Abstract
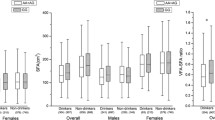
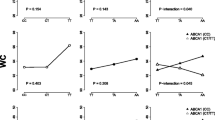
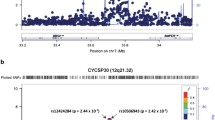
Abdominal obesity is characterized by accumulation of subcutaneous and visceral fat in the abdomen and has been reported to be largely responsible for many metabolic and vascular diseases. Although substantial effort has been dedicated to identification of genetic factors associated with abdominal obesity, as measured by the waist-hip ratio and waist circumference, only a few studies have explored associations with visceral fat accumulation in the abdomen. Furthermore, genetic studies of abdominal visceral adiposity conducted in Asian ethnic groups are rare. To gain insight into the genetic basis for visceral adiposity in Asian subjects, we conducted genome-wide association analysis for a pool of 1594 Korean subjects. Abdominal visceral fat area was estimated by computed tomography. After adjustment for age, linear association analysis identified three loci showing suggestive evidence of association (P < 5 × 10−6) in ASIC2, SLC35F3, and 5q14.2. Stratification by sex revealed one female-specific locus (rs17104731) located near LINC01519 with a genome-wide significant association for visceral adiposity (P = 4.66 × 10−8). Since visceral fat has been suggested to influence metabolic traits, we analyzed associations of the loci identified in this study with metabolic indicators, such as glucose, insulin, and lipid levels, and markers of kidney function. A locus (rs6699737) in SLC35F3 showed a nominal association (P < 5 × 10−2) with alanine transaminase, aspartate transaminase, and fasting plasma insulin. In addition, the linear association test using genetic risk score demonstrated that visceral adiposity loci detected in this study had a cumulative effect on abdominal visceral fat area, waist-hip-ratio, total cholesterol, and low density lipoprotein cholesterol. In summary, this study reports new loci associated with visceral adiposity and provides evidence supporting involvement of these loci in several metabolic traits in Korean populations.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chambers JC, Elliott P, Zabaneh D, Zhang W, Li Y, Froguel P, Balding D, Scott J, Kooner JS (2008) Common genetic variation near MC4R is associated with waist circumference and insulin resistance. Nat Genet 40:716–718
Cho YS, Go MJ, Kim YJ, Heo JY, Oh JH, Ban HJ, Yoon D, Lee MH, Kim DJ, Park M et al (2009) A large-scale genome-wide association study of Asian populations uncovers genetic factors influencing eight quantitative traits. Nat Genet 41:527–534
Cigolini M, Targher G, Bergamo Andreis IA, Tonoli M, Agostino G, De Sandre G (1996) Visceral fat accumulation and its relation to plasma hemostatic factors in healthy men. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 16:368–374
Croteau-Chonka DC, Marvelle AF, Lange EM, Lee NR, Adair LS, Lange LA, Mohlke KL (2011) Genome-wide association study of anthropometric traits and evidence of interactions with age and study year in Filipino women. Obesity 19:1019–1027
Despres JP (1998) The insulin resistance-dyslipidemic syndrome of visceral obesity: effect on patients’ risk. Obes Res 6(Suppl 1):8S–17S
Deurenberg P, Deurenberg-Yap M, Guricci S (2002) Asians are different from Caucasians and from each other in their body mass index/body fat per cent relationship. Obes Rev 3:141–146
Fox CS, Heard-Costa N, Cupples LA, Dupuis J, Vasan RS, Atwood LD (2007a) Genome-wide association to body mass index and waist circumference: the Framingham heart study 100 K project. BMC Med Genet 8(Suppl 1):S18
Fox CS, Massaro JM, Hoffmann U, Pou KM, Maurovich-Horvat P, Liu CY, Vasan RS, Murabito JM, Meigs JB, Cupples LA et al (2007b) Abdominal visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue compartments: association with metabolic risk factors in the Framingham heart study. Circulation 116:39–48
Fox CS, Liu Y, White CC, Feitosa M, Smith AV, Heard-Costa N, Lohman K, Consortium G, Consortium M, Consortium G et al (2012) Genome-wide association for abdominal subcutaneous and visceral adipose reveals a novel locus for visceral fat in women. PLoS Genet 8:e1002695
