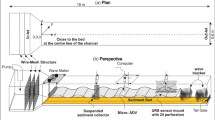
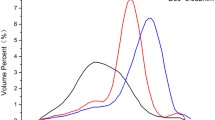
Abstract
In this study, we investigated the sediment suspension process over a ripple, using large eddy simulation and a Lagrangian particle tracking model to numerically calculate the individual motion of sediment grains in turbulent boundary layer flows. We examined the relationship of the sediment convection process with the formation of lee eddies at the back of the ripple. We tested three flow conditions by changing the oscillating period while keeping other conditions. In all three cases lee eddies developed, but they formed at different flow phases and differed in their duration. These lee eddies significantly influenced the turbulent kinetic energy distribution and sediment suspension pattern as they showed phase differences between the cases, according to their lee eddy formation. We compared two types of sediment suspension rates by counting the number of suspended sediment grains. Both these rates showed that maximum sediment pick-up occurred earlier in the oscillating flow phase as the period increased, but the magnitude of the pick-up rate decreased with increasing period. The results of our study indicate that the suspension pattern may vary significantly with the period. Therefore, formulas for sediment pick-up rates, which usually give maximum rates at the time of flow reversal over ripples, may require an additional controlling factor—the oscillation period. The sediment suspension pattern, however, shows some discrepancies from that observed by van der Werf et al. (2007) as the sediments were not suspended at the time of flow reversal. This is likely due to the low steepness of the ripple and the employment of an unrealistically small sediment size in our study experiment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amoudry, L. O., Bell, P. S., Thorne, P. D., and Souza, A. J. (2013). “Toward representing wave-induced sediment suspension over sand ripples in RANS models.” J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 118, No. 5, pp. 2378–2392, DOI: 10.1002/jgrc.20188.
Amoudry, L. O., Souza, A. J., Thorne, P. D., and Liu, P. (2016). “Parameterization of intrawave ripple-averaged sediment pickup above steep ripples.” J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 121, No. 1, pp. 658–673, DOI: 10.1002/2015JC011185.
Bagnold, B. A. (1946). “Motion of waves in shallow water: Interaction between waves and sand bottoms.” Proc. R. Soc. London Ser. A, Vol. 187, No. A1008, pp. 1–15, DOI: 10.1098/rspa.1946.0062.
Bagnold, B. A. (1954). “The flow of cohesionless grains in fluids.” Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. Lond., Vol. 249, No. 964, pp. 235–296, DOI: 10.1098/rsta.1956.0020.
Balaras, E. (1995). “Finite difference computations of high reynoldsnumber flows using the dynamic subgrid-scale model.” Theor. Comp. Fluid Dyn., Vol. 7, No. 3, pp. 207–216, DOI: 10.1007/BF00312363.
Balaras, E. (2004). “Modeling complex boundaries using an external force field on fixed cartesian grids in large-eddy simulations.” Computers and Fluids., Vol. 33, No. 3, pp. 375–404, DOI: 10.1016/S0045-7930(03)00058-6.
Bijker, E., van Hijun, E., and Vellinga, P. (1977). “Sand transport by waves.” Proc.15th Int. Conf. Coastal Eng., pp. 1149–1167, ASCE, DOI: 10.9753/icce.v15.%25p.
Blondeaux, P. (1990). “Sand ripples under sea wave; Part 1. Ripple formation.” J. Fluid Mech., Vol. 218, No. 1, pp. 1–17, DOI: 10.1017/S0022112090000908.
Blondeaux, P., Bruschi, A., Lalli, F., Pesarino, V., and Vittori, G. (2012). “Steady streaming and sediment transport at the bottom of sea waves.” J. Fluid Mech., Vol. 697, No. 1, pp. 115–149, DOI: 10.1017/jfm.2012.50.
Breuer, M. and Alletto, M. (2012). “Efficient simulation of particleladen flows with high mass loadings using les.” Int. J. Heat and Fluid Flows, Vol. 35, No. 1, pp. 2–12, DOI: 10.1016/j.ijheatfluidflow. 2012.01.001.
Chang, Y. S. and Scotti, A. (2004). “Modeling unsteady turbulent flows over ripples: Raynolds-averaged navier-stokes equations (rans) versus large-eddy simulation (les).” J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 109, No. C9, DOI: 10.1029/2003JC002208.
Chang, Y. S. and Scotti, A. (2006). “Turbulent convection of suspended sediments due to flow reversal.” J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 111, No. C07001, DOI: 10.1029/2005JC003240.
Chang, Y. S., Ahn, K., Hwang, J. H., and Park, Y. G. (2013). “Sediment particulate motions over a ripple under different wave amplitude conditions.” J. Korean Soc. Coastal and Ocean Engineers, Vol. 25, No. 6, pp. 374–385, DOI: 10.9765/KSCOE.2013.25.6.374.
