Abstract
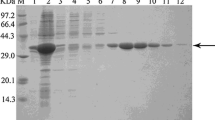
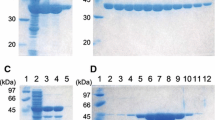
Acetohydroxy-acid synthases (AHAS) of two mutant strains Streptomyces cinnamonensis ACB-NLR-2 and BVR-18 were chosen for this study for their apparent activation by valine, which regularly acts as an allosteric inhibitor. Sequencing the ilvB genes coding for the AHAS catalytic subunit revealed two distant changes in the mutants, ΔQ217 and E139A, respectively. Homology modeling was used to propose the structural changes caused by those mutations. In the mutant strain ACB-NLR-2 (resistant to 2-amino-3-chlorobutyrate and norleucine), deletion of Q217 affected a helix in ß-domain, distant from the active center. As no mutation was found in the regulatory subunit of this strain, ΔQ217 in IlvB was supposed to be responsible for the observed valine activation, probably via changed properties on the proposed regulatory-catalytic subunit interface. In mutant strain BVR-18 (resistant to 2-oxobutyrate), substitution E139A occurred in a conservative loop near the active center. In vitro AHAS activity assay with the enzyme reconstituted from the wild-type regulatory and BVR-18 catalytic subunits proved that the substitution in the catalytic subunit led to the apparent activation of AHAS by valine. We suggest that the conservative loop participated in a conformational change transfer to the active center during the allosteric regulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chipman D., Barak Z., Schloss J.V.: Biosynthesis of 2-aceto-2-hydroxy acids: acetolactate synthases and acetohydroxyacid synthases. Biochim.Biophys.Acta 1385, 401–419 (1998).
Day L.E., Chamberlin J.W., Gordee E.Z., Chen S., Gorman M., Hamill R.L., Ness T., Weeks R.E., Stroshane R.: Biosynthesis of monensin. Antimicrob.Agents Chemother. 4, 410–414 (1973).
De Rossi E., Leva R., Gusberti L., Manachini P.L., Riccardi G.: Cloning sequencing and expression of the ilvBNC gene cluster from Streptomyces avermitilis. Gene 166, 127–132 (1995).
Eoyang L., Silverman P.M.: Role of small subunit (IlvN polypeptide) of acetohydroxyacid synthase I from Escherichia coli K-12 in sensitivity of the enzyme to valine inhibition. J.Bacteriol. 166, 901–904 (1986).
Guex N., Peitsch M.C.: SWISS-MODEL and the Swiss-PdbViewer: an environment for comparative protein modeling. Electrophoresis 18, 2714–2723 (1997).
Hervieu F., Vaucheret H.: A single amino acid change in acetolactate synthase confers resistance to valine in tobacco. Mol.Gen. Genet. 251, 220–224 (1996).
Kopecký J., Janata J., Pospíšil S., Felsberg J., Spížek J.: Mutations in two distinct regions of acetolactate synthase regulatory subunit from Streptomyces cinnamonensis result in the lack of sensitivity to end-product inhibition. Biochem.Biophys.Res.Commun. 266, 162–166 (1999).
Mitra A., Sarma S.P.: Escherichia coli ilvN interacts with the FAD-binding domain of ilvB and activates the AHAS I enzyme. Biochemistry 47, 1518–1531 (2008).
Muller Y.A., Schulz G.E.: Structure of the thiamine- and flavin-dependent enzyme pyruvate oxidase. Science 259, 965–967 (1993).
Murray V.: Improved double-stranded DNA sequencing using the linear polymerase chain reaction. Nucl.Acids Res. 17, 8889 (1989).
Pang S.S., Duggleby R.G., Guddat L.W.: Crystal structure of yeast acetohydroxyacid synthase: a target for herbicidal inhibitors. J.Mol.Biol. 317, 249–262 (2002).
Pospíšil S., Sedmera P., Havránek M., Krumphanzl V., Vaněk Z.: Biosynthesis of monensins A and B. J.Antibiot. 36, 617–619 (1983).
Pospíšil S., Peterková M., Krumphanzl V., Vaněk Z.: Regulatory mutants of Streptomyces cinnamonensis producing monensin A. FEMS Microbiol.Lett. 24, 209–213 (1984).
Pospíšil S., Kopecký J., Přikrylová V.: Derepression and altered feedback regulation of valine biosynthetic pathway in analogueresistant mutants of Streptomyces cinnamonensis resulting in 2-ketoisovalerate excretion. J.Appl.Microbiol. 85, 9–16 (1998).
Pospíšil S., Kopecký J., Přikrylová V., Spížek J.: Overproduction of 2-ketoisovalerate and monensin production by regulatory mutants of Streptomyces cinnamonensis resistant to 2-ketobutyrate and amino acids. FEMS Microbiol.Lett. 172, 197–204 (1999).
Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A.R.: DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc.Nat.Acad.Sci.USA 74, 5463–5467 (1977).
Schwede T., Kopp J., Guex N., Peitsch M.C.: SWISS-MODEL: an automated protein homology-modeling server. Nucl.Acids Res. 31, 3381–3385 (2003).
Vyazmensky M., Sella C., Barak Z., Chipman D.M.: Isolation and characterization of subunits of acetohydroxy acid synthase isozyme III and reconstitution of the holoenzyme. Biochemistry 35, 10339–10346 (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kopecký, J., Kyselková, M., Šigutová, L. et al. Deregulation of acetohydroxy-acid synthase: Loss of allosteric inhibition conferred by mutations in the catalytic subunit. Folia Microbiol 53, 467–471 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-008-0073-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-008-0073-3