Abstract
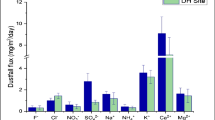
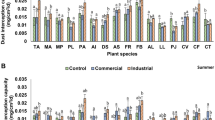
The present work is an attempt to investigate pollution effect on an ornamental tree species Thevetia peruviana (Pers.) K. Schum. The study was conducted in various green spaces of institutional, industrial, residential and near traffic site representing as different status of air pollution concentration depending on land-use type. The resistance index calculated for selected species had mean value of 14.57 ± 0.41 observed at study sites. The dust deposition was found in range of 5.14–7.74 mg cm−2 on foliar surface of 12 cm2. The examination of leaf structure with scanning electron microscope showed presence of airborne dust particles in coarse and fine sizes with higher deposition found in industrial and residential sites. The epicuticular wax layer on upper surface of foliar was found eroded at industrial and traffic regions. The equivalent diameter of particles was observed to range from 0.45 to 12.71 µm in Poisson distributional pattern. The density of number concentration of dust particles was observed 1411 and 3703 in institutional and industrial area deposited on 0.22 mm2 of foliar surface. The elemental distribution on leaves of Thevetia peruviana has revealed a mixture of carbonaceous and soil matrix elements such as C, O, Al, Na, Si, K and Mg observed in proportion of X-rays counts per second. The whole experiment gave a positive indication for plant species as a tolerant bio-indicator of air pollutants in Delhi. The diverse flora present in city provides an opportunity for reducing harmful concentration of PM10 and PM2.5 and improving quality of air for human health.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- APTI:
-
Air pollution tolerance index
- RWC:
-
Relative water content
- PM:
-
Particulate matter
- SEM-EDX:
-
Scanning electron microscope-energy-dispersive X-ray
References
Beckett KP, Freer Smith PH, Taylor G (2000) The capture of particulate pollution by trees at five contrasting urban sites. Arboric J 24:209–230. doi:10.1080/03071375.2000.9747273
Bhalla P, Bhattacharya P (2015) Urban biodiversity and green spaces in Delhi: A case study of new settlement and Lutyen’s Delhi. J Hum Ecol 51(2):77–81. ISSN: 0970-9274
Breed CA, Arocena JM, Sutherland D (2002) Possible sources of PM10 in Prince George (Canada) as revealed by morphology and in situ chemical composition of particulate. Atmos Environ 36(10):1721–1731. doi:10.1016/S1352-2310(01)00500-3
Buseck PR, Jacob DJ, Posfai M, Li J, Anderson JR (2000) Minerals in the air: an environmental perspective. Int Geol Rev 42(7):577–593. doi:10.1080/00206810009465101
Chow JC (1995) Measurement methods to determine compliance with ambient air quality standards for suspended particles. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 45(5):320–382. doi:10.1080/10473289.1995.10467369
Govindaraju M, Ganeshkumar RS, Muthukumaran VR, Visvanathan P (2012) Identification and evaluation of air-pollution-tolerant plants around lignite-based thermal power station for greenbelt development. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:1210–1223. doi:10.1007/s11356-011-0637-7
Guttikunda SK, Goel R, Pant P (2014) Nature of air pollution, emission sources, and management in the Indian cities. Atmos Environ 95:501–510. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.07.006
Hochella MF, Lower SK, Maurice PA, Penn RL, Sahai N, Sparks DL, Twining BS (2008) Nanominerals, mineral nanoparticles and earth systems. Science 319:1631–1635. doi:10.1126/science.1141134
Jamil S, Abhilash PC, Singh A, Singh N, Behl HM (2009) Fly ash trapping and metal accumulating capacity of plants: Implications for green belt around thermal power plants. Landsc Urban Plan 92:136–147. doi:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2009.04.002
Janhall S (2015) Review on urban vegetation and particle air pollution—deposition and dispersion. Atmos Environ 105:130–137. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.01.052
Kocic K, Spasić T, Urošević MA, Tomašević M (2014) Trees as natural barriers against heavy metal pollution and their role in the protection of cultural heritage. J Cult Heritage 15(3):227–233. doi:10.1016/j.culher.2013.05.001
Kumar P, Gupta NC (2016) Commuter exposure to inhalable, thoracic and alveolic particles in various transportation modes in Delhi. Sci Total Environ 541:535–541. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.09.076
Kumar B, Verma K, Kulshrestha U (2014) Deposition and mineralogical characteristics of atmospheric dust in relation to land use and land cover change in Delhi (India). Geogr J. doi:10.1155/2014/325612
Laskin A, Cowin JP, Iedema MJ (2006) Analysis of individual environmental particles using modern methods of electron microscopy and X-ray microanalysis. J Electron Spectrosc Relat Phenom 150(2):260–274. doi:10.1016/j.elspec.2005.06.008
