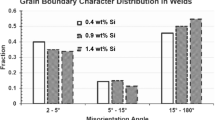
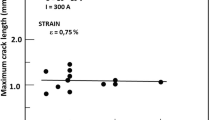
Abstract
Hot crack prevention in materials production and processing is an essential prerequisite for welded component safety. The causes of hot cracking can ultimately be attributed to the occurrence of metallurgical effects and to structural loads. More than 140 hot cracking test procedures have hitherto been developed for determining the hot cracking resistance. In principle, they are divided in self-restraint and externally loaded hot cracking tests with diverse process variants. Only some of the hot cracking tests are international standardized. Although various factors are known that encourage or prevent hot cracking, it is often not possible even with defined welding conditions to draw immediate conclusions about the hot cracking resistance of a welded component alone from a metallurgical composition of the base and filler materials. Based on an evaluation of the existing theories relating to hot cracking susceptibility assessment, this study summarizes the major hot cracking test procedures and highlights the application limits of the test procedures by presenting overviews along with explanations. It shows that weld hot cracking tests can generally be used to rank materials, welding consumables, and welding conditions. The evaluation of hot cracking test results and of their transferability among one another and to real components always requires consideration of the close relationships between metallurgy, welding process, and parameters, respectively, and prevailing restraint conditions.




























Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Designation of a special universal testing facility made by Dynamic Systems Inc., Poestenkill, NY, USA
References
Lippold, J.C.: Recent developments in weldability testing for advanced materials, ASM International, www.asminternational.org/bookstore, 2005.
Thomas RD (1984) HAZ-cracking in thick sections of austenitic stainless steels—part II. Weld J 63(12):24–32
Schobbert H, Böllinghaus T, Wolf M (2003) Hot cracking resistance of laser and hybrid welded austenitic stainless steels. Trends in Welding Research 6:76–81
Stelling, K.; Böllinghaus, Th.; Wolf, M.; Schöler, A.; Burkert, A. u. A.; Isecke, B.: Hot cracks as stress corrosion cracking initiation sites in laser welded corrosion resistant alloys. Book: Hot Cracking Phenomena in Welds, Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, ISBN 3-540-22332-0, pp. 165–182, 2005.
Nissley, N.E.; Collins, M.G.; Guaytima, G.; Lippold, J.C.: Development of the strain-to-fracture test for evaluating ductility-dip cracking in austenitic stainless steels and Ni-base alloys. IIW-1570-02, 2002.
Hemsworth B, Boniszewski T, Eaton NF (1969) Classification and definition of high temperature welding cracks in alloys. Met Constr Br Weld J 1(1):5–15
Wolf, M.; Schobbert, H.; Böllinghaus, Th.: Influence of the weld pool geometry on solidification crack formation. In: Hot cracking phenomena in welds. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, ISBN 3-540-22332-0, pp. 243–268, 2005.
Lippold JC, Kotecki DJ (2005) Welding metallurgy and weldability of stainless steels. John Wiley & Sons, Inc, Hoboken, New Jersey, p 357, 2005, ISBN 0-471-47379-0
Böllinghaus, Th.; Herold, H. (Eds.): Hot cracking phenomena in welds. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, ISBN: 3-540-22332-0, 2005.
Böllinghaus, Th.; Herold, H.; Cross, C.E.; Lippold, J.C. (Eds.).: Hot cracking phenomena in welds II. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, ISBN 978-3-540-78627-6, 2008.
Lippold, J.C.; Böllinghaus, Th.; Cross, C.E. (Eds.): Hot cracking phenomena in welds III. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, ISBN 978-3-642-16863-5, 2011.
Kannengiesser, Th.; Wolf, M.; Schobbert, H.: Recent developments in nickel base material welding considering the influence of shielding gas on the hot cracking resistance. Stainless Steel World 2004, KCI Publishing BV, ISBN 90-73168-23-6, pp. 156-167, 2004.
Goodwin GM (1988) The effects of heat input and weld process on hot cracking in stainless steel. Weld J vol. 67(4):88s–94s
Shankar V, Gill TPS, Mannan SL, Sundaresan S (2003) Solidification cracking in austenitic stainless steel welds. Sãhhanã vol. 28(parts 3 & 4):359–382
Cross, C.E.: On the origin of weld solidification cracking. Hot cracking phenomena in welds. Book, Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, ISBN 3-540-22332-0, pp. 3–18, 2005.
