Abstract
Background
Researchers have been examining the relationship between obesity and hypertension. However, whether overall or abdominal obesity better explains senior adults’ hypertension has not been studied.
Objectives
The purpose of the study was to examine whether body mass index or waist circumference better predicts hypertension in Chinese senior adults and how the magnitude of the relationship is attenuated as they continue to age.
Methods
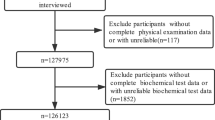
The study was based on the 2010 National Physique Monitoring data. There were 7,542 senior adults aged 60–69 years living in urban, suburban, and rural areas of Shanghai City. The participants were categorized into five age groups: 60–61, 62–63, 64–65, 66–67, and 68–69 years.
Results
The percentage of participants who had hypertension increased as people aged, which was mainly caused by the increase of systolic blood pressure. Logistic regression analysis showed that when body mass index or waist circumference was entered into the model, both were significant predictors for hypertension (p < 0.05). However, when body mass index and waist circumference were mutually entered into the model, body mass index was the only important predictor (p < 0.05). The values of odds ratios were found to decrease from the 60–61 to 68–69 years age groups. More senior adults have hypertension as they age.
Conclusion
Body mass index, and not waist circumference, better predicts Chinese senior adults’ hypertension. However, age attenuates the effects of obesity on hypertension as the senior adults continue to age.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu Y, Huxley R, Li M, Ma J (2009) The growing burden of overweight and obesity in contemporary China. CVD Prev Control 4(1):19–26
Kelly T, Yang W, Chen CS, Reynolds K, He J (2008) Global burden of obesity in 2005 and projections to 2030. Int J Obes 32(9):1431–1437
Din-Dzietham R, Liu Y, Bielo MV, Shamsa F (2007) High blood pressure trends in children and adolescents in national surveys, 1963 to 2002. Circulation 116(13):1488–1496
Freedman DS, Dietz WH, Srinivasan SR, Berenson GS (1999) The relation of overweight to cardiovascular risk factors among children and adolescents: the Bogalusa Heart Study. Pediatrics 103(6):1175–1182
Lawes CM, Vander Hoorn S, Rodgers A (2008) Global burden of blood-pressure-related disease, 2001. Lancet 371(9623):1513–1518
He J, Gu D, Wu X, Reynolds K, Duan X, Yao C, Wang J, Chen CS, Chen J, Wildman RP, Klag MJ, Whelton PK (2005) Major causes of death among men and women in China. N Engl J Med 353(11):1124–1134
Donini LM, Savina C, Gennaro E, De Felice M, Rosano A, Pandolfo M, Del Balzo V, Cannella C, Ritz P, Chumlea WC (2012) A systematic review of the literature concerning the relationship between obesity and mortality in the elderly. J Nutr Health Aging 16(1):89–98
Bales CW, Buhr G (2008) Is obesity bad for older persons? A systematic review of the pros and cons of weight reduction in later life. J Am Med Dir Assoc 9(5):302–312
Chen Y, Rennie DC, Reeder BA (1995) Age-related association between body mass index and blood pressure: the Humboldt study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 19(11):825–831
Arroyo P, Fernandez V, Avila-Rosas H (1997) Overweight and hypertension: data from the 1992–1993 Mexican survey. Hypertension 30(3 Pt 2):646–649
Uhernik AI, Milanovic SM (2009) Anthropometric indices of obesity and hypertension in different age and gender groups of Croatian population. Coll Antropol 1:75–80
Pikilidou MI, Scuteri A, Morrell C, Lakatta EG (2013) The burden of obesity on blood pressure is reduced in older persons: the SardiNIA study. Obesity 21(1):20010
Brown D, Miller W (1998) Normative data for strength and flexibility of women throughout life. Eur J Appl Physiol 78(1):77–82
Guagnano MT, Ballone E, Colagrande V, Della Vecchia R, Manigrasso MR, Merlitti D, Riccioni G, Sensi S (2001) Large waist circumference and risk of hypertension. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 25(9):1360–1364
Gus M, Fuchs SC, Moreira LB, Moraes RS, Wiehe M, Silva AF, Albers F, Fuchs FD (2004) Association between different measurements of obesity and the incidence of hypertension. Am J Hypertens 17(1):50–53
Chang SH, Beason TS, Hunleth JM, Colditz GA (2012) A systematic review of body fat distribution and mortality in older people. Maturitas 72(3):175–191
WHO/IASO/IOTF (2000) The Asia-Pacific perspective: Redefining obesity and its treatment. Health Commun, Sydney
Rizzo NS, Ruiz JR, Hurtig-Wennlöf A, Ortega FB, Sjöström M (2007) Relationship of physical activity, fitness, and fatness with clustered metabolic risk in children and adolescents: the European youth heart study. J Pediatr 150(4):388–394
