Abstract
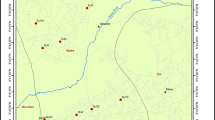
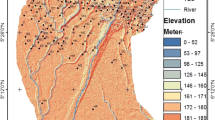
A large number of valleys and basin systems are present in the northwestern part of the Himalayas in Pakistan which form significant aquifers in the region. Hydrogeophysical investigations in the western part of Nowshera District, a part of the intermontane Peshawar basin, were undertaken to help to determine the availability of groundwater resources in the region. Thirty vertical electrical resistivity soundings (VES) were acquired using a Schlumberger expanding array configuration with a maximum current electrode spacing (AB/2) of 150 m in delineating the groundwater potential in the study area. The results of the interpreted VES data using a combination of curve matching technique and computer iterative modeling methods suggest that the area is underlain by 3 to 5 geo-electric layers. The interpretation results showed that the geo-electrical succession consists of alluvium comprising of alternating layers of clay, silty clay, fine to coarse sands, sand with gravels and gravels of variable thickness. High subsurface resistivity values are correlated with gravel–sand units and low resistivity values with the presence of clays and silts. The modeled VES results were correlated with the pumping tests results and lithological logs of the existing wells. The pumping test suggests the transmissivity of the aquifer sediments is variable corresponding to different sediments within the area. The gravel–sand intervals having high resistivity value show high transmissivity values, whereas clay–silt sediments show low transmissivities. It is concluded that majority of the high resistive gravel–sand sediments belong to an alluvial fan environment. These gravel–sand zones are promising zones for groundwater abstraction which are concentrated in the central part of the study area.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhter G, Farid A, Ahmed Z (2012) Determining the depositional pattern by resistivity–seismic inversion for the aquifer system of Maira Area, Pakistan. Environ Monit Assess 184:161–170
Allen JE (1964) Quaternary stratigraphic sequence in the Potwar basin and adjacent northwest Pakistan. Geol Bull Univ Peshawar 17:231–233
Basharat M, Siddique M, Ashraf J, Ismail M (2009) Assessment of groundwater development potential in district Nowshera using groundwater modeling. Pak J Water Resour 13(2):17–27
Bowling JC, Rodriguez AB, Harry DL, Zheng C (2005) Delineating alluvial aquifer heterogeneity using resistivity and GPR data. Groundwater 43(6):890–903
Burbank DW, Raynolds RGH (1988) Stratigraphic keys to the timing of deformation; an example from the northwestern Himalayan foredeep. In: Paola C, Kleinspehn K (eds) New perspectives in basin analysis. Springer, New York, pp 331–351
Cornwell K (1998) Quaternary break-out flood sediments in the Peshawar basin of northern Pakistan. Geomorphology 25:225–248
Elwaseif M, Ismail A, Abdalla M, Abdel-Rahman M, Hafeez MA (2012) Geophysical and hydrological investigations at the west bank of Nile River (Luxor, Egypt). Environ Earth Sci 67(3):911–922
Farid A, Jadoon K, Akhter G, Iqbal MA (2013) Hydrostratigraphy and hydrogeology of the western part of Maira area, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa: a case study by using electrical resistivity. Environ Monit Assess 185(3):2407–2422
Farid A, Khalid P, Jadoon KZ, Jouini MS (2014) The depositional setting of the late quaternary sedimentary fill in southern Bannu basin, northwest Himalayan fold and thrust belt Pakistan. Environ Monit Assess 186(8):6587–6604
Farid A, Khalid P, Jadoon KZ, Iqbal MA, Shafique M (2017) Applications of variogram modeling to electrical resistivity data for the occurrence and distribution of saline groundwater in Domail Plain, northwestern Himalayan fold and thrust belt, Pakistan. J Mt Sci 14(1):158–174
Hamada GM, Almajed AA, Okasha TM, Algathe AA (2013) Uncertainty analysis of Archie’s parameters determination techniques in carbonate reservoirs. J Pet Explor Prod Technol 3(1):1–10
Haneef M, Jan MQ, Rabbi F (1986) Fracture fills or sedimentary dykes in the lake sediments of Jalala, N.W.F.P., a preliminary report. Geol Bull Univ Peshawar 19:151–156