Kannengiesser, Th.; Cross, C.E.: Effect of tack placement on local weld displacement and solidification cracking during welding of aluminium alloy 6083. Proceedings to The First South-East Asia IIW Conference, Bangkok, Thailand, pp 480- 491, 21./22.11.2006.
Borland, J.C.: Generalized theory of super-solidus cracking in welds (and Castings). British Welding Journal, pp. 508–512, 1960.
Holt M, Olson DL, Cross GE (1992) Interfacial tension driven fluid flow model for hot cracking. Scripta metallurgica et materialia 26:1119–1124
Applett WR, Pellini WS (1954) Factors which influence weld hot cracking. Weld J 33(2):83–90
Prokhorov, N. N.: The technological strength of metals while crystallising during welding. Doc IX-479-65, 1965.
Prokhorov NN (1956) The problem of the strength of metals while solidifying during welding. Svar Proiz 6:5–11
Prokhorov NN, Prokhorov NN (1969) A general equation for the surface of the solidification front during welding. Svar Proiz no 8:1–4
Arata Y, Matsuda F, Nakagawa H, Katayama S (1978) Solidification crack susceptibility in weld metals of fully austenitic stainless steels (report IV). Trans JWRI 7(2):21–24
Matsuda F, Nakagawa H, Katayama S, Arata Y (1982) Solidification crack susceptibility in weld metals of fully austenitic stainless steels (report VII). Trans JWRI 11(2):79–85
Matsuda F, Nakata K, Arai K, Tsukamoto K (1982) Assessment of solidification cracking test for aluminium alloy welds. Trans JWRI 11(1):67–77
Serizawa H (2003) Theoretical prediction of welding hot cracking and its control. Trans JWRI 32(1):223–226
Senda T, Matsuda F, Takano G (1973) Studies on solidification crack susceptibility for weld metals with Trans-Varestraint test. J Japanese Welding Soc 42:48–56
Matsuda K, Nakata K, Harada S (1980) Moving characteristics of weld edges during solidification in relation to solidification cracking in GTA weld of aluminum alloy thin sheet. Trans JWRI vol.9(no. 2):225–235
Feng, Z., Zacharia, T. and David, S.A.: On the thermomechanical conditions for weld metal solidification cracking. In: Mathematical modelling of welding phenomena 3, 984 Seiten, Maney Publishing, ISBN: 186125010 X, pp. 114 – 148, 1997.
Feng, Z.; Zacharia, T; David S.A.: Thermal stress development in a nickel based superalloy during weldability test. Welding Research Supplement: November, pp. 470 – 483, 1997.
Zacharia, T; Aramayo G.A.: Modelling of thermal stresses in welds. International Conference Proceedings on Modelling and Control of Joining Processes, 8.–10.12.1993, Orlando, Florida, USA, pp. 533 – 540.
Zacharia T (1994) Dynamic stresses in weld metal hot cracking. Weld J vol. 73(no. 7):164s–172s
Feurer U (1977) Influence of alloy composition and solidification conditions on dendrite arm spacing, feeding and hot tearing properties of aluminium alloys. Proceedings International Symposium on Engineering Alloys, Delft, The Netherlands, pp 131–145
Rappaz M, Drezet JM, Gremaud M (1999) A new hot-tearing criterion. Met Mat Trans 30A:449–455
Kromm, A.; Kannengiesser, Th.: Influence of local weld deformation on the solidification cracking susceptibility of a fully austenitic stainless steel. Hot cracking phenomena in welds II, Buch, Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, ISBN 978-3-540-78627-6, pp. 77 - 92, 2008.
Wolf, M.; Kannengiesser, Th.; Boellinghaus, Th.: Determination of critical strain rate for solidification cracking by numerical simulation. Hot cracking phenomena in welds II, Buch, Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, ISBN 978-3-540-78627-6, pp. 77 - 92, 2008.
Kannengiesser, Th.; Kromm, A.: Design-specific influences on local weld displacement and hot cracking. Proceedings to II. International Conference in Welding Joining of Materials-ICWJM 2007, Cusco, Peru, ISBN 978-9972-42-806-7, pp.1-9, 2007.
Olson, D.L.; Edwards, G.R.: Interfacially driven mass transport in joining and coating technologies. Marangoni and Interfacial Phenomena in Materials Processing, The Royal Society, Cambridge, ISBN: 1-86125-056-8, pp. 113 – 126, 1998.
