Abstract
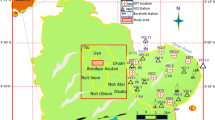
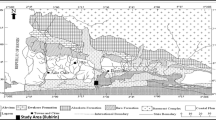
The present study is an attempt to upgrade the previously used semi-analytical inverse slope method. The upgrade method was applied to the interpretation of VES’s measured with different electrode arrays in two and three layers laboratory tank model. Then the method was applied on VES’s measured at different sites of different geologic conditions. The study showed that the inverse slope method is a quick method for obtaining depths to interfaces. The method can be implemented on a hand-held calculator or more efficiently on a small microcomputer where the data can be processed at a faster rate than that of conventional data acquisition systems. This allows the method to be potent tools for infield data analysis and more cost effective to assess the success of a sounding on-the-spot and modify the experimental set-up as appropriate. The comparison between the results obtained from this method and the traditional digital computerized methods indicated that the geoelectrical models derived from inverse slope method have a good correlation with the actual model. Also, when applying the method on VES’s measured by using Schlumberger and Wenner arrays at areas of different geologic setting, gave results in comfortable with the actual lithology obtained from the lithologic data of the neighboring wells. The results obtained from the lab experiment and field survey indicated that the inverse slope method has the potential to be applied on VES data collected with any electrode array, the advantage that is not available with all the traditional interpretation methods available nowadays.


























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel Aal GZ (1998) Geophysical and geotechnical studies on El-Salam suburb area, Kharga, Egypt, M.Sc. Thesis, Geol. Dept. Assiut Univ. Assiut, Egypt, 177pp
Ghosh DP (1971) Inverse filter coefficients for computation of apparent resistivity standard curves for a horizontally stratified earth. Geophysical Prospecting 19:769–775
Hassan SO (1985) Geophysical (geoelectric) studies on Wadi Qena area, Eastern desert, M.Sc. Thesis, Geol. Dept. Assiut Univ. Assiut, Egypt. 108 p
Ibrahim HA, Bakheit AA, Omran AA, Riad S, EL- Hussaini A, Soliman MA (1994) Resistivity measurements for groundwater exploration in the eastern part of Kom Ombo plain, Eastern Desert, Egypt. Bull Fac Sci, Assiut Univ 23(1-F):247–269
Koefoed O (1979) Recent development in the direct interpretation of resistivity sounding. Geophys Explor 14:243–250
Orellane E, Mooney H M (1966) Master tables and curves for vertical electrical sounding over layered structures. Interciencia de Los Angeles, 150p. Madrid, Spain
Sankaranarayan PV, Ramanujachary KR (1967) An inverse slope method of determining absolute resistivity. Geophysics 6:32
Senosy MM, Khalil MMF, Ebraheem AM (2003) Application of 2D imaging earth resistivity method for determining the hydrogeological conditions of the coastal area between Marsa Matruh and Ras El Hekma, Mediterranean coast, Egypt. N Jb Geol Paläont Abh 229(2):255–279
Senosy MM, Khalil MMF (2006) Earth resistivity surveying for ground water exploration in the area around Gebel Abraq, Southern eastern desert, Egypt. Assiut Univ J of Geology 35(1):39–56
Senosy MM, Omran AA, (2008) Geophysical Exploration Report for Groundwater, King Saud University Campus internal report
Senosy MM, Dahab KA, Khalil MF and Ebraheem AM (2004) Environmental impact of ground water level rising using the 2D methods in Markaz Badr district, west of Nile delta, Egypt, Proc. 3ra International Symposium on Geophysics, Tanta, pp. 520–540
Szalai S, Szarka L (2007) Auxiliary results of collection and classification of surface geoelectric arrays, Near Surface 2007, Istanbul, Turkey, A09
Szalai S, Szarka L (2008) On the classification of surface geoelectric arrays. Geophys Prospect 56(2):159–175
Zohdy AAR (1975) Automatic interpretation of Schlumberger sounding curves using modified Dar Zarrouk Function, Bull. B.B. E., U.S. Geol.surv
Zohdy AAR (1989) A new method for the interpretation of Schlumberger and Wenner sounding curves. Geophysics 54:245–253
Zohdy AAR, Bischorf RJ (1989) Programs for the automatic processing and interpretation of Schlumberger sounding curves. US Geol Surv Open-File Rept 64:89–137
Zohdy AAR (1974) Application of surface geophysics to groundwater investigations. Chapter D1, electrical methods, techniques of water resource investigations of the U.S. geol. Surv.66pp
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohamed, H.S., Senosy, M.M. & Abdel Aal, G.Z. Upgrading of the inverse slope method for quantitative interpretation of earth resistivity measurements. Arab J Geosci 7, 4059–4077 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-1075-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-1075-2