Abstract
Purpose
Paeonol is a natural chemical medicine derived from the bark of peony root, which has been found to inhibit tumor activity in various tumor cell lines, and can play a synergistic anti-tumor effect with chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
Methods
We used paeonol to act on human bladder cancer T24 and 5637 cells, and established xenograft tumor in nude mice by subcutaneous injection of T24 cells.
Results
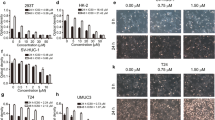
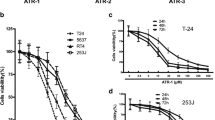
CCK-8 assay and plate cloning experiments showed that paeonol could inhibit the proliferation of T24 and 5637 cells in vitro. The results of flow cytometry and the detection of BAX, Bcl-2 and Caspase-3 proteins suggested that paeonol can induce apoptosis of T24 and 5637 cells in vitro. Tumor formation, TUNEL detection and immunohistochemical results of Ki67, BAX, Bcl-2 and Caspase-3 in nude mice showed that paeonol could inhibit T24 cell proliferation and induce apoptosis in vivo, thus inhibiting tumor growth. Further research revealed that paeonol could reduce phosphorylation expression of PI3K and AKT in T24 and 5637 cells.
Conclusion
We confirmed that paeonol could inhibit proliferation and induce apoptosis of human bladder cancer T24 and 5637 cells in vitro and in vivo, inhibit the growth of T24 tumor-forming nude mice, and possibly play a role by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, so as to provide a potential therapeutic drug for bladder cancer.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69:7–34.
Mertens LS, Neuzillet Y, Horenblas S, van Rhijn BWG. Landmarks in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Nat Rev Urol. 2014;11:476–80.
Fernández MI, Brausi M, Clark PE, Cookson MS, Grossman HB, Khochikar M, Kiemeney LA, Malavaud B, Sanchez-Salas R, Soloway MS, Svatek RS, Vikram R, Vrieling A, Kamat AM. Epidemiology, prevention, screening, diagnosis, and evaluation: update of the ICUD–SIU joint consultation on bladder cancer. World J Urol. 2018;37:3–13.
Griffiths TR, Action on Bladder C. Current perspectives in bladder cancer management. Int J Clin Pract. 2013;67:435–48.
Cragg GM, Newman DJ. Plants as a source of anti-cancer agents. J Ethnopharmacol. 2005;100:72–9.
Bai X, Zhang Y, Jiang H, Yang P, Li H, Zhang Y, He P. Effects of maslinic acid on the proliferation and apoptosis of A549 lung cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 2016;13:117–22.
Boufridi A, Quinn RJ. Harnessing the properties of natural products. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018;58:451–70.
Lei H, Wen Q, Li H, Du S, Wu JJ, Chen J, Huang H, Chen D, Li Y, Zhang S, Zhou J, Deng R, Yang Q. Paeonol inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced HMGB1 translocation from the nucleus to the cytoplasm in RAW264.7 cells. Inflammation. 2016;39:1177–87.
Xu Q, Liu X, Mei L, Wen Q, Chen J, Miao J, Lei H, Huang H, Chen D, Du S, Liu A, Zhang S, Zhou J, Deng R, Li Y, Li C, Li H. Paeonol reduces the nucleocytoplasmic transportation of HMGB1 by upregulating HDAC3 in LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells. Inflammation. 2018;41:1536–45.
Kim SA, Lee HJ, Ahn KS, Lee HJ, Lee EO, Ahn KS, Choi SH, Jung SJ, Kim JY, Baek N, Kim SH. Paeonol exerts anti-angiogenic and anti-metastatic activities through downmodulation of Akt activation and inactivation of matrix metalloproteinases. Biol Pharm Bull. 2009;32:1142–7.
Zhang L, Li D-C, Liu L-F. Paeonol: pharmacological effects and mechanisms of action. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;72:413–21.
Li N, Fan LL, Sun GP, Wan XA, Wang ZG, Wu Q, Wang H. Paeonol inhibits tumor growth in gastric cancerin vitroandin vivo. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16:4483–90.
Xu Y, Zhu J-Y, Lei Z-M, Wan L-J, Zhu X-W, Ye F, Tong Y-Y. Anti-proliferative effects of paeonol on human prostate cancer cell lines DU145 and PC-3. J Physiol Biochem. 2016;73:157–65.
Ou Y, Li Q, Wang J, Li K, Zhou S. Antitumor and apoptosis induction effects of paeonol on mice bearing EMT6 breast carcinoma. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2014;22:341–6.
Lyu ZK, Li CL, Jin Y, Liu YZ, Zhang X, Zhang F, Ning LN, Liang ES, Ma M, Gao W, Zhang MX, Liu DS. Paeonol exerts potential activities to inhibit the growth, migration and invasion of human gastric cancer BGC823 cells via downregulating MMP2 and MMP9. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16:7513–9.
Li M, Tan SY, Wang XF. Paeonol exerts an anticancer effect on human colorectal cancer cells through inhibition of PGE(2) synthesis and COX-2 expression. Oncol Rep. 2014;32:2845–53.
Li M, Tan SY, Zhang J, You HX. Effects of paeonol on intracellular calcium concentration and expression of RUNX3 in LoVo human colon cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 2013;7:1425–30.
Xu SP, Sun GP, Shen YX, Peng WR, Wang H, Wei W. Synergistic effect of combining paeonol and cisplatin on apoptotic induction of human hepatoma cell lines. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2007;28:869–78.