Liu L, Guan D, Peart MR (2012) The morphological structure of leaves and the dust-retaining capability of afforested plants in urban Guangzhou, South China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19(8):3440–3449. doi:10.1007/s11356-012-0876-2
Nadgorska-Socha A, Kandziora-Ciupa M, Ciepał R, Barczyk G (2016) Robinia pseudoacacia and Melandrium album in trace elements biomonitoring and air pollution tolerance index study. Int J Environ Sci Technol 13:1741–1752. doi:10.1007/s13762-016-1010-7
Ottele M, Van Bohemen HD, Fraaij AL (2010) Quantifying the deposition of particulate matter on climber vegetation on living walls. Ecol Eng 36(2):154–162. doi:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2009.02.007
Pal A, Kulshreshtha K, Ahmad KJ, Behl HM (2002) Do leaf surface characters play a role in plant resistance to auto-exhaust pollution? Flora-Morphol Distrib Funct Ecol Plants 197(1):47–55. doi:10.1078/0367-2530-00014
Poschl U (2005) Atmospheric aerosols: composition, transformation, climate and health effects. Angew Chem Int Ed 44:7520–7540. doi:10.1002/anie.200501122
Prusty BAK, Mishra PC, Azeez PA (2005) Dust accumulation and leaf pigment content in vegetation near the national highway at Sambalpur, Orissa, India. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 60(2):228–235. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2003.12.013
Rai A, Kulshreshtha K, Srivastava PK, Mohanty CS (2010) Leaf surface structure alterations due to particulate pollution in some common plants. Environmentalist 30(1):18–23. doi:10.1007/s10669-009-9238-0
Ram SS, Kumar RV, Chaudhuri P, Chanda S, Santra SC, Sudarshan M, Chakraborty A (2014) Physico-chemical characterization of street dust and re-suspended dust on plant canopies: an approach for finger printing the urban environment. Ecol Indic 36:334–338. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2013.08.010
Satsangi PG, Yadav S (2014) Characterization of PM2.5 by X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy-energy dispersive spectrometer: its relation with different pollution sources. Int J Environ Sci Technol 11(1):217–232. doi:10.1007/s13762-012-0173-0
Singh SK, Rao DN, Agrawal M, Pandey J, Naryan D (1991) Air pollution tolerance index of plants. J Environ Manage 32(1):45–55. doi:10.1016/S0301-4797(05)80080-5
Smith WH, Staskawicz BJ (1977) Removal of atmospheric particles by leaves and twigs of urban trees: some preliminary observations and assessment of research needs. Environ Manage 1(4):317–330. doi:10.1007/BF01865859
Tomasevic M, Vukmirovic Z, Rajsic S, Tasic M, Stevanovic B (2005) Characterization of trace metal particles deposited on some deciduous tree leaves in an urban area. Chemosphere 61(6):753–760. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.03.077
Varma V, Osuri AM (2013) Black Spot: a platform for automated and rapid estimation of leaf area from scanned images. Plant Ecol 214(12):1529–1534. doi:10.1007/s11258-013-0273-z
Wang H, Shi H, Wang Y (2015) Effects of weather, time, and pollution level on the amount of particulate matter deposited on leaves of Ligustrum lucidum. Sci J. doi:10.1155/2015/935942
Wolterbeek HT, Garty J, Reis MA, Freitas MC (2003) Biomonitors in use: lichens and metal air pollution. Trace Metals Other Contam Environ 6:377–419. doi:10.1016/S0927-5215(03)80141-8
Yang J, Yu Q, Gong P (2008) Quantifying air pollution removal by green roofs in Chicago. Atmos Environ 42(31):7266–7273. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2008.07.003
Zampieri MCT, Sarkis JE, Pestana RC, Tavares AR, Melo-de-Pinna GF (2013) Characterization of Tibouchina granulosa (Desr.) Cong. (Melastomataceae) as a biomonitor of air pollution and quantification of particulate matter adsorbed by leaves. Ecol Eng 61:316–327. doi:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2013.09.050
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Dean, University School of Environment Management affiliated with Guru Gobind Singh Indraprastha University for facilitating the laboratory work. One of the authors Ms. Simpy Singh is thankful to University Grants Commission (UGC) for providing financial support through senior research fellowship. The authors are thankful to Sophisticated Advanced Instrumentation Facility (SAIF) AIIMS for plant leaf specimen preparation and SAIF Cochin for SEM–EDX facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Rupali Datta.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, S., Bhattacharya, P. & Gupta, N.C. Dust particles characterization and innate resistance for Thevetia peruviana in different land-use pattern of urban area. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 15, 1061–1072 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1461-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1461-5