Abstract
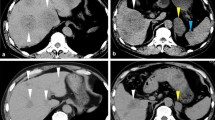
A 50-year-old woman presented with epigastralgia. Computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen revealed a 6-cm well-enhanced mass extending from the left lobe of the liver to the abdominal wall, suggestive of cholangiocarcinoma. Liver and skin mass biopsies did not provide evidence of hepatic malignancy but were rich in plasma cells and sclerotic lesions. Subsequent detection of elevated serum immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) led to a diagnosis IgG4-related inflammatory pseudotumor (IPT) of the liver. Treatment with systemic corticosteroids resulted in rapid clinical improvement. This case is the first report of an IgG4-related hepatic IPT invading the abdominal wall.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ntinas Achilleas, Kardassis Dimitrios, Miliaras Dimosthenis, et al. Inflammatory pseudotumor of the liver: a case report and review of the literature. J Med Case Rep. 2011;5:196.
Obana T, Yamasaki S, Nishio K, et al. A case of hepatic inflammatory pseudotumor protruding from the liver surface. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2015;8:340–4.
Zen Y, Fujii T, Sato Y, et al. Pathological classification of hepatic inflammatory pseudotumor with respect to IgG4-related disease. Mod Pathol. 2007;20:884–94.
Horiuchi R, Uchida T, Kojima T, et al. Inflammatory pseudotumor of the liver. Clinicopathologic study and review of the literature. Cancer. 1990;65:1583–90.
Shek TW, Ng IO, Chan KW. Inflammatory pseudotumor of the liver. Report of four cases and review of the literature. Am J Surg Pathol. 1993;17:231–8.
Takeshita K, Furui S, Fukusato T. Imaging of inflammatory pseudotumor of the liver. Liver Cancer. 2009;15:151–6 (In Japanese).
Nam KJ, Kang HK, Lim JH. Inflammatory pseudotumor of the liver: CT and sonographic imagings. Am J Roentgenol. 1996;167:485–7.
Park JY, Moon SC, Lim YS, et al. Clinical features, image findings, and prognosis of inflammatory pseudotumor of the liver: a multicenter experience of 45 cases. Gut Liver. 2014;8:58–63.
Fukuya T, Honda H, Matsumata T, et al. Diagnosis of inflammatory pseudotumor of the liver: value of CT. Am J Roentgenol. 1994;163:1087–91.
Yoon KH, Ha HK, Lee JS, et al. Inflammatory pseudotumor of the liver in patients with recurrent pyogenic cholangitis: CT histopathologic correlation. Radiology. 1999;211:373–9.
Memis A, Oran I, Calli C, et al. Transcatheter arterial embolization of internal mammary artery in a hepatocellular carcinoma with abdominal wall invasion. Eur J Radiol. 1998;28:160–3.
Matsumoto K, Kosaka T, Satoh Y, et al. A case of mucin—producing cholangiocarcinoma with invading the abdominal wall. Tando. 2000;14:373–8 (In Japanese with English abstract).
Ha HK, Lee HJ, Kim H, et al. Abdominal actinomycosis: CT findings in 10 patients. Am J Roentgenol. 1993;161:791–4.
Mulki R, Garg S, Manatsathit W, et al. IgG4-related inflammatory pseudotumour mimicking a hepatic abscess impending rupture. BMJ Case Rep. 2015. doi:10.1136/bcr-2015-211893.
Zen Y, Harada K, Sasaki M, et al. IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis with and without hepatic inflammatory pseudotumor, and sclerosing pancreatitis-associated sclerosing cholangitis: do they belong to a spectrum of sclerosing pancreatitis? Am J Surg Pathol. 2004;28:1193–203.
Li LF, Tse PY, Tsang FC, et al. IgG4-related hypertrophic pachymeningitis at the falx cerebrii with brain parenchymal invasion: a case report. World Neurosurg. 2015;84:591.
Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y, et al. 2012) Comprehensive Diagnostic Criteria for IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD. Mod Rheumatol. 2012;22:21–30.
Acknowledgements
I thank Kumi Fujita, Pathological Department of Tenri Hospital and Mizue Yamamoto, Dermatology Department of Chiba University for contributing useful comments on the draft version.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest:
Shinji Miyajima, Akihiro Okano and Masaya Ohana declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human Rights:
All procedures followed have been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments.
Informed Consent:
Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miyajima, S., Okano, A. & Ohana, M. Immunoglobulin G4-related hepatic inflammatory pseudotumor invading the abdominal wall. Clin J Gastroenterol 10, 57–62 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-016-0701-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-016-0701-4