Rindler, W.; Kozeschnik, E.; Enzinger, N.; Buchmayr, B.: A modified hot tearing criterion for steels. Mathematical modelling of weld phenomena 6, Book 0784 Maney Publishing, ISBN: 1-902653-56-4, pp. 819 – 835, 2002.
Wang N, Mokadem S, Rappaz M, Kurz W (2004) Solidification cracking of superalloy single and bi-crystals. Acta Mater 52:3173–3182
Radaj D (1988) Wärmewirkungen des Schweißens, in german, Springer Verlag, ISBN 3-540-18695-6
Goodwin GM (1987) Development of a new hot-cracking test—the Sigmajig. Weld J 66:33–38
Feng, Z.; Tsai, C.L.: Modelling the thermomechanical conditions at weld pool. International Conference Proceedings on Modelling and Control of Joining Processes, 8 – 10 December 1993, Orlando, Florida, USA, pp. 525 – 532,1993.
Herold, H.; Streitenberger, M.; Pshennikov: Prevention of centreline solidification cracking during one-side welding. IIW-Doc. IX-2000-01, Online Dokument, Juli 2001.
Chihoski, R.A.: The character of stress fields around a weld arc moving on aluminum sheet. Welding Research Supplement, no. 1, pp. 9 – 18, 1972.
Johnson, L.: Formation of plastic strains during welding of aluminum alloys. Welding Research Supplement, no. 7, pp. 298 – 305, 1973.
Matsuda F, Nakagawa H, Nakata K, Kohomoto H, Honda Y (1983) Quantitative evaluation of solidification brittleness of weld metal during solidification by means of in-situ observation and measurement. Trans JWRI 12(1):65–72
Matsuda F, Nakagawa H, Matsubara Y (1983) Quantitative evaluation of solidification brittleness of weld metal during solidification by means of in-situ observation and measurement (report II). Trans JWRI 12(1):73–80
Muramatsu Y, Kuroda S, Shiga C (2003) Strain measurement during welding procedure. Application of laser speckle method to strain measurement in welding process (report 5). Weld Int vol. 5(no. 8):9–17
Matsuda F, Nakagawa H, Sorada K (1982) Dynamic observation of solidification and solidification cracking during welding with optical microscope. Trans JWRI 11(2):67–77
Wei, Y., Dong, Z.: Simulation and predicting weld solidification cracks. Book: Hot cracking phenomena in welds, Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, ISBN 3-540-22332-0, pp. 185 - 222, 2005.
Goodwin, G.M.: Test methods for evaluation hot cracking: review and perspective, Proceedings of the United States–Japan Symposium on Advances in Welding Metallurgy 1, pp. 59 – 78, 1990.
Perfilev AN, Yakushin BF, Logvinov VI (1972) Deformability of the seam metal in the crystallization process during welding of chrome-nickel steels. Chem Pet Eng 8(8):746–749
Savage WG, Lundin CD (1965) The Varestraint test. Weld J vol. 44 (no. 10):433s–442s
Savage WF, Lundin CD (1966) Application of the Varestraint technique to the study of weldability. Weld J 45(11):497–503
DIN EN ISO 17641: Destructive tests on welds in metallic materials—hot cracking tests for weldments, part 1–3—arc welding processes (2005).
Lippold, J.C.: Recent Developments in Weldability Testing. Book: Hot cracking phenomena in welds, Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, ISBN 3-540-22332-0, pp. 271-290, 2005.
Vallant, R.: The influence of different Nb-contents on the hot cracking susceptibility of Ni-base weld metals type 70/20. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, ISBN 3-540-22332-0, pp. 145-169, 2005.
Genis, K.; Wilken, K.; Bauer, S.: Microfissue test program: austenitic stainless steel—nickel-base and nickel-copper weld metal, IIW-Document IX-1693-92, International Institute of Welding, 1992.
Stout RD, Doty WD (1953) Weldability of steels, 1st edn. Welding Research Council, New York
Houldcroft PT (1955) A simple cracking test for use with argon-arc welding. Br Weld J 2(10):471–475
Phillips AL (1968) Welding handbook. American Welding Society, New York
Radhakrishnan, V.M.: Welding technology and design, New Age International (P) Limited, Publishers, ISBN 8122416721.
Mishler, H.W.; Monroe, R.E.; Rieppel, P.J.: WADC technical report, vol. 8; pp. 59-531, 1959.
