Abstract
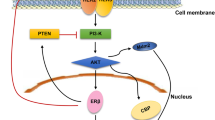
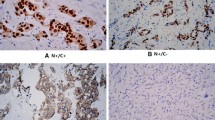
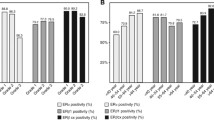
The aim of the study was to investigate the effects of estrogen receptor (ER) subtypes (ERα and ERβ) on breast cancer development and progression. The expression level of ERα and ERβ in breast cancer tissues and paired normal breast tissues were detected by Western blot analysis and immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining. The features of ERα and ERβ status in cancer tissues or normal breast tissues and the correlations between clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis were analyzed. The expression levels of ERα and ERβ in breast cancer tissues are significantly lower than those in the paired normal tissues. The expression of ERβ is decreased more than that of ERα. ERα expression levels in cancer tissues are associated with tumor diameter, tumor–node–metastasis (TNM) stage, and progesterone receptor (PR) status. However, ERβ expression levels in cancer tissues are not correlated with clinicopathological factors of patients with breast cancer. In conclusion, ER subtypes might play different roles in the development of breast cancer.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heldring N, Pike A, Andersson S, Matthews J, Cheng G, Hartman J, et al. Estrogen receptors: how do they signal and what are their targets. Physiol Rev. 2007;87:905–31.
Paris O, Ferraro L, Grober OMV, Ravo M, De Filippo MR, Giurato G, et al. Direct regulation of microRNA biogenesis and expression by estrogen receptor beta in hormone-responsive breast cancer. Oncogene. 2012;31(38):4196–206.
Hopp TA, Weiss HL, Parra IS, Cui Y, Osborne CK, Fuqua SA. Low levels of estrogen receptor beta protein predict resistance to tamoxifen therapy in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:7490–9.
Murphy LC, Leygue E, Niu Y, Snell L, Ho SM, Watson PH. Relationship of coregulator and estrogen receptor isoform expression to de novo tamoxifen resistance in human breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 2002;87:1411–6.
Osborne CK, Schiff R, Fuqua SA, Shou J. Estrogen receptor: current understanding of its activation and modulation. Clin Cancer Res. 2001;7:4338s–42s. discussion 4411s—4412s.
Barone I, Brusco L, Fuqua SA. Estrogen receptor mutations and changes in downstream gene expression and signaling. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16:2702–8.
Chang EC, Frasor J, Komm B, Katzenellenbogen BS. Impact of estrogen receptor beta on gene networks regulated by estrogen receptor alpha in breast cancer cells. Endocrinology. 2006;147:4831–42.
Helguero LA, Faulds MH, Gustafsson JA, Haldosén LA. Estrogen receptors alfa (ERalpha) and beta (ERbeta) differentially regulate proliferation and apoptosis of the normal murine mammary epithelial cell line HC11. Oncogene. 2005;24:6605–16.
Cato AC, Nestl A, Mink S. Rapid actions of steroid receptors in cellular signaling pathways. Science STKE. 2002;138:re9.
Nemere I, Pietras RJ, Blackmore PF. Membrane receptors for steroid hormones: signal transduction and physiological significance. J Cell Biochem. 2003;88:438–45.
Ordonez-Moran P, Munoz A. Nuclear receptors: genomic and nongenomic effects converge. Cell Cycle. 2009;8:1675–80.
Paech K, Webb P, Kuiper GG, Nilsson S, Gustafsson J, Kushner PJ, et al. Differential ligand activation of estrogen receptors ERα and ERβ at AP1 sites. Science. 1997;277:1508–10.
Salvatori L, Pallante P, Ravenna L, Chinzari P, Frati L, Russo MA, et al. Estrogens and selective estrogen receptor (ER) modulators regulate EGF receptor gene expression through human ERα and β subtypes via an Sp1 site. Oncogene. 2003;22:4875–81.
Safe S, Kim K. Nuclear receptor-mediated transactivation through interaction with Sp proteins. Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2004;77:1–36.
Panno ML, Mauro L, Marsico S, Bellizzi D, Rizza P, Morelli C, et al. Evidence that mouse IRS-1 belongs to the family gene which promoter is activated by ERα through its interaction with Sp-1. J Mol Endocrinol. 2006;36:91–105.
Mauro L, Catalano S, Bossi G, Pellegrino M, Barone I, Morales S, et al. Evidence that leptin upregulates E-cadherin expression in breast cancer effects on tumor growth and progression. Cancer Res. 2007;67:3412–21.
Higgins KJ, Shengxi L, Abdelrahim M, Vanderlaag K, Liu X, Porter W, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 expression is down-regulated by 17 beta estradiol in MCF-7 breast cancer cells by estrogen receptor alpha/Sp-1 proteins. Mol Endocrinol. 2008;22:388–402.
Varlakhanova N, Snyder C, Jose S, Hahm JB, Privalsky ML. Estrogen receptors recruit SMRT and N-CoR corepressors through newly recognized contacts between the corepressor N terminus and the receptor DNA binding domain. Mol Cell Biol. 2010;30:1434–45.
Cheng L, Li J, Han Y, Lin J, Niu C, Zhou Z, et al. PES1 promotes breast cancer by differentially regulating ERα and ERβ. J Clin Invest. 2012;122:2857–70.
Leygue E, Dotzlaw H, Watson PH, Murphy LC. Altered estrogen receptor α and β messenger RNA expression during human breast tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 1998;58:3197–201.
Jarvinen TA, Pelto-Huikko M, Holli K, Isola J. Estrogen receptor β is coexpressed with ERα and PR and associated with nodal status, grade and proliferation rate in breast cancer. Am J Pathol. 2000;156:29–35.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Social Developmental Scientific Project of Yinzhou (No. 200553).
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, W., Gu, C., Xia, M. et al. Significance of estrogen receptor subtypes in breast tumorigenesis and progression. Tumor Biol. 35, 9111–9117 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2152-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2152-1