Chang, Y. S., Hwang, J. H., and Park, Y. G. (2015). “Numerical simulation of sediment particles released at the edge of the viscous sublayer in steady and oscillating turbulent boundary layers.” J. Hydro-Environ. Res., Vol. 9, No. 1, pp. 36–48, DOI: 10.1016/j.jher.2013.07.002.
Chang, Y. S. and Park, Y. G. (2016). “Suspension of sediment particles over a ripple due to turbulent convection under unsteady flow conditions.” Ocean Sci. J., Vol. 51, No. 1, pp. 127–135, DOI: 10.1007/s12601-016-0011-2.
Davies, A. G. and Thorne, P. D. (2005). “Modeling and measurement of sediment transport by waves in the vortex ripple regime.” J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 111, No. C05017, DOI: 10.1029/2004JC002468.
Harries, J. C. and Grilli, S. T. (2014). “Large eddy simulation of sediment transport over rippled beds.” Nonlin. Processes Geophys., Vol. 21, No. 6, pp. 1169–1184, DOI: 10.5194/npg-21-1169-2014.
Hunt, J. C. R. and Moin, J. F. (2000). “Eddy structure in turbulent boundary layers.” Eur. Mech. B-Fluids., Vol. 19, No. 1, pp. 673–694, DOI: 10.1016/S0997-7546(00)00129-17546(00)00129-1.
Hudson, J. D., Dykhno, L., and Hanratty, T. J. (1996). “Turbulence production in a flow over a wavy wall.” Exp. Fluids, Vol. 20, No. 4, pp. 257–265, DOI: 10.1007/BF00192670.
Li, Z. and Davis, A. G. (1996). “Towards predicting sediment transport in combined wave-current flow.” J. Wat. Port Coast. Ocean Engrg., Vol. 122, No. 4, pp. 157–164, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-950X (1996)122:4(157).
Li, Y., McLaughlin, J. B., Kontomaris K., and Portela, L. (2001). “Numerical simulation of particle-laden turbulent channel flow.” Phys. Fluids, Vol. 13, No. 10, pp. 2957–2967, DOI: 10.1063/1.1396846.
Mattioli, M., Alsina, J.M., Mancinelli, A., Miozzi, M., and Brocchini, M. (2012). “Experimental investigation of the nearbed dynamics around a submarine pipeline laying on a different types of seabed: The interaction between turbulent structures and particles.” Adv. Water Res., Vol. 48, No. 1, pp. 31–46, DOI: 10.1016/j.advwatres. 2012.04. 010.
Mattioli, M., Mancinelli, A., and Brocchini, M. (2013). “Experimental investigation of the wave-induced flow around a surface-touching cylinder.” J. Fluids Struct., Vol. 37, No. 1, pp. 62–87, DOI: 10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2012.10.002.
Meneveau, C., Lund T. S., and Cabot, W. H. (1996). “A lagrangian dynamic subgrid-scale model of turbulence.” J. Fluid Mech., Vol. 319, No. 1, DOI: 10.1017/S0022112096007379.
Meneveau, C. and Katz, J. (2000). “Scale invariance and turbulence models for large-eddy simulation.” Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech., Vol. 32, No. 1, pp. 1–32, DOI: 10.1146/annurev.fluid.32.1.1.
Maxey, M. R. and Riley, J. (1983). “Equation of motion for a small rigid sphere in a non-uniform flow.” Phys. Fluids, Vol. 26, No. 4, pp. 883–889.
Nielsen, P. (1979). “Some basic concepts of wave sediment transport.” Inst. of Hydrodynamics and Hydr. Engrg., ISVA, Tech. Univ. Denmark, 20.
Nielsen, P. (1988). “Three simple models of wave sediment transport.” Coastal Engrg., Vol. 12, No. 2, pp. 43–62, DOI: 10.1016/0378-3839 (88)90014-2.
Nielsen, P. (1992). Coastal bottom boundary layers and sediment transport. volume 4. World Scientific, River Egde, NJ.O’Hara
Murray, R. B., Thorne, P. D., and Hodgson, D. M. (2011). “Infrawave observations of sediment entrainment processes above sand ripples under irregular waves.” J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 116, No. C01001, DOI: 10.1029/2010JC006216.
Patankar, N. A., Ko, T., Choi, H. G., and Joseph, D. D. (2001). “A correlation for the lift-off of many particles in plane poiseuille flows of newtonian fluids.” J. Fluid Mech., Vol. 445, No. 1, pp. 55–76, DOI: 10.1017/S0022112001005274.
