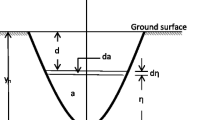
Abstract
The need for optimum design of water conveyance structures provides an active area of study in water resources engineering. A literature review on optimum design of circular channels indicates that variation of Manning’s roughness coefficient (n) with water depth is not taken into account. In this study, this variation has been implemented in the optimum design of lined circular channels. The significant discrepancy between the results obtained for constant and variable roughness scenarios demonstrates the necessity for considering roughness coefficient variability with water depth in circular sections. Furthermore, a new explicit equation for optimum design of section parameters has been proposed using a hybrid optimization technique, which combines the Modified Honey Bee Mating Optimization with Generalized Reduced Gradient algorithms. Solving a typical design problem in the literature by the proposed equation showed not only its adequate performance but also the necessity for considering variable roughness in circular channels design procedure.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afzali SH (2016) Variable-parameter Muskingum model. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civ Eng 40(1):59–68
Afzali SH, Darabi A, Niazkar M (2016) Steel frame optimal design using MHBMO algorithm. Int J Steel Struct 16(2):455–465
Akgiray O (2004) Simple formulae for velocity, depth of flow, and slope calculations in partially filled circular pipes. Environ Eng Sci 21(3):371–385
Aksoy B, Altan-Sakarya AB (2006) Optimal lined channel design. Can J Civ Eng 33(5):535–545
Bhattacharjya RK, Satish MG (2007) Optimal design of a stable trapezoidal channel section using hybrid optimization techniques. J Irrig Drain Eng 133(4):323–329
Chow VT (1959) Open-channel hydraulics. McGraw-Hill, New York
Chow VT (1973) Open-channel hydraulics. McGraw-Hill, New York
Esmi Jahromi M, Afzali S (2014) Application of the HBMO approach to predict the total sediment discharge. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civ Eng 38(C1):123–135
French RH (1994) Open-channel hydraulics. McGraw-Hill, New York
Guo CY, Hughes WC (1984) Optimal channel cross section with freeboard. J Irrig Drain Eng 110(3):304–314
Jain A, Bhattacharjya RK, Sanaga S (2004) Optimal design of composite channels using genetic algorithm. J Irrig Drain Eng 130(4):286–295
Kaveh A, Talatahari S, Farhmand Azar B (2012) Optimum design of composite channels using charged system search algorithm. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civ Eng 36(C1):67–77
Loganathan G (1991) Optimal design of parabolic canals. J Irrig Drain Eng 117(5):716–735
Monadjemi P (1994) General formulation of best hydraulic channel section. J Irrig Drain Eng 120(1):27–35
Niazkar M, Afzali SH (2014) Assessment of modified honey bee mating optimization for parameter estimation of nonlinear Muskingum models. J Hydrol Eng 20(4):04014055
Niazkar M, Afzali SH (2015a) Optimum design of lined channel sections. Water Resour Manag 29(6):1921–1932
Niazkar M, and Afzali SH (2015b) Application of Excel spreadsheet in engineering education. In: Proceeding of the first international and fourth national conference on engineering education, Shiraz University, Shiraz, 10–12 Nov
Niazkar M, Afzali SH (2016a) Application of new hybrid optimization technique for parameter estimation of new improved version of Muskingum model. Water Resour Manag 30(13):4713–4730
Niazkar M, Afzali SH (2016b) Parameter estimation of an improved nonlinear Muskingum model using a new hybrid model. Hydrol Res 48(4):1253–1267. https://doi.org/10.2166/nh.2016.089
Niazkar M, Afzali SH (2016c) Streamline performance of Excel in stepwise implementation of numerical solutions. Comput Appl Civ Eng 24(4):555–566
Niazkar M, Afzali SH (2017a) Application of new hybrid method in developing a new semicircular-weir discharge model. Alex Eng J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2017.05.004
Niazkar M, Afzali SH (2017b) New nonlinear variable-parameter Muskingum Models. KSCE J Civ Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-017-0652-4
Niazkar M, Afzali SH (2017c) Analysis of water distribution networks using MATLAB and Excel spreadsheet: h-based methods. Comput Appl Eng Educ 25(1):129–141
Niazkar M, Afzali SH (2017d) Analysis of water distribution networks using MATLAB and Excel spreadsheet: Q-based methods. Comput Appl Eng Educ 25(2):277–289
Nourani V, Talatahari S, Monadjemi P, Shahradfar S (2009) Application of ant colony optimization to optimal design of open channels. J Hydraul Res 47(5):656–665
Swamee PK (1995) Optimal irrigation canal sections. J Irrig Drain Eng 121(6):467–469
Swamee PK, Bhatia KG (1972) Economic open channel section. J Irrig Power 29(2):169–176
Swamee PK, Mishra GC, Chahar BR (2000) Minimum cost design of lined canal sections. Water Resour Manag 14(1):1–12
Turan ME, Yurdusev MA (2011) Optimization of open canal cross sections by differential evolution algorithm. Math Comput Appl 16(1):77
Wilcox ER (1924) A comparative test of the flow of water in 8-inch concrete and vitrified clay sewer pipes. University of Washington, Engineering Experiment Station, Bulletin no. 27
Yarnell DL, Woodward SM (1920) The flow of water in drain tile. US Department of Agriculture, Washington, DC, Bulletin no. 854
Zaghloul NA (1992) Gradually varied flow in circular channels with variable roughness. Adv Eng Softw 15(1):33–42
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niazkar, M., Rakhshandehroo, G.R. & Afzali, S.H. Deriving Explicit Equations for Optimum Design of a Circular Channel Incorporating a Variable Roughness. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civ Eng 42, 133–142 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-017-0091-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-017-0091-y