Abstract
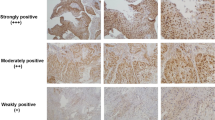
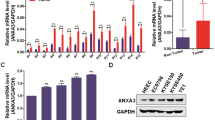
Eph/ephrin signaling system plays a very important role in the tumorigenesis and the formation of blood vessel. However, the function of EphB4 and its ligand ephrin B2 in the carcinogenesis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is not fully understood. Here, it was found that the expression of EphB4 was up-regulated in ESCC tissues compared with the paired normal tissues, while ephrin B2 was down-regulated in ESCC samples. Phosphorylation of EphB4 induced by its ligand ephrin B2-Fc inhibited the growth, migration and colony formation of ESCC cells. Moreover, over-expression of EphB4 or EphB4 kinase dead mutant (EphB4 KD) in ESCC cells promoted cell growth and migration, suggesting EphB4 promoted cell growth and migration independent of its kinase activity. Furthermore, we found that EphB4 interacted with the adaptor protein RACK1 and RACK1 decreased the phosphorylation level of EphB4. Taken together, our study revealed the important function and regulation of EphB4 in the progression of ESCC and suggested EphB4 as a novel target for the treatment of ESCC.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;60:277–300.
Enzinger PC, Mayer RJ. Esophageal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:2241–52.
Tachibana M, Kinugasa S, Yoshimura, et al. Extended esophagectomy with 3-field lymph node dissection for esophageal cancer. Arch Surg. 2003;138:1383–9.
Kopreski MS, Witters L, Brennan WAJ, et al. Protein tyrosine kinase activity in breast cancer and its relation to prognostic indicators. Anticancer Res. 1996;16:3037–41.
Lindberg RA, Hunter T. cDNA cloning and characterization of eck, an epithelial cell receptor protein tyrosine kinase in the eph/elk family of protein kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1990;10:6316–24.
Surawska H, Ma PC, Salgia R. The role of ephrins and Eph receptors in cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2004;15:419–33.
Kim YH, Hu H, Guevara GS, et al. Artery and vein size is balanced by Notch and ephrin B2/B4 during angiogenesis. Development. 2008;135:3755–64.
Bruhl T, Urbich C, Aicher D, et al. Homeobox A9 transcriptionally regulates the EphB4 receptor to modulate endothelial cell migration and tube formation. Circ Res. 2004;94:743–51.
Steinle JJ, Meininger CJ, Forough R, et al. EphB4 receptor signaling mediates endothelial cell migration and proliferation via PI3K pathway. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:43830–5.
Hasina R, Mollberg N, Kawada I. Critical role for the receptor tyrosine kinase EPHB4 in esophageal cancers. Cancer Res. 2013;73:184–94.
Hu HQ, Tao Z, Wang MS, et al. RACK1 promoted the growth and migration of the cancer cells in the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 2013;34:3893–9.
Xia G, Kumar SR, Masood R, et al. EphB4 expression and biological significance in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2005;65:4623–32.
Xia G, Kumar SR, Stein JP, et al. EphB4 receptor tyrosine kinase is expressed in bladder cancer and provides signals for cell survival. Oncogene. 2006;25:769–80.
Kumar SR, Masood R, Spannuth WA, et al. The receptor tyrosine kinase Ephb4 is overexpressed in ovarian cancer, provides signals and predicts poor outcome. Br J Cancer. 2007;96:1083–91.
Noren NK, Foos G, Hauser CA, et al. The EphB4 receptor suppresses breast cancer cell tumorigenecity through an Abl–Crk pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8:815–25.
Deng YZ, Yao F, Li JJ, et al. RACK1 Suppresses gastric tumorigenesis by stabilizing beta-catenin destruction complex. Gastroenterology. 2012;142:812–23.
Li G, Ji XD, Gao H, et al. EphB3 mediates kinase-dependent suppression of non-small-cell lung cancer metastasis via a PP2A/RACK1/Akt signaling complex. Nat Commun. 2012;3:667. doi:10.1038/ncomms1675.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
F. Hu and Z. Tao contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, F., Tao, Z., Shen, Z. et al. Down-regulation of EphB4 phosphorylation is necessary for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tumorigenecity. Tumor Biol. 35, 7225–7232 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-1955-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-1955-4