Pedinotti, S, Mariotti, G., and Banerjee, S. (1992). “Direct numerical simulation of particle behavior in the wall region of turbulent flows in horizontal channels.” Int. J. Multiphase Flow, Vol. 18, No. 6, pp. 927–941, DOI: 10.1016/0301-9322(92)90068-R.
Piomelli, U. (1999). “Large-eddy simulation: Achievements and challenges.” Prog. Aerosp. Sci., Vol. 35, No. 4, pp. 335–362, DOI: 10.1016/S0376-0421(98)00014-1.
Piomelli, U., Balaras, E., and Pascarelli, A. (2000). “Turbulent structures in accelerating boundary layers.” J. of Turbulence, Vol. 1, No. 1, pp. 1–12, DOI: 10.1088/1468-5248/1/1/001.
Robinson, S. K. (1991). “Coherent motions in the turbulent boundary layer.” Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech., Vol. 23, No. 00, pp. 601–639, DOI: 10.1146/annurev.fl.23.010191.003125.
Scandura, P., Vittori, G., and Blondeaux, P. (2000). “Three-dimensional oscillatory flow over steep ripples.” J. Fluid Mech., Vol. 412, No. 1, pp. 355–378.
Scotti, A. and Piomelli, U. (2001). “Numerical simulation of pulsating turbulent channel flow.” Phys. Fluids, Vol. 13, No. 5, pp. 1367–1384, DOI: 10.1063/1.1359766.
Sleath, J. F. A. (1982). “The suspension of sands by waves.” J. Hydraulic Res., Vol. 20, No. 5, pp. 439–452, DOI: 10.1080/00221688209499472.
Smagorinsky, J. (1963). “General circulation experiments with the primitive equations, i. the basic experiment.” Monthly Weather Rev., Vol. 91, No. 3, pp. 99–164, DOI: 10.1175/1520-0493(1963)091 <0099:GCEWTP>2.3.CO;2.
Soldati, A. and Marchioli, C. (2012). “Sediment transport in steady turbulent boundary layers: Potentials, limitations, and perspectives for lagrangian tracking in dns and les.” Adv. Wat. Res., Vol. 48, No. 1, pp. 18–30, DOI: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2012.05.011.
Thorne, P. D., Davis, A. G., and Williams, J. J. (2003). “Measurements of near-bed infra-wave sediment entrainment above vortex ripples.” Geophys. Res. Lett., Vol. 30, No. 20, DOI: 10.1029/2003GL018427.
Thorne, P. D., Davis, A. G., and Bell, P. S. (2009). “Observations and analysis of sediment diffusivity profiles over sandy rippled beds under waves.” J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 114, No. C02023, DOI: 10.1029/2008JC004944.
Wang, Q. and Squires, K. D. (1996). “Large eddy simulation of particleladen turbulent channel flow.” Phys. Fluids, Vol. 8, No. 5, pp. 1207–1223, DOI: 10.1063/1.868911.
Van der Werf, J. J., Doucette, J. S., O’Donoghue, T., and Ribberink, J. S. (2007). “Detailed measurements of velocities and suspended sand concentration over full-scale ripples in regular oscillatory flow.” J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 112, No. F02012, DOI: 1 0.1029/2006JF000614.
Van der Werf, J. J., Magar, V., Malarkey, J., Guizien, K., and O’Donohue, T. (2008). “2DV modelling of sediment transport processes over fullscale ripples in regular asymmetric oscillatory flow.” Continental Shelf Res., Vol. 28, No. 8, pp. 1040–1056, DOI: 10.1016/j.csr.2008. 02.007.
Villard, P. V. and Osborne, P. D. (2002). “Visualization of wave-induced suspension patterns over two-dimensional bedforms.” Sedimentology, Vol. 49, No. 2, pp. 363–378, DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-3091.2002.00448.
Vinokur, M. (1983). “On one-dimensional stretching functions for finitedifference calculations.” J. Computational Phys., Vol. 50, No. 2, pp. 215–234, DOI: 10.1016/0021-9991(83)90065-7.
Wiberg, P. L. and Smith, J. D. (1985). “A theoretical model for saltating grains in water.” J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 90, No. C4, pp. 7341–7354, DOI: 10.1029/JC090iC04p07341.
Zedler, E. A. and Street, R. L. (2006). “Sediment transport over ripples in oscillatory flow.” J. Hydraulic Engrg., Vol. 132, No. 2, pp. 180–193, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2006)132:2(180).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, Y.S., Hwang, J.H. & Park, YG. Sensitivity of suspension pattern of numerically simulated sediments to oscillating periods of channel flows over a rippled bed. KSCE J Civ Eng 21, 1503–1515 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-016-0516-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-016-0516-3