Abstract
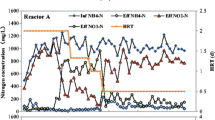
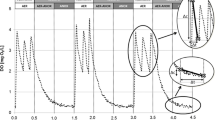
Nitritation is an innovative biological nitrogen removal method in wastewater, and it has the advantages of energy and economy. The correlation between a nitrite conversion rate and the gene copy numbers of ammonia oxidizing bacteria (AOB) in a nitritation reactor was examined to measure the effectiveness of removing a nitrogen content in a biological nitrogen removal process, using a biological process of nitritation. A laboratory scale reactor was prepared and operated for over a year, using digester supernatant to induce a stable nitritation, and to optimize the operational conditions by adjusting various operating factors. The relationship between operational results of nitritation reactor and the AOB gene copies was approximated through identification and quantitative analysis of AOB. A stable nitritation can be artificially led with the control of SRT, while treating anaerobic digester supernatant from MWTPs. And AOB gene copies showed a correlation with free ammonia (FA) inhibition and performance of nitritation, and AOB activity. Thus, AOB gene copies were found important when it comes to analyzing nitritation.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Public Health Association (APHA) (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water, 20th edn. American Public Health Association, US
Anthonisen AC, Loehr RC, Prakasam TB, Srinath EG (1976) Inhibition of nitrification by ammonia and nitrous acid. J Wat Pollut Control Fed 48:835–852
Bae HK, Park KS, Jung YC, Jung JY (2006) Analysis of microbal community structure of red granule in the anaerobic ammonium oxidation reactor. J Korean Soc Environ Eng 28:1055–1064 (in Korean)
Choi JH, Lee YW, Yun ZW (2001) Removal of concentration nitrogen from the recycle water by biological nitritation–denitritation. J Korean Soc Environ Eng 23:371–381 (in Korean)
Gali A, Dosta J, Lopez-palau S, Mata-Alvarez J (2008) SBR technology for high ammonium loading rates. Wat Sci Tech 58:467–472
Gil KI (2006) Nitritation of anaerobic digester supernatant from sludge processing in MWTP. J Korean Soc Wat Qual 22(3):540–545 (in Korean)
Gil K, Choi E (2002) Estimation of nitrite concentration in the biological nitritation process using enzymatic inhibition kinetics. J Microbiol Biotechnol 12:377–381
Gil KI, Rho HY, Kim DI, Michael KS (2012) Comparison of Bio-P module and the modified Bio-P module in the step-feed biological nutrient removal process. Environ Earth Sci 65:929–936
Han DJ, Kang SW, Rim JM (1998) Factors influencing nitrite build-up in nitrification of high strength ammonia wastewater. Korean J Sanitation 13(2):128–138 (in Korean)
Hellinga C, Schellen AAJC, Mulder JW, van Loosdrecht MCM, Heijnen JJ (1998) The Sharon process: an innovative method for nitrogen removal from ammonium-rich waste water. Wat Sci Tech 37:135–142
Hermansson A, Lindgren PE (2000) Quantification of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in arable soil by real-time PCR. Appl Environ Microbial 67:972–976
Im JY, Gil KI (2011) Effect of anaerobic digestion on the high rate of nitritation treating piggery wastewater. J Environ Sci 23(11):1787–1793
Jung JY, Kang SH, Kim YO, Chung YC (2005) Effects of seeding microorganisms, hydrazine, and nitrite concentration on the anammox acticity. J Korean Soc Wat Qual 21:477–483 (in Korean)
Park HD, Wells GF, Bae HK, Criddle CS, Francis CA (2006) Occurrence of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in wastewater treatment plant bioreactors. Appl Environ Microbial 72:5643–5647
Ruiz G, Jeison D, Chamy R (2003) Nitrification with high nitrite accumulation for the treatment of wastewater with high ammonia concentration. Wat Sci Tech 37:1371–1377
Wang J, Yang N (2004) Partial nitrification under limited dissolved oxygen conditions. Process Biochem 39:1223–1229
Yoo IK, Lim KJ, Lee WS, Kim DJ, Cha GC (2006) Study on operation factors in a nitrite-accumulating submerged membrane bioreactor. J Microbiol Biotechnol 16:469–474
Yu JC, Park JJ, Hur SH, Kim YJ, Byun IG, Lee TH, Park TJ (2007) Effect of DO concentration on ammonia oxidizing bacteria in aerobic biofilm reactor. Korean Soc Environ Eng 29:106–112 (in Korean)
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIP) (No. 2013R1A2A2A01068579).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Im, J., Jung, J., Bae, H. et al. Correlation between nitrite accumulation and the concentration of AOB in a nitritation reactor. Environ Earth Sci 72, 289–297 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3285-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3285-7