Abstract
Background
Molecular-targeting drugs able to treat breast cancer expressing epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) would be clinically valuable. The aim of the current study was to determine the further significance of immunohistochemical expression of EGFR in breast cancer.
Methods
The immunohistochemical expression of EGFR was examined in 37 women with breast cancer who had been treated with surgical resection. Relationship of EGFR expression and clinicopathological characteristics was investigated.
Results
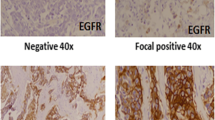
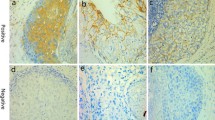
EGFR expression proved to be comparatively more frequent among triple-negative (estrogen receptor negative, progesterone receptor negative, and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 negative) breast cancers (P = 0.067).
Conclusions
Knowledge of a patient’s immunohistochemical EGFR expression, which could be one of the key molecular findings related to molecular-targeting therapy, might be useful information to treat triple-negative breast cancer.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- TNBC:
-
Triple negative breast cancer
- TBS:
-
Tris-buffered saline
References
Guillamo JS, de Boüard S, Valable S, Marteau L, Leuraud P, Marie Y, et al. Molecular mechanisms underlying effects of epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition on invasion, proliferation, and angiogenesis in experimental glioma. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:3697–704.
Wang KL, Wu TT, Choi IS, Wang H, Resetkova E, Correa AM, et al. Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor in esophageal and esophagogastric junction adenocarcinomas: association with poor outcome. Cancer. 2007;109:658–67.
Gamboa-Dominguez A, Dominguez-Fonseca C, Quintanilla-Martinez L, Reyes-Gutierrez E, Green D, Angeles-Angeles A, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor expression correlates with poor survival in gastric adenocarcinoma from Mexican patients: a multivariate analysis using a standardized immunohistochemical detection system. Mod Pathol. 2004;17:579–87.
Putti TC, To KF, Hsu HC, Chan AT, Lai GM, Tse G, et al. Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor in head and neck cancers correlates with clinical progression: a multicentre immunohistochemical study in the Asia-Pacific region. Histopathology. 2002;41:144–51.
Psyrri A, Kassar M, Yu Z, Bamias A, Weinberger PM, Markakis S, et al. Effect of epidermal growth factor receptor expression level on survival in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:8637–43.
Buchholz TA, Tu X, Ang KK, Esteva FJ, Kuerer HM, Pusztai L, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor expression correlates with poor survival in patients who have breast carcinoma treated with doxorubicin-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Cancer. 2005;104:676–81.
Tsutsui S, Ohno S, Murakami S, Hachitanda Y, Oda S. Prognostic value of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and its relationship to the estrogen receptor status in 1029 patients with breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2002;71:67–75.
Nogi H, Kobayashi T, Suzuki M, Tabei I, Kawase K, Toriumi Y, et al. EGFR as paradoxical predictor of chemosensitivity and outcome among triple-negative breast cancer. Oncol Rep. 2009;21:413–7.
Cleator S, Heller W, Coombes RC. Triple-negative breast cancer: therapeutic options. Lancet Oncol. 2007;8:235–44.
Japanese Breast Cancer Society. General rules for clinical and pathological recording of breast cancer. Breast Cancer. 2005;12:S12–4.
Kammerer U, Kapp M, Gassel AM, Richter T, Tank C, Dietl J, et al. A new rapid immunohistochemical staining technique using the EnVision antibody complex. J Histochem Cytochem. 2001;49:623–30.
Guler G, Huebner K, Himmetoglu C, Jimenez RE, Costinean S, Volinia S, et al. Fragile histidine triad protein, WW domain-containing oxidoreductase protein Wwox, and activator protein 2gamma expression levels correlate with basal phenotype in breast cancer. Cancer. 2009;115:899–908.
Capdevila J, Elez E, Macarulla T, Ramos FJ, Ruiz-Echarri M, Tabernero J. Anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibodies in cancer treatment. Cancer Treat Rev. 2009;35:354–63.
Magkou C, Nakopoulou L, Zoubouli C, Karali K, Theohari I, Bakarakos P, et al. Expression of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and the phosphorylated EGFR in invasive breast carcinomas. Breast Cancer Res. 2008;10:49–55.
Talley L, Chhieng DC, Bell WC, Grizzle WE, Frost AR. Immunohistochemical detection of EGFR, p185(erbB-2), Bcl-2 and p53 in breast carcinomas in pre-menopausal and post-menopausal women. Biotech Histochem. 2008;83:5–14.
Yoshimoto M, Tada K, Hori H, Morota A, Tanabe M, Nishimura S, et al. Improvement in the prognosis of Japanese breast cancer patients from 1946 to 2001—an institutional review. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2004;34:457–62.
Rakha EA, El-Sayed ME, Green AR, Lee AH, Robertson JF, Ellis IO. Prognostic markers in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer. 2007;109:25–32.
Irvin WJ Jr, Carey LA. What is triple-negative breast cancer? Eur J Cancer. 2008;44:2799–805.
Cho EY, Han JJ, Choi YL, Kim KM, Oh YL. Comparison of Her-2, EGFR and cyclin D1 in primary breast cancer and paired metastatic lymph nodes: an immunohistochemical and chromogenic in situ hybridization study. J Korean Med Sci. 2008;23:1053–61.
Corkery B, Crown J, Clynes M, O’Donovan N. Epidermal growth factor receptor as a potential therapeutic target in triple-negative breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2009;20:862–7.
Oliveras-Ferraros C, Vazquez-Martin A, López-Bonet E, Martín-Castillo B, Del Barco S, Brunet J, et al. Growth and molecular interactions of the anti-EGFR antibody cetuximab and the DNA cross-linking agent cisplatin in gefitinib-resistant MDA-MB-468 cells: new prospects in the treatment of triple-negative/basal-like breast cancer. Int J Oncol. 2008;33:1165–76.
Gholam D, Chebib A, Hauteville D, Bralet MP, Jasmin C. Combined paclitaxel and cetuximab achieved a major response on the skin metastases of a patient with epidermal growth factor receptor-positive, estrogen receptor-negative, progesterone receptor-negative and human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-negative (triple-negative) breast cancer. Anticancer Drugs. 2007;18:835–7.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank our pathology technicians, Mr. Y. Sei and Mrs. K. Matsumoto, for their assistance and cooperation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Nozoe, T., Mori, E., Iguchi, T. et al. Immunohistochemical expression of epidermal growth factor receptor in breast cancer. Breast Cancer 18, 37–41 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-010-0200-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-010-0200-2