Wu J, Xue X, Zhang B, Cao H, Kong F, Jiang W, Li J, Sun D, Guo R. Enhanced antitumor activity and attenuated cardiotoxicity of Epirubicin combined with Paeonol against breast cancer. Tumour Biol. 2016;37:12301–13.
Lei Y, Li HX, Jin WS, Peng WR, Zhang CJ, Bu LJ, Du YY, Ma T, Sun GP. The radiosensitizing effect of Paeonol on lung adenocarcinoma by augmentation of radiation-induced apoptosis and inhibition of the PI3K/Akt pathway. Int J Radiat Biol. 2013;89:1079–86.
Lin MY, Lee YR, Chiang SY, Li YZ, Chen YS, Hsu CD, Liu YW. Cortex moutan induces bladder cancer cell death via apoptosis and retards tumor growth in mouse bladders. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:207279.
Zhang L, Tao L, Shi T, Zhang F, Sheng X, Cao Y, Zheng S, Wang A, Qian W, Jiang L, Lu Y. Paeonol inhibits B16F10 melanoma metastasis in vitro and in vivo via disrupting proinflammatory cytokines-mediated NF-kappaB and STAT3 pathways. IUBMB Life. 2015;67:778–88.
Zhou HM, Sun QX, Cheng Y. Paeonol enhances the sensitivity of human ovarian cancer cells to radiotherapy-induced apoptosis due to downregulation of the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/Akt/phosphatase and tensin homolog pathway and inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14:3213–20.
Malaguarnera L. Implications of apoptosis regulators in tumorigenesis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2004;23:367–87.
Sun GP, Wan X, Xu SP, Wang H, Liu SH, Wang ZG. Antiproliferation and apoptosis induction of paeonol in human esophageal cancer cell lines. Dis Esophagus. 2008;21:723–9.
Ramachandhiran D, Vinothkumar V, Babukumar S. Paeonol exhibits anti-tumor effects by apoptotic and anti-inflammatory activities in 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene induced oral carcinogenesis. Biotech Histochem. 2019;94:10–25.
Li LT, Jiang G, Chen Q, Zheng JN. Ki67 is a promising molecular target in the diagnosis of cancer. Mol Med Rep. 2015;11:1566–72 [Review].
Katiyar SK, Roy AM, Baliga MS. Silymarin induces apoptosis primarily through a p53-dependent pathway involving Bcl-2/Bax, cytochrome c release, and caspase activation. Mol Cancer Ther. 2005;4:207–16.
Reagan-Shaw S, Nihal M, Ahsan H, Mukhtar H, Ahmad N. Combination of vitamin E and selenium causes an induction of apoptosis of human prostate cancer cells by enhancing Bax/Bcl-2 ratio. Prostate. 2008;68:1624–34.
Choudhary GS, Al-Harbi S, Almasan A. Caspase-3 activation is a critical determinant of genotoxic stress-induced apoptosis. Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1219:1–9.
Skommer J, Brittain T, Raychaudhuri S. Bcl-2 inhibits apoptosis by increasing the time-to-death and intrinsic cell-to-cell variations in the mitochondrial pathway of cell death. Apoptosis. 2010;15:1223–33.
Zhao Y, Zhang CL, Zeng BF, Wu XS, Gao TT, Oda Y. Enhanced chemosensitivity of drug-resistant osteosarcoma cells by lentivirus-mediated Bcl-2 silencing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;390:642–7.
Majtnerová P, Roušar T. An overview of apoptosis assays detecting DNA fragmentation. Mol Med Rep. 2018;45:1469–78.
Martini M, De Santis MC, Braccini L, Gulluni F, Hirsch E. PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and cancer: an updated review. Ann Med. 2014;46:372–83.
Jiang BH, Liu LZ. PI3K/PTEN signaling in angiogenesis and tumorigenesis. Adv Cancer Res. 2009;102:19–65.
Oka N, Tanimoto S, Taue R, Nakatsuji H, Kishimoto T, Izaki H, Fukumori T, Takahashi M, Nishitani M, Kanayama HO. Role of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/Akt pathway in bladder cancer cell apoptosis induced by tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. Cancer Sci. 2006;97:1093–8.
Zeng SX, Zhu Y, Ma AH, Yu W, Zhang H, Lin TY, Shi W, Tepper CG, Henderson PT, Airhart S, Guo JM, Xu CL, deVere White RW, Pan CX. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway as a potential therapeutic target in bladder cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23:6580–91.
Soler A, Figueiredo AM, Castel P, Martin L, Monelli E, Angulo-Urarte A, Milà-Guasch M, Viñals F, Baselga J, Casanovas O, Graupera M. Therapeutic benefit of selective inhibition of p110alpha PI3-kinase in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22:5805–17.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the medical innovation team of Jiangsu Province (CXTDA2017048), Suqian Sci&Tech Program (K201901) and the Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China (19KJB320008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JJZ and LJC designed the study and drafted the manuscript. KP, YD and ZGZ were responsible for the collection and analysis of the experimental data. BL, RL and CHH revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by Ethical Committee of the Animal Experiment Center of Xuzhou Medical University and conducted in accordance with the ethical standards. (Ethics number: xz2019100801L).
Informed consent
Yes.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
J. J. Zhang and L.J. Cai contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J.J., Cai, L.J., Pang, K. et al. Paeonol inhibits proliferation and induces cell apoptosis of human T24 and 5637 bladder cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Clin Transl Oncol 23, 601–611 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-020-02455-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-020-02455-y