Hardy OT, Czech MP, Corvera S (2012) What causes the insulin resistance underlying obesity? Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 19:81–87
Haslam DW, James WP (2005) Obesity. Lancet 366:1197–1209
Heard-Costa NL, Zillikens MC, Monda KL, Johansson A, Harris TB, Fu M, Haritunians T, Feitosa MF, Aspelund T, Eiriksdottir G et al (2009) NRXN3 is a novel locus for waist circumference: a genome-wide association study from the CHARGE Consortium. PLoS Genet 5:e1000539
Heid IM, Jackson AU, Randall JC, Winkler TW, Qi L, Steinthorsdottir V, Thorleifsson G, Zillikens MC, Speliotes EK, Magi R et al (2010) Meta-analysis identifies 13 new loci associated with waist-hip ratio and reveals sexual dimorphism in the genetic basis of fat distribution. Nat Genet 42:949–960
Lindgren CM, Heid IM, Randall JC, Lamina C, Steinthorsdottir V, Qi L, Speliotes EK, Thorleifsson G, Willer CJ, Herrera BM, Jackson AU et al (2009) Genome-wide association scan meta-analysis identifies three Loci influencing adiposity and fat distribution. PLoS Genet 5:e1000508
Liu CT, Monda KL, Taylor KC, Lange L, Demerath EW, Palmas W, Wojczynski MK, Ellis JC, Vitolins MZ, Liu S et al (2013) Genome-wide association of body fat distribution in African ancestry populations suggests new loci. PLoS Genet 9:e1003681
Locke AE, Kahali B, Berndt SI, Justice AE, Pers TH, Day FR, Powell C, Vedantam S, Buchkovich ML, Yang J et al (2015) Genetic studies of body mass index yield new insights for obesity biology. Nature 518:197–206
Patel P, Abate N (2013) Body fat distribution and insulin resistance. Nutrients 5:2019–2027
Razay G, Vreugdenhil A, Wilcock G (2006) Obesity, abdominal obesity and Alzheimer disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 22:173–176
Shungin D, Winkler TW, Croteau-Chonka DC, Ferreira T, Locke AE, Magi R, Strawbridge RJ, Pers TH, Fischer K, Justice AE et al (2015) New genetic loci link adipose and insulin biology to body fat distribution. Nature 518:187–196
Speliotes EK, Willer CJ, Berndt SI, Monda KL, Thorleifsson G, Jackson AU, Lango Allen H, Lindgren CM, Luan J, Magi R et al (2010) Association analyses of 249,796 individuals reveal 18 new loci associated with body mass index. Nat Genet 42:937–948
Wagenknecht LE, Langefeld CD, Scherzinger AL, Norris JM, Haffner SM, Saad MF, Bergman RN (2003) Insulin sensitivity, insulin secretion, and abdominal fat: the insulin resistance atherosclerosis study (IRAS) family study. Diabetes 52:2490–2496
Wen W, Cho YS, Zheng W, Dorajoo R, Kato N, Qi L, Chen CH, Delahanty RJ, Okada Y, Tabara Y et al (2012) Meta-analysis identifies common variants associated with body mass index in East Asians. Nat Genet 44:307–311
Wen W, Kato N, Hwang JY, Guo X, Tabara Y, Li H, Dorajoo R, Yang X, Tsai FJ, Li S et al (2016) Genome-wide association studies in East Asians identify new loci for waist-hip ratio and waist circumference. Sci Rep 6:17958
Willyard C (2014) Heritability: the family roots of obesity. Nature 508:S58–S60
Young JA, Hwang SJ, Sarnak MJ, Hoffmann U, Massaro JM, Levy D, Benjamin EJ, Larson MG, Vasan RS, O’Donnell CJ et al (2008) Association of visceral and subcutaneous adiposity with kidney function. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 3:1786–1791
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Hallym University Research Fund 2016 (HRF-201608-006), Biospecimens and data were obtained from the Korean genome analysis project (4845-301), the Korean genome and epidemiology study (4851-302), and the Korea biobank project (4851-307, KBP-2015-029), which are supported by the Korea center for disease control and prevention, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Yoon Shin Cho and Jin Tae Hong declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
Genetic and epidemiological data were provided by the Korea center for disease control and prevention, Republic of Korea. This study was approved by the Hallym University Institutional Review Board (HIRB-2014-59 and HIRB-2015-028).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, J.T., Cho, Y.S. Identification of genetic loci associated with abdominal visceral adiposity in Korean populations. Genes Genom 39, 541–548 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-017-0520-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-017-0520-0