Stout RD, Tör SS, McGeady LJ, Doan GE (1946) Quantitative measurement of the cracking tendency in welds. Welding Journal, Welding Research Supplement vol. 25(no. 9):522–531
Stout RD, Tör SS, McGeady LJ, Doan GE (1947) Some additional tests on the Lehigh Restraint specimen. Welding Journal, Welding Reseach Supplement 26(11):673–682
Gavrilin SV (1997) Methods of determining the hot cracking resistance of Al alloys. The Paton Welding Journal 9(8):425–430
Rogerson, J.H.; Cotterell, B.; Borland, J.C.: An analysis and evaluation of the Houldcroft weldc test. Welding Research Supplement, pp. 264-268, June 1963.
Shibahara M, Serizawa H, Murakawa H (2000) Finite element method for hot cracking using temperature dependent interface element (report II)—mechanical study of Houldcroft test. Trans JWRI vo. 29(no. 1):59–64
Messler, R.W.: Joining of materials and structures. Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann Inc. ISBN 0-7506-7757-0, 2004.
Brooks, J.A.; Dike, J.J.; Krafcik, J.S.: On modelling weld solidification cracking. Proceedings, International Conference Proceedings on Modelling and Control of Joining Processes, 8 – 10 December, Orlando, Florida, USA, pp.174 – 185, 1993.
Dike, J.J.; Brooks, J.A.; Krafcik, J.S.: Finite element modelling and verification of thermal–mechanical behavior in the weld pool region. Trends in Welding Research, Proceedings of the 4th International Conference, 5.–8.6 (1995) Gatlinburg. Tennessee, USA, pp 159–164
Matsuda F, Nakata K, Arai K, Tsukamoto K (1982) Assessment of solidification cracking test for aluminium alloy welds. Trans JWRI 11(1):67–77
Nelson TW, Lippold JC, Lin W, Baeslack WA (1997) Evaluation of the circular patch test for assessing weld solidification cracking, part I—development of a test method. Weld J vol. 76(no. 3):110s–119s
Davidson, J.A.; Konkol, P.J.; Sovak, J.F.: Assessing fracture toughness and cracking susceptibility of steel weldments—a review. Welding Research Council Bulletin 345, ISSN 0043-2326, 1989.
Stout RD, Doty WD (1978) Weldability of steels, 3rd edn. Welding Research Council, New York
Wooding WH (1950) Welding air-hardening alloy steels, welding journal. Welding Research Supplement 29(11):552–564
Mousavi MG, Cross CE, Grong O (1999) Effect of scandium and titanium-boron on grain refinement and hot cracking of aluminium alloy 7108. Sci Technol Weld Join 4(6):381–387
Hockett JE, Seaborn LO (1952) Evaluation of the circular patch weld test. Weld J vol. 31(no. 8):387s–392s
Hoerl A, Moore TJ (1957) The welding of type 347 steels. Weld J 36(10):442–448
Steinberger AW, DeSimone BJ, Stoop J (1950) Crack sensitivity of aircraft steels. Weld J 29(9):752–764
Zhang YC, Nakagawa H, Matsuda F (1986) Development of restraint-relaxation U-form hot cracking test device. Trans JWRI 15(1):159–163
Shinozaki K, Kuroki H, Luo X, Ariyoshi H, Shirai M (1999) Comparison of hot-cracking susceptibilities of various Ni-base, heat-resistant superalloys by U-type hot cracking test. Study of laser weldability of Ni-base, heat-resistant superalloys (2nd report). Weld Int vol. 13(no. 12):952–959
Schnadt, H.M.: Über eine neue Prüftechnik zur Bestimmung der Warmrißanfälligkeit von Schweißraupen. Oerlikon Schweißmitteilungen, Nr. 27, S. 31-42, in german, 1957.
North TH, Rothwell AB, Glover AG, Pick RJ (1982) Weldability of high strength line pipe steels. Weld J vol. 61(no. 8):243s–257s
Satoh K, Matsui S, Nishimura I, Iiyama H, Chiba N (1977) Effect of intensity of bending restraint on weld cracking in multipass weld. Transactions of the Japan Welding Society 8(1):42–49
Hull FC (1959) Cast-pin tear test for susceptibility to hot cracking. Weld J vol. 38:176s–181s
Alexandrov, B.T.Lippold, J.C: Development of the cast pin tear test to study solidification cracking. Welding in the World, ISSN 0043-2288, vol. 57, DOI 10.1007/s40194-013-0061-3, pp. 635-648, 2013.
Alexandrov, B.T.; Nissley, N.E; Lippold, J.C.: Evaluation of weld solidification cracking in Ni-base superalloys using the cast pin tear test, hot cracking phenomena in welds II, ISBN 978-3-540-78627-6, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp.193-214, 2008.
