Abstract
Background:
In order to develop region-specific diagnostic assays and prevent hepatitis E virus (HEV), it is essential to understand epidemiology and genotypic variation within different populations. However, the epidemiological data of HEV infections in Jilin is shortage.
Methods:
The seroepidemiological study was conducted by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and the conserved genomic sequences of open reading frame 2 (348 bp) was detected using reverse transcription-PCR.
Results:
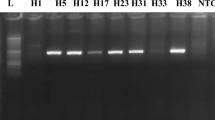
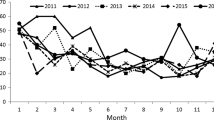
Overall, 1,289 serum samples were positive to HEV-specific immunoglobulin G (IgG), and 180 serum samples were positive to HEV-specific immunoglobulin M (IgM). The seroprevalence of HEV-specific IgG was 26.3%, 27.9%, 25.3%, 32.7% in 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006, respectively. Acute HEV infection mainly occurred in male, people aged from 20 to 69 were more susceptible to infection, and cases with IgM anti-HEV reaction mainly occurred from July to November. HEV RNA was detectable in the serum samples or stool suspension of 15 patients with HEV-specific IgM, and all of these belonged to genotype IV.
Conclusions:
Our results indicate that HEV is widely spread in Jilin and confined to genotype IV.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dr. G. Zhu and Dr. Y. Qu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, G., Qu, Y., Jin, N. et al. Seroepidemiology and Molecular Characterization of Hepatitis E Virus in Jilin, China. Infection 36, 140–146 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s15010-007-7130-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s15010-007-7130-8