Abstract
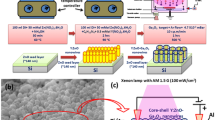
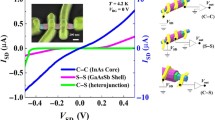
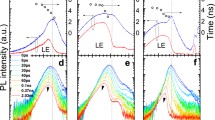
A ternary InAsyP1−y alloy is suitable for an application to near-infrared (NIR) optical devices as their direct bandgap energy covers the entire NIR band. A nanowire (NW) system allows an epitaxial integration of InAsyP1−y alloy on any type of substrate since the lattice mismatch strain can be relieved through the NW sidewall. Nevertheless, the very large surface to volume ratio feature of the NWs leads to enormous surface states which are susceptible to surface recombination of free carriers. Here, ternary InAs0.75P0.25 NWs are grown with InP passivation layer (i.e., core–shell structure) to minimize the influence of the surface states, thus increasing their optical and electrical properties. A photoresponse study was achieved through the modeled band structure of the grown NWs. The model and experimental results suggest that 5-nm-thick InP shell efficiently passivates the surface states of the InAs0.75P0.25 NWs. The fabricated core–shell photodetectors and field-effect transistors exhibit improved photoresponse and transport properties compared to its counterpart core-only structure.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, J.E., Hemesath, E.R., Perea, D.E., Lensch-Falk, J.L., Li, Z., Yin, F., Gass, M.H., Wang, P., Bleloch, A.L., Palmer, R.E., Lauhon, L.J.: High-resolution detection of Au catalyst atoms in Si nanowires. Nat. Nanotechnol. 3, 168–173 (2008)
Breuer, S., Pfüller, C., Flissikowski, T., Brandt, O., Grahn, H.T., Geelhaar, L., Riechert, H.: Suitability of Au-and self-assisted GaAs nanowires for optoelectronic applications. Nano Lett. 11, 1276–1279 (2011)
Chang, C.-C., Chi, C.-Y., Yao, M., Huang, N., Chen, C.-C., Theiss, J., Bushmaker, A.W., LaLumondiere, S., Yeh, T.-W., Povinelli, M.L.: Electrical and optical characterization of surface passivation in GaAs nanowires. Nano Lett. 12, 4484–4489 (2012)
Choi, C.H., Kim, H., Hwang, J., Cho, M., Shin, J.C.: Electrical properties of InAs/InP core–shell nanowires. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 16, 11535–11537 (2016)
Cornet, C., Schliwa, A., Even, J., Doré, F., Celebi, C., Létoublon, A., Macé, E., Paranthoen, C., Simon, A., Koenraad, P.: Electronic and optical properties of InAs/InP quantum dots on InP (100) and InP (311) B substrates: theory and experiment. Phys. Rev. B 74, 035312 (2006)
Dai, X., Zhang, S., Wang, Z., Adamo, G., Liu, H., Huang, Y., Couteau, C., Soci, C.: GaAs/AlGaAs nanowire photodetector (2016). arXiv preprint arXiv:1601.02312
Demarina, N., Grützmacher, D.: Influence of surface states on electronic band structure and electron density in InAs nanowires and InAs shell nanowires. ECS Trans. 64, 95–99 (2014)
Holloway, G.W., Song, Y., Haapamaki, C.M., LaPierre, R.R., Baugh, J.: Electron transport in InAs–InAlAs core–shell nanowires. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 043115 (2013)
Jiang, X., Xiong, Q., Nam, S., Qian, F., Li, Y., Lieber, C.M.: InAs/InP radial nanowire heterostructures as high electron mobility devices. Nano Lett. 7, 3214–3218 (2007)
Kasanaboina, P.K., Ojha, S.K., Sami, S.U., Reynolds, L., Liu, Y., Iyer, S.: Tailoring of GaAs/GaAsSb Core–Shell Structured Nanowires for IR Photodetector Applications, pp. 937307–937309. International Society for Optics and Photonics, Bellingham (2015)
Kavanagh, K.L., Saveliev, I., Blumin, M., Swadener, G., Ruda, H.E.: Faster radial strain relaxation in InAs–GaAs core–shell heterowires. J. Appl. Phys. 111, 044301 (2012)