Alexandrov, B.T.Lippold, J.C: Development of the cast pin tear test for evaluating solidification cracking in Ni-base alloys, hot cracking phenomena in welds III, Eds. T. Boellinghaus, C. Cross, and J. Lippold, Springer-Verlag Berlin, ISBN 978-3-642-16863-5, pp.393-414, 2011.
http://www.matsceng.ohio-state.edu/wjmg/cpttImprovement.htmlx.
Wilken, K.: Investigation to compare hot cracking tests—externally loaded specimen—final report. IIS/IIW-Subcommission IX-H/II-C, Doc IX-1945-99, 1999.
Kannengiesser, Th., McInerney, T., Florian, W., Böllinghaus, Th. and Cross, C.E.: The influence of local weld deformation on hot cracking susceptibility, mathematical modelling of weld phenomena 6, Manley, pp. 803-818, ISBN 1-902653-56-4, 2002.
Cross, C.E.; Böllinghaus, Th.: The effect of restraint on weld solidification cracking in aluminium. Welding in the world, ISSN 0043-2288, vol. 49, special issue, pp. 458-463, 2005.
Gollnow, C.; Kannengiesser, Th.: Hot cracking analysis using in situ digital image correlation technique. Welding in the world, ISSN 0043-2288, vol. 57, no. 3, DOI 10.1007/s40194-013-0061-3, pp. 277-284, 2013.
Weiss B, Grotke GE, Stickler R (1970) Physical metallurgy of hot ductility testing. Weld J vol. 49(no. 10):471-s–487-s
Mandziej, S.T.: Testing for susceptibility to hot cracking on Gleeble® physical simulator. Book: Hot cracking phenomena in welds, Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, ISBN 3-540-22332-0, pp. 347-376, 2005.
Caliskanoglu, O.; Ilie, S.; Sommitsch, C.: Hot ductility behavior of a continuously cast steel during solidification. Proceedings of STEELSIM 2013, 5th Intern. Conference, TU of Ostrava, Czech Republic, 10.-12.9. 2013.
Faria, G.; Wu, L.; Alonso, T.; Isaac, A.; Piton, J.; Neuenschwander, R.; Ramirez, A.J.: Advanced facility for parallel thermo-mechanical simulation and synchrotron X-ray diffraction. Book: In-situ studies with photons, neutrons and electrons scattering II, Springer-Verlag, in print.
Messler, R.W.: Principles of welding. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KG, Weinheim, ISBN 0471-25376-6, 2004.
Lampman, S.; Davidson, G.M.; Powers, C.L.: Weld integrity and performance. ASM International, Materials Park, OH 44073-0002, ISBN 0-87170-600-8, 2001.
Wenderoth, M.: Hochtemperaturverformung. www.metalle.uni-bayreuth.de
Lin W (1992) A model for heat-affected zone liquation cracking. Welding in the World 30(9/10):236–242
Ramirez, A.J., Lippold, J.C.: New insight into the mechanism of ductility-dip cracking in Ni-base weld metlas. Book: Hot cracking phenomena in welds, Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, ISBN 3-540-22332-0, pp. 19 - 41, 2005.
Nippes EF, Savage WF, Grotke G (1957) Further studies of the hot-ductility of high-temperature alloys. Weld Res Counc Bull(33)
Lundin CD, Qiao CYP, Gill TPS, Goodwin GM (1993) Hot ductility and hot cracking behavior of modified 316 stainless steels designed for high temperature service. Weld J 72:189–200
Herold, H.; Pshennikov, A.; Streitenberger, M.: Influence of the deformation rate of different tests on hot cracking formation. Hot cracking phenomena in welds, Book: Hot cracking phenomena in welds, Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, ISBN 3-540-22332-0, pp. 328-346, 2005.
Herold, H., Streitenberger, M. and Pchennikov, A.: Modelling of the PVR-test to examine the origin of different hot cracking types, mathematical modelling of weld phenomena 5, (ed. Cerjak). IOM Communications Ltd., London, ISBN 1861251157, ISBN 1861251157, pp. 783-792, 2001.
Heuser, H.: Value of different hot cracking tests for the manufacturer of filler metals. Book: Hot cracking phenomena in welds, Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, ISBN 3-540-22332-0, pp. 303-327, 2005.