Isaaks H, Srivastava RM (1989) An introduction to applied geostatistics. Oxford University Press, New York
Kazakis N, Pavlou A, Vargemezis G, Voudouris KS, Soulios G, Plikas F, Tsokas G (2016) Seawater intrusion mapping using electrical resistivity tomography and hydrochemical data. An application in the coastal area of eastern Thermaikos Gulf, Greece. Sci Total Environ 543:373–387. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.11.041
Kazmi AH, Jan MQ (1997) Geology and tectonics of Pakistan. Graphic Publishers, Karachi
Kruseman GP, Naqavi SAH (1988) Hydrogeology and groundwater resources of the North-West Frontier Province Pakistan/ Peshawar: WAPDA Hydrogeology Directorate, p 110
Levanon A, Ginzburg A (1976) Determination of salt–water interface by electric resistivity depth soundings. Hydrol Sci Bull 21(4):561–568
Martinelli E (1978) Groundwater exploration by geoelectrical methods in Southern Africa. Bull Assoc Eng Geol 15:113–124
McArthur SAQ, Allen DM, Luzitano RD (2011) Resolving scales of aquifer heterogeneity using ground penetrating radar and borehole geophysical logging. Environ Earth Sci 63(3):581–593. doi:10.1007/s12665-010-0726-9
Muchingami I, Hlawtwayo DJ, Nel JM, Chum C (2012) Electrical resistivity survey for groundwater investigations and shallow subsurface evaluation of the basaltic-greenstone formation of the urban. Phys Chem Earth 50–52:44–51
Nag SK, Ray S (2015) Deciphering groundwater potential zones using geospatial technology: a study in Bankura blocks I and block II, Bankura district, West Bengal. Arab J Sci Eng 40:205–214
Nag SK, Saha S (2014) Integration of GIS and remote sensing in groundwater investigations: a case study in Gangajalghati block, Bankura district, West Bengal, India. Arab J Sci Eng 39:5543–5553
Okiongbo KS, Akpofure E (2016) Hydrogeophysical characterization of shallow unconsolidated alluvial aquifer in Yenagoa and environs, Southern Nigeria. Arab J Sci Eng 41:2261–2270
Olatunji S, Musa A (2014) Estimation of aquifer hydraulic characteristics from surface geoelectrical methods: case study of the Rima basin, North Western Nigeria. Arab J Sci Eng 39:5475–5487
Salem HS (1999) Determination of fluid transmissivity and electric transverse resistance for shallow aquifers and deep reservoirs from surface well log electric measurements. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 3(3):421–427
Sultan SA, Mekhemer HM, Santos FAM, AbdAlla M (2009) Geophysical measurements for subsurface mapping and groundwater exploration at the central part of the Sinai Peninsula, Egypt. Arab J Sci Eng 34(1A):103–119
Telford E, Geldart WM, Sheriff RE (1990) Applied Geophysics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Uil H (1983) Technical report on groundwater resources in Domail Plain, Bannu and Karak Districts, N. W. F. P. Hydrogeology Directorate, Peshawar Pakistan, Report No. IV-1
Zananiri I, Memou T, Lachanas G (2006) Vertical electrical sounding (VES) survey at the central part of Kos Island, Aegean, Greece. Geosciences 411–413
Zohdy AAR, Jackson DB (1969) Application of deep electrical sounding for groundwater exploration in Hawaii. Geophysics 34(4):584–600
Zohdy AAR, Bisdorf RJ, Gates JS (1994) A direct current resistivity survey of the Beaver Dam Wash drainage in southwest Utah, southeast Nevada, and northwest Arizona. US Geol Surv 87:94–676
Acknowledgements
The authors are very thankful to Mr. Asam Farid, Mr. Saif Ullah and Christophe D. for their valuable suggestions and help to improve this manuscript. The authors are very thankful to the reviewers for their valuable suggestions and attention in order to improve the quality of this manuscript. This work is related to Ph.D. research project of Mr. Sher Muhammad. WAPADA is also acknowledged for providing data used in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muhammad, S., Khalid, P. Hydrogeophysical investigations for assessing the groundwater potential in part of the Peshawar basin, Pakistan. Environ Earth Sci 76, 494 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6833-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6833-0