Kawaguchi, K., Sudo, H., Matsuda, M., Takemoto, K., Yamamoto, T., Arakawa, Y.: Radial InP/InAsP/InP heterostructure nanowires on patterned Si substrates using self-catalyzed growth for vertical-type optical devices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 106, 0120107 (2015)
Li, H.-Y., Wunnicke, O., Borgström, M., Immink, W., Van Weert, M., Verheijen, M., Bakkers, E.: Remote p-doping of InAs nanowires. Nano Lett. 7, 1144–1148 (2007)
Lin, A., Shapiro, J.N., Scofield, A.C., Liang, B., Huffaker, D.L.: Enhanced InAs nanopillar electrical transport by in situ passivation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 053115 (2013)
Manual A Us: Device Simulation Software. Silvaco Int, Santa Clara (2008)
Popovitz-Biro, R., Kretinin, A., Von Huth, P., Shtrikman, H.: InAs/GaAs core–shell nanowires. Cryst. Growth Des. 11, 3858–3865 (2011)
Rieger, T., Luysberg, M., Schäpers, T., Grützmacher, D., Lepsa, M.I.: Molecular beam epitaxy growth of GaAs/InAs core–shell nanowires and fabrication of InAs nanotubes. Nano Lett. 12, 5559–5564 (2012)
Shin, J.C., Lee, A., Katal Mohseni, P., Kim, D.Y., Yu, L., Kim, J.H., Kim, H.J., Choi, W.J., Wasserman, D., Choi, K.J., Li, X.: Wafer-scale production of uniform InAsyP1−y nanowire array on silicon for heterogeneous integration. ACS Nano 7, 5463–5471 (2013)
Shin, J.C., Lee, A., Kim, H.J., Kim, J.H., Choi, K.J., Kim, Y.H., Kim, N., Bae, M.-H., Kim, J.-J., Kim, B.-K.: Growth characteristics and electrical properties of diameter-selective InAs nanowires. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 62, 1678–1682 (2013)
Tchernycheva, M., Cirlin, G.E., Patriarche, G., Travers, L., Zwiller, V., Perinetti, U., Harmand, J.-C.: Growth and characterization of InP nanowires with InAsP insertions. Nano Lett. 7, 1500–1504 (2007)
Tretiak, S., Piryatinski, A.: Modeling photoexcited carrier interactions in semiconductor nanostructures. Nano Lett. 5, 865–871 (2005)
Treu, J., Bormann, M., Schmeiduch, H., Döblinger, M., Morkötter, S., Matich, S., Wiecha, P., Saller, K., Mayer, B., Bichler, M.: Enhanced luminescence properties of InAs–InAsP core–shell nanowires. Nano Lett. 13, 6070–6077 (2013)
Van Tilburg, J., Algra, R., Immink, W., Verheijen, M., Bakkers, E., Kouwenhoven, L.: Surface passivated InAs/InP core/shell nanowires. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 25, 024011 (2010)
Woodall, J.M., Pettit, G.D., Jackson, T.N., Lanza, C., Kavanagh, K.L., Mayer, J.W.: Fermi-level pinning by misfit dislocations at GaAs interfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 51, 1783–1786 (1983)
Xie, S., Kim, H., Lee, W.J., Farrell, A.C., David, J.P., Huffaker, D.L.: InAs/InAsP core/shell nanowire photodiode on a Si substrate. Nano Adv. 1, 110–114 (2016)
Zhang, Y., Wu, J., Aagesen, M., Liu, H.: III–V nanowires and nanowire optoelectronic devices. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 48, 463001 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2017R1C1B2010906 and NRF-2017M1A2A2048904) and was a part of the project titled ‘Development of real-time measuring system of basic environment for the water quality monitoring of the aquaculture farm,’ funded by the Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries, Korea (No. 20150303).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, R., Jo, M.H., Kim, T. et al. Photoresponse and Field Effect Transport Studies in InAsP–InP Core–Shell Nanowires. Electron. Mater. Lett. 14, 357–362 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-018-0041-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-018-0041-2