Lin W, Lippold J, Baeslack W (1993) An evaluation of heat-affected zone liquation cracking susceptibility—part 1: development of a method for quantification. Weld J vol. 72(no. 4):135-s–153-s
McKewon D (1970) Versatile weld metal cracking tests. Metal Construction & British Welding Journal 2(8):351–352
Senda, T.; Matsuda, F.; Takano, G.; Watanabe, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Matsuzaka, T.: Fundamental investigation on solidification crack susceptibility for weld metals with Trans-Varestraint test. Cracking and fracture in welds; Proceedings of the 1. International Symposium on the Precaution of Cracking in Welded Structures, Tokyo, 8.-10.11.1971.
Savage WF, Nippes EF, Goodwin GM (1977) Effect of minor elements on hot-cracking tendencies of Inconel 600. Weld J vol. 56(no. 8):245s–253-s
Wilken, K.; Kleistner, H.: The classification and evaluation of hot cracking tests for weldments. IIW-Dok. IX-1379-85.
Schobbert, H.; Böllinghaus, Th.; Wolf, M.: Metastable primary solidification modes in the Fe-Cr-Ni system during laser welding. Book: Solidification and crystallization, Ed. D.M. Herlach, WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbHCo. KGaA, ISBN 3-527-31011-8, pp.213-226, 2004.
Matsuda EH, Nakagawa H, Nakata K, Okada H (1979) The VDR cracking test solidification crack susceptibility on weld metals and its application of aluminium alloys. Transactions of the JWRJ vol. 8 (no.1):85–95
Fredricks H, van der Toorn LT (1967) The KSLA hot crack testing apparatus. Br Weld J 14(6):298–303
Bergmann HW, Hilbinger RM (1998) Numerical simulation of centre line hot cracks in laser beam welding of aluminium close to the sheet edge. Mathematical modelling of weld phenomena 4 (ed. Cerjak). IOM Communications Ltd, London, pp 658–668
Rollason EC, Roberts DFT (1954) Operating data for the Murex hot-crack testing machines. Br Weld J 1(10):441–447
Kurz, W., D.J. Fisher: Fundamentals of solidification. Buch, 305 Seiten, Third Edition, Trans Tech Publications, ISBN 0-87849-522-3, 1992.
Hilbinger, R.M.; Bergmann, H.W.; Köhler, W.; Palm, F.: Considering of dynamic mechanical boundary conditions in the characterisation of a hot cracking test by means of numerical simulation. Mathematical modelling of weld phenomena 5 (ed. Cerjak). IOM Communications Ltd., London, ISBN 1861251157, pp. 847 – 862, 2001.
Ploshikhin, V.; Prikhodovsky, A.; Makhutin, M.; Ilin, A.; Zoch, H.-W.: Integrated mechanical–metallurgical approach to modelling of solidification cracking in welds. Buch, 2005.
Dike JJ, Brooks JA, Li M (1998) Comparison of failure criteria in weld solidification cracking simulations. Mathematical modelling of weld phenomena 4. Maney Publishing, London, pp 199–222
Brooks JA, Dike JJ (1998) Modelling weld solidification cracking behavior in aluminum alloys—analysis of fracture initiation. Trends in welding research, Proceedings of the 5th International Conference, 1.–5.6. Pine Mountain, Georgia, USA, pp 695–699
Wei YH, Liu RP, Dong ZJ (2003) Software package for simulation and prediction of welding solidification cracks. Sci Technol Weld Join 8(5):325–333
Guo, W.; Kar, A.: Prediction of microstructures in laser materials processing. Laser materials processing conf. ICALEO’97. Pt.1, San Diego, USA, 17.-20.11.1997, vol. 83, pp. 189-197, 1997.
Balbi, M.; Vedani, M.: Weldability of Al-Al204 composites. The ASM International European Conference on Welding and Joining Science and Technology, Madrid, 10.-12.03.1997, pp. 416-424, 1997.
Ohta S, Asai K (1993) The behavior of temperature decreasing and fraction solid increasing in solid–liquid coexisting zone in solidification process of aluminum alloy weld metal. Transactions of the Japan Welding Society 24(2):131–139
Huang C (2001) Kou, S.: Partially melted zone in aluminum welds-planar and cellular solidification. Welding J N Y 80(2):46–53
Katayama S (2000) Solidification phenomena of weld metals. Report 1. Characteristic solidification morphologies, microstructures and solidification theory. Weld Int vol. 14(no. 12):939–951
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Doc. IIW-2441, recommended for publication by Commission II “Arc Welding and Filler Metals”.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kannengiesser, T., Boellinghaus, T. Hot cracking tests—an overview of present technologies and applications. Weld World 58, 397–421 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-014-0126-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-014-0126-y