Abstract
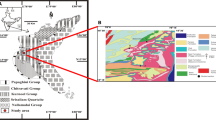
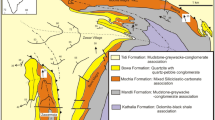
The Pranhita-Godavari Graben (PGG) represents a major lineament in south Indian Peninsular cratonic province, which preserves a thick column of sediments. In geological time scale, these sedimentary units correspond to Mesoproterozoic to Mesozoic period. The Mesoproterozoic sedimentation has been confined mainly to southern part of the PGG, while Neoproterozoic sediments are exposed at northern tip of the graben. In the area of investigation siliciclastic sedimentation units are exposed, wherein five major lithofacies have been marked out. These lithofacies are i) breccia (Br), ii) large scale trough cross-bedded sandstone (Ls), iii) small-scale trough cross-bedded sandstone (Sss), iv) horizontal bedded sandstone (Hs) and v) ripple laminated sandstone (Rs). The amalgamation of these lithofacies strongly divulges that the lower part of the succession was deposited in braided-streams, whereas the upper part was deposited in erg environment.
The unimodal paleocurrent is evident in lower part of the succession while bimodal paleocurrent is noticed from sandstones at upper part of the succession. In general, the sandstones exhibit northwesterly paleocurrent direction. The petrographic studies point out that the sandstones are arenites and were deposited in interior type of continental block provenance under semi-arid to hot humid palaeoclimate. The high percentage of floating grains and the low percentage of interpenetrative contacts as well as the low value of contact index for these sandstones divulge that the grains did not suffer much compaction thereby pointing to shallow burial. The sub-angular zircon and tourmaline suggest that these minerals have travelled short distance from the source rocks. The high percentage of garnet and presence of epidote, staurolite, sillimanite, zoisite, amphibole and kyanite indicate that the sediments were derived from the nearby metamorphic source rocks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auden, J.B. (1993) Vindhyan sedimentation in Son Valley, Mirzapur District. Memoir, Geological Survey of India, v.62(II), pp.141–250.
Allen, P.A. (1981) Sediments and processes on a small stream flow dominated, Devonian alluvial fan, Shetland, Island. Sediment. Geol., v.29, pp.31–66.
Balance, P.F. (1984) Sheet flow dominated gravel fans of the non marine Middle Cenozoic Simmler, Central California, Sediment. Geol., v.38, pp.337–359.
Berner, R.A. (1971) Principles of Chemical Sedimentology. Mc Graw Hill Co, New York.
Biswas, S.K. (2003) Regional tectonic framework of Pranhita-Godavari basin. Jour.Asian Earth Sci., v.21, pp.543–551.
Blair, T.C. (1987) Sedimentary processes, vertical stratification sequences and geomorphology of the Roaring River alluvial fan, Rocky Mountain Nation Park, Colorado, Jour. Sed. Petrol., v.57, pp.845–862.
Blatt, H. (1982) Sedimentary Petrology. W.H.Freeman and Company, San Francisco.
Boggs, S.Jr. (1987) Principals of Sedimentology and Stratigraphy. Merrill Publishing Company, Columbus Toronto London Melbourne.
Borgohain, R., Khound, D. J., Bhuyan, D. and Phukan, J. (1999) Petrography of the basal sandstone unit of the Upper Assam basin. Jour. Indian Assoc. Sedimentologists, v.18, pp.51–71.
Brierley, G.J., Liu, K. and Crook, K.A.W. (1993) Sedimentology of coarse grained alluvial fans in the Markham valley, Papua, New Guinea, Sediment. Geol., v.86, pp.297–324.
Cant, D.J. and Walker, R.G. (1976) Development of braided fluvial facies model, Devonian Battery point sandstone, Quebec, Can. Jour. Earth Sci., v.13, pp.102–119.
Casshyap, S.M. (1970) Sedimentary cycles and environment of deposition of the Barakar Coal measures of Lower Gondwana India. Jour. Sedimen. Petrol., v.40, pp.1302–1317.
