Abstract
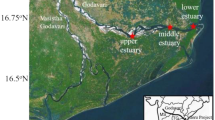
In June 2003 and 2006 concentrations of nutrient were determined in the Changjiang Estuary. The data indicated that phosphate and nitrate did not behave conservatively in the estuary, but silicate behaved conservatively. An important mobilization of phosphate and nitrate was observed from the river up to halfway in the estuary. Both input flux (from river to estuary) and output flux (from estuary to coastal zone) of phosphate, silicate and nitrate were calculated from statistical interpretations of the salinity profiles. There was a large discrepancy between input and output fluxes of phosphate and nitrate. The river fluxes of silicate, phosphate and nitrate (f r) are augmented 5.3%, 28.9% and 36.6% in June 2003 and 1.0%, 62.5%, 31.7% in June 2006 by internal inputs (f i). The phosphate and nitrate fluxes are enhanced through the estuarine process, while silicate flux is unaltered. The authors present some long-term data for nutrient concentrations and the ratios of silicon to nitrogen to phosphorus in the Changjiang Estuary. Silicate level falled in the last two decades, while concentration of nitrate increased. Phosphate concentration had no significant change.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beardsley R C, Limeburner R, Yu H, et al. 1985. Discharge of the Changjiang into the East China Sea. Continental Shelf Research, 4: 57–76
Boyle E, Collier R, Dengler A T, et al. 1974. On the chemical mass-balance in estuaries. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 38: 1719–1728
Chen Changsheng, Zhu Jianrong, Beardsley R C, et al. 2003. Physical-biological sources for dense alga blooms near the Changjiang River. Geophysical Research Letters, 30(10): 1515–1518
Gao Shengquan, Lin Yian, Jin Mingming, et al. 2004. Distribution features of nutrients and nutrient structure in the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea in spring and autumn. Donghai Marine Science (in Chinese), 22(4): 38–50
Gao Xuelu, Song Jinming. 2005. Phytoplankton distri butions and their relationship with the environment in the Changjiang Estuary, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 50: 327–335
Grasshoff K, Kremling K, Ehrhardt M. 1999. Methods of Seawater Analysis. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, 600
Han Xiurong, Wang Xiulin, Sun Xia, et al. 2003. Nutrient distribution and its relationship with occurrence of red tide in coastal area of East China Sea. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (in Chinese), 14(7): 1097–1101
Hu Fangxi, Hu Hui, Gu Guochuan. 2002. Studies of fronts in the Changjiang estuary. Shanghai: Press of East China Normal University, 87–89
Huang Ziqiang, Ji Weidong. 1994. The distribution and relationship of TP, OP and phosphate in the Changjiang estuary. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 16(1): 51–60
Huang Shanggao, Yang Jiadong, Ji Weidong, et al. 1986. Spatial and temporal variation of reactive Si, N, P and their reliationship in the Changjiang Estuary water. Taiwan Strait (in Chinese), 5: 114–123
Hutchins D A, Bruland K W. 1998. Iron-limited diatom growth and Si:N uptake ratios in a coastal upwelling regime. Nature, 393(11): 561–564
Kaul L W, Philip N F. 1984. Modeling estuarine nutrient geochemistry in a simple system. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 48: 1417–1433
Li Maotian, Xu Kaiqing, Masataka W, et al. 2007. Long-term variations in dissolved silicate, nitrogen, and phosphorus flux from the Yangtze River into the East China Sea and impacts on estuarine ecosystem. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 71: 3–12
Liu Ruiyu, Luo Bingzheng. 1992. Impact of the Three Gorges Project on the ecology and environment of Changjiang river estuary and adjacent waters. Studia Marina Sinica (in Chinese), 33: 1–13
Officer. 1979. Discussion of the behavior of nonconservative dissolved constituents in estuaries. Estuarine Coastal Marine Science Letter, 9: 91–94
Qin Xiao, Gao Yanyao. 1997. Technological researches on removabilitis of nitrogen and phosphor in sewage disposal. Shainghai Chemical Industry (in Chinese), 22(3): 11–15
Shen Zhiliang, Lu Jiaping, Liu Xingjun. 1992. The distribution of nutrients and the effect of TGD in the Changjiang Estuary. Journal of Marine Science (in Chinese), 33: 107–129
Sun Bingyi, Yu Shengrui, Hao Enliang. 1986. Comprehensive survey and research report on the sea areas adjacent to the Changjiang estuary and Chejudo island: Chapter 4. Marine Chemistry. Journal of Shangdong College of Oceanology (in Chinese), 16(1): 130–210
Sun Xia, Wang Baodong, Wang Xiulin, et al. 2004. Spatial and temporal distribution of the nutrients and its controlling factors in the high-frequency HAB occurrence area in the East China Sea. Marine Science (in Chinese), 28(8): 28–32
Wang Baodong. 2003. Nutrient distributions and their limination on phytoplankton in the Yellow Sea and the East Chian Sea. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (in Chinese), 14(7): 1122–1126
Wang Baodong. 2006. Cultural eutrophication in the Changjiang (Yangtze River) plume: History and perspective. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 69: 471–477
Wang Xiulin, Sun Xia, Han Xiurong, et al. 2004. Comparison in Macronutrent distributions and composition for high frequency HAB occurrence areas in East China Sea between summer and spring 2002. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica (in Chinese), 35(4): 324–330
Wang Jianing, Yan Weijin, Jia Xiaodong. 2006. Modeling the export of point sources of nutrients from the Yangtze River basin and discussing countermeasures. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae (in Chinese), 26(4): 658–665
Wang Zhengfang, Yao Longkui, Yuan Xiaozheng. 1983. Distribution and characteristics of nutrients (N, P, Si) in the estuary of Changjiang River in June, 1980. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinca (in Chinese), 14(4): 324–332
Wang Baodong, Zhan Run, Zang Jiaye. 2002. Distributions and transportation of nutrients in Changjiang River Estuary and its adjacent sea areas. Acta Oceanologica Sinca (in Chinese), 24(1): 53–58
Ye Xiansen, Zhang Yong, Xiang Youtang. 2000. Characteristic of Nitrate Distribution in the Changjiang River Estuary and its Cause of Formation. Marine Science Bulletin (in Chinese), 19(1): 89–92
Zhang Jing. 1996. Nutrient elements in large Chinese estuaries. Continental Shelf Research, 16: 1023–1045
Zhang Jing, Yu Zhigang, Liu Sumei, et al. 1997. Nutrient element dynamics of three North China estuaries: Luanhe, Shuangtaizihe and Yalujiang. Estuaries, 20: 110–123
Zhang Jing, Zhang Zaifeng, Liu Sumei, et al. 1999. Human impacts on the large world rivers: Would the Changjiang (Yangtze River) be an illustration? Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 13: 1099–1106
Zhang Shen, Zhang Chaosheng, Wang Lijun, et al. 1997. Contents of trace elements and mass transport rate of C, N, P, S in the Changjiang River. In: Zhou Jiayi, ed. Sources, Transport and Environmental of Contaminants in the Coastal and Estuarine Areas of China. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 155
Zhu Genhai, Xu Weiyi, Zhu Dedi, et al. 2003. Distribution of phytoplankton and water dynamical environmental factors in high red tide occurrence area of Changjiang River estuary. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 14(7): 1135–1139
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: The National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under contract No. 30490232; Chinese “973” Project under contract Nos 2002CB412405 and 2005CB422305.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Yu, Z., Yao, Q. et al. Nutrient concentrations and fluxes in the Changjiang Estuary during summer. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 29, 107–119 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-010-0029-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-010-0029-8