Masaki KH, Curb JD, Chiu D, Petrovitch H, Rodriguez BL (1997) Association of body mass index with blood pressure in elderly Japanese American men. The Honolulu Heart Program. Hypertension 29(2):673–677
Javed F, Aziz EF, Sabharwal MS, Nadkarni GN, Khan SA, Cordova JP, Benjo AM, Gallagher D, Herzog E, Messerli FH, Pi-Sunyer FX (2011) Association of BMI and cardiovascular risk stratification in the elderly African-American females. Obesity 19(6):1182–1186
Kumar A, Sudhir U, Srinivasan G, Punith K (2008) Association of Body Mass Index with Blood Pressure in the Elderly. J Indian Acad Clin Med 9(4):275
Lu FH, Tang SJ, Wu JS, Yang YC, Chang CJ (2000) Hypertension in elderly persons: its prevalence and associated cardiovascular risk factors in Tainan City, southern Taiwan. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 55(8):M463–M468
Beaufrère B, Morio B (2000) Fat and protein redistribution with aging: metabolic considerations. Eur J Clin Nutr 54(Suppl 3):S48–S53
Redon J, Cea-Calvo L, Moreno B, Monereo S, Gil-Guillen V, Lozano JV, Marti-Canales JC, Llisterri JL, Aznar J, Fernandez-Perez C (2008) Independent impact of obesity and fat distribution in hypertension prevalence and control in the elderly. J Hypertens 26(9):1757–1764
Rodrigues Barbosa A, Balduino Munaretti D, Da Silva Coqueiro R, Ferreti Borgatto A (2011) Anthropometric indexes of obesity and hypertension in elderly from Cuba and Barbados. J Nutr Health Aging 15(1):17–21
Wu Y, Huxley R, Li L, Anna V, Xie G, Yao C, Woodward M, Li X, Chalmers J, Gao R, Kong L, Yang X (2008) Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in China: data from the China National Nutrition and Health Survey 2002. Circulation 118(25):2679–2686
Shirakawa T, Ozono R, Kasagi F, Oshima T, Kamada N, Kambe M (2006) Differential impact of family history on age-associated increase in the prevalence of hypertension and diabetes in male Japanese workers. Hypertens Res 29(2):81–87
Anderson GH (1999) Effect of age on hypertension: analysis of over 4,800 referred hypertensive patients. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl 10(3):286–297
Franklin SS, Wt Gustin, Wong ND, Larson MG, Weber MA, Kannel WB, Levy D (1997) Hemodynamic patterns of age-related changes in blood pressure. The Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 96(1):308–315
Franklin SS, Jacobs MJ, Wong ND, L’Italien GJ, Lapuerta P (2001) Predominance of isolated systolic hypertension among middle-aged and elderly US hypertensives: analysis based on National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) III. Hypertension 37(3):869–874
O’Rourke MF, Nichols WW (2005) Aortic diameter, aortic stiffness, and wave reflection increase with age and isolated systolic hypertension. Hypertension 45(4):652–658
Wakabayashi I (2004) Relationships of body mass index with blood pressure and serum cholesterol concentrations at different ages. Aging Clin Exp Res 16(6):461–466
Huang Z, Willett WC, Manson JE, Rosner B, Stampfer MJ, Speizer FE, Colditz GA (1998) Body weight, weight change, and risk for hypertension in women. Ann Intern Med 128(2):81–88
Must A, Spadano J, Coakley EH, Field AE, Colditz G, Dietz WH (1999) The disease burden associated with overweight and obesity. JAMA 282(16):1523–1529
Miller SL, Wolfe RR (2008) The danger of weight loss in the elderly. J Nutr Health Aging 12(7):487–491
Waters DL, Ward AL, Villareal DT (2013) Weight loss in obese adults 65 years and older: a review of the controversy. Exp Gerontol 48(10):1054–1061
Beavers KM, Beavers DP, Nesbit BA, Ambrosius WT, Marsh AP, Nicklas BJ, Rejeski WJ (2014) Effect of an 18-month physical activity and weight loss intervention on body composition in overweight and obese older adults. Obesity 22(2):325–331
Beavers DP, Beavers KM, Lyles MF, Nicklas BJ (2013) Cardiometabolic risk after weight loss and subsequent weight regain in overweight and obese postmenopausal women. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 68(6):691–698
Meneton P, Jeunemaitre X, de Wardener HE, MacGregor GA (2005) Links between dietary salt intake, renal salt handling, blood pressure, and cardiovascular diseases. Physiol Rev 85(2):679–715
Acknowledgments
Jun helped retrieve the data; Han and Jun analyzed the data; Han and Jun contributed to the writing of the article; Han had primary responsibility for the final content. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all the authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Dai, J. BMI better explains hypertension in Chinese senior adults and the relationship declines with age. Aging Clin Exp Res 27, 271–279 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-014-0285-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-014-0285-0