Chakraborty, C. (1996) Sedimentary records of erg development over a braidplain: Proterozoic Dhandraul Sandstone, Vindhyan Supergroup, Son valley. In: A. Bhattachrya (Ed.), Recent advances in Vindhyan Geology. Mem. Geol. Soc. India, v.36, pp.77–99.
Chakraborty, C. and Bhattacharyya, A. (1996) Fan-delta sedimentation in a foreland moat; Deoland Formation, Vindhyan Supergroup, Son valley. In: A. Bhattachrya (Ed.), Recent advances in Vindhyan Geology. Mem. Geol. Soc. India, no.36, pp.27–48.
Chakraborty, T. (1991) Sedimentology of Proterozoic erg: the Venkatapur Sandstone, P.G. Valley, South India. Sedimentology, v.38, pp.301–322.
Chakraborty, T. and Chaudhuri, A.K. (1993) Fluvial-eolian interactions in a Proterozoic alluvial plain: example from Mancherial Quartzite, Pranhita Godavari Valley, India. In: K. Pye, (Ed.), Dynamics and environmental context of Aeolian sedimentary systems. Geol. Soc. London, Spec. Publ., v.72, pp.127–141.
Chamyal, L.S., Khadkikar, A.S., Malik, J.N. and Maurya, D.M. (1997) Sedimentology of Narmada alluvial fan, Western India. Sediment. Geol., v.107, pp.263–279.
Chaudhuri, A.K. (1985) Stratigraphy of the Purana Supergroup, Andhra Pradesh. Jour. Geol Soc. India, v.21, pp.301–314.
Chaudhuri, A.K. (2003) Stratigraphy and Paleogeography of the Godavari Supergroup in the central part of the Pranhita-Godavari valley, South India. Jour.Asian Earth Sci., v.21, pp.595–611.
Chaudhuri, A.K. and Chanda, S.K. (1991) The Proterozoic basin of Pranhita-Godavari Valley: an overview. In: S.K. Tandon, C.C. Pant and S.B. Casshyap, (Eds.), Sedimentary Basins of India: tectonic context, Ganodaya Prakashan, Nainital, pp.13–30.
Chaudhuri, A.K. and Deb, G.K. (2004) Proterozoic rifting in Pranhita-Godavari valley: implication on India-Antarctica linkage. Gondwana Res., v.7(2), pp.301–312.
Costa, J.E. (1984) Physical geomorphology of debris-flows. Springer-Verlag. Berlin.
Davis, J.C. (2002) Statistics and data analysis in geology. John Wiley and Sons
Desai, G. and Hardas, M.G. (1982) Significance of heavy mineral assemblage of Wagad Mesozoic sediments of Eastern Kutch, India. Jour. Earth Sci., v.9, pp.59–66.
Dickinson, W. R. and Suczek, C. A. (1979) Plate tectonics and sandstones composition. Bull. Amer. Assoc. Petrol. Geologists, v.63, pp.2164–2182.
Einsele, G. (1992) Sedimentary Basins. Springer-Verlag. Berlin Heidelberg.
Folk, R.L. (1965) Petrology of sedimentary rocks. Hemphill’s Austin, Texas.
Galloway, W.E. and Hobday, D.K. (1983) Terrigenous Clastic Depositional Systems. Springer-Verlag. Berlin Heidelberg.
GSI (1979) Geological Survey of India, Published map.
GSI (2008) Geology and mineral resources of Maharashtra. Misc. Publ.
Gloppen, T.G. and Steel, R.J. (1981) The deposits, internal structure and geometry in six alluvial fan-fandelta bodies (Devonian, Norway)-a study in the significance of bedding sequences in conglomerates. In: F.G. Ethridge and R.M. Flores (Eds.), Ancient non marine depositional environments: Models and for exploration. Spec. Publ., Soc. Econ. Paleo. Mineral., v.31, pp.49–69.
