behavior of wire arc spray copper coatings. Surf Coat Technol. 233, 74–79 (2013)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the University of Malaya for providing necessary resources and facilities for this study. The authors are also grateful to Research Affairs of Islamic Azad University, Najafabad Branch for supporting of this research.
Funding information
This project was funded by UMRG grant number RP035A-15AET and UM postgraduate research grant (PPP) PG130-2015B.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rafieerad, A.R., Bushroa, A.R., Nasiri-Tabrizi, B. et al. Anodic pine cone-like WO3/MoO3/TiO2 film with well-defined nanoflakes on Ti–6Al–7Nb implant. J Aust Ceram Soc 54, 129–137 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-017-0134-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-017-0134-7