Harms, J.C., Mackenzie, D.B. and Mccubbin, D.G. (1963) Stratification in modern sands of Red river, Lousania. Jour. Geol., v.71, pp.566–580.
Harms, J.C., Southard, J.B., Spearing, D.R. and Walker, R.G. (1975) Depositional Environments as Interpreted from Primary Sedimentary Structures and Stratification Sequences. Dallas, Texas.
Hatch, F.H. and Rastall, R.H. (1965) Petrology of Sedimentary Rocks. Thomas Murby and Co., London.
Himanshu, K.S. and Ghosh, S.K. (1996) Fluid inclusion study of the Neoproterozoic Nagthat siliciclastic sediments, NW Kumaun Lesser Himalaya: Implication to quartz cementation history. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.47, pp.107–114.
Hota, R.N. (2011) Practical approach to petrology. CBS Publishers and distributors Pvt Ltd. New Delhi.
Hota, R.N., Pandya, K.L. and Maejima, W. (2003) Cyclic sedimentation and facies organization of the coal bearing Barakar Formation, Talchir Gondwana basin, Orissa, India: a statistical analysis of subsurface logs. Jour. Geosciences. Osaka City University, v.46, pp.1–11.
Hubert, J.F. (1971) Analysis of heavy mineral assemblages. In: A.V. Carver (Ed.), Procedures in sedimentary petrology. John Wiley and Sons, New York London, pp.453–478
Kumar, R., Bagati, T.N. and Mazari, R.K. (1994) Uplifted Late Quaternary debris fan in the upper Spity valley (H.P.) and its environmental significance. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.43, pp.603–611.
Larsen, V. and Steel, R.J. (1978) The sedimentary history of a debris-flow dominated Devonian alluvial fan-study of textural inversion. Sedimentology, v.25, pp.37–59.
Lindholm, R.C. (1987) A practical approach to sedimentology. Allen and Unwin, London.
Mallet, F.R. (1869) On the Vindhyan series as exhibited in the northwestern and central provinces of India. Mem. Geol. Surv. India, v.1, pp.1–129.
Miall, A.D. (1985) Architectural-element analysis: A new method of facies analysis applied to fluvial deposits. In: R.M. Flores, F.G. Ethridge, A.D. Miall, W.E. Galloway and T.D. Flouch (Eds.), Recognition of fluvial depositional system and their resource potential. Soc. Econ. Paleont. Mineral., Short course., v.19, pp.33–82.
Mitra, N.D. (1996) Some problems of Vindhyan geology. In: A. Bhattachrya (Ed.), Recent advances in Vindhyan Geology. Mem. Geol.Soc. India, no.36, pp.1–4.
Mukhopadhyay, J. and Chudhuri, A.K. (2003) Proterozoic Penganga Group, Pranhita Godavari valley, South India: depositional setting and Paleogeography of the deep water cratonic succession. Jour. Asian Earth Sci., v.21, pp.613–622.
Murkute, Y.A. (2001) Textural parameters and petrography of Kamthi sandstones around Minjhari, Chandrapur District, Maharashtra. Jour. Indian Assoc. Sedimentologists, v.20, pp.97–108.
Murkute, Y. A. (2003) Sources of cements in Barakar sandstones from Umrer Coalfield, Nagpur. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.62, pp.99–102.
Murkute, Y. A. (2009) Petrography of Upper Member Barakar Sediments, Umrer coal Basin, Nagpur District. Gondwana Geol. Mag., v.24, pp.19–27.
Nemec, W. and Steel, R.J. (1984) Alluvial and coastal conglomerates: their significant features and some comments on gravelly mass-flow deposits. Can. Soc. Petro. Geol., Mem., no.10, pp.1–31.
Oldham, T. (1856) Remarks on the classification of rocks of Central India resulting from the investigation of the geological survey. Jour. Asiatic Society, Bengal, v.25, pp.224–256.
Pascoe, E.H. (1973) A manual of the geology of India and Burma.VIII, Govt. of India Publication, New Delhi.
Pettijohn, F.J. (1984) Sedimentary Rocks. (3rd edition) CBS Publishers and Distributors, Delhi.
Pettijohn, F.J., Potter, P.E. and Siever, R. (1987) Sand and Sandstone. Springer Verlag, New York.
Potter, P.E. and Pettijohn, F.J. (1977) Paleocurrent and Basin Analysis. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York.
Postma, G. (1990) Depositional architecture and facies of river and fan deltas: a synthesis. In: A. Colella and D.B. Prior (Eds.), Coarse grained deltas, Internat. Assoc. Sedimentologists, Spec. Publ., no.10, pp.13–27.
Raja Rao, C. S. (1982) Coal resources of Tamilnadu, Andhra Pradesh, Orissa and Maharashtra. Bull. Geol. Surv. India, Series A., v.45, pp.66–90.
Reading, H. G. (1981) Sedimentary Environment and Facies. Blackwell Scientific Publication, Oxford London.
Reineck, H.E. and Singh, I.B. (1973) Depositional Sedimentary Environments. Springer Verlag, Berlin New York.
Ramamohan Rao, T. (1964) Age of Pakhals of Godavari valley. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci., v.60, pp.70–80.
Roe, S.L. (1987) Cross strata and bed forms of probable transitional dune to upper stage plane bed origin from a late Precambrian fluvial sandstone, Northern Norway, Sedimentology, v.34, pp.89–101.
Sarkar, S., Chakrabothy, P.P. and Bose, P.K. (1996) Proterozoic Lakheri Limestone, Central india: Facies, Paleogeography and Physiography. In: A. Bhattachrya (Ed.), Recent advances in Vindhyan Geology. Mem. Geol. Soc. India, no.36, pp.5–26.
Schultz, A.W. (1984) Subaerial debris flow deposits in the Upper Paleozoic Cutler Formation, Western Colorado. Jour. Sed. Petrol., v.54, pp.759–772.
Sharma, M. (1996) Microbialites (Stromatolites) from Mesoproterozoic Salkhan limestone, Semri Group, Rohtas, Bihar: their systematic and significance. In: A. Bhattachrya (Ed.), Recent advances in Vindhyan Geology. Mem. Geol. Soc. India, no.36, pp.167–196.
Spalletti, L.A., Limarino, C.O. and Colombo Pinol, F. (2010). Internal anatomy of an erg sequence from the aeolian-fluvial system of the De La cuesta Formation (Paganzo Basin, northwestern Argentina. Geologica Acta, v.8, pp.431–447.
Suttner, L.J. and Dutta, P.K. (1986) Alluvial sandstone composition and palaeoclimate framework mineralogy, Jour. Sedimen. Petrol., v.56, pp.329–345.
Taylor, M. (1950) Pore space reduction in sandstones. Amer. Assoc. Petro. Geol. Bull., no.34, pp.321–328.
Terner, B.R. (1977) Fluviatile cross bedding patterns in the upper Triassic Molteno Formation of the Karoo (Gondwana) Supergroup in south Africa and Lesotho. Trans. Geol. Soc. South Africa., v.80, pp.241–242.
Tewari, R.C., Hota, R.N. and Maejima, W. (2012). Fluvial architecture of Early Permian Barakar rocks of Korba Gondwana basin, eastern-central India. Jour.Asian Earth Sci., v.52, pp.43–52.
Turnbridge, I.P. (1981) Sandy high energy flood sedimentationsome criteria for recognition with example of the Devonian of SW England. Sediment. Geol., v.28, pp.79–95.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murkute, Y.A., Joshi, S.P. Neoproterozoic siliciclastic sedimentation around Kampa-Tenpa area, Pranhita Godavari Graben (PGG), Central India: Facies analysis, petrography and depositional environment. J Geol Soc India 83, 423–432 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-014-0059-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-014-0059-5