Abstract
Purpose
Patients with hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg)-positive chronic hepatitis B, who achieve HBeAg seroconversion 6 months after completing 48 weeks of peginterferon alfa-2a therapy, have an increased chance of clearing hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) during long-term treatment-free follow-up. This analysis aimed to determine whether HBsAg quantification during treatment could be used to identify posttreatment response.
Methods
Patients (n = 399) treated with peginterferon alfa-2a (180 μg/week) alone or in combination with lamivudine (100 mg/day) for 48 weeks during a large, randomized study were included in this retrospective analysis. Receiver-operating characteristic analyses were used to identify baseline and on-treatment HBsAg levels associated with response (HBeAg seroconversion 6 months posttreatment).
Results
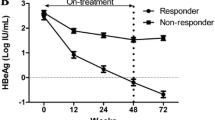
Baseline HBsAg levels were lower in patients achieving posttreatment response than in nonresponders (3.97 and 4.21 IU/mL, respectively, p = 0.039). Two baseline HBsAg cutoff levels (5,000 and 50,000 IU/mL) provided a positive predictive value of 42% and a negative predictive value of 77%. HBsAg decline was significantly greater during and posttreatment in responders than in nonresponders (p < 0.0001). HBeAg seroconversion rates 6 months posttreatment were significantly higher in patients with HBsAg < 1,500 IU/mL at weeks 12 and 24 (56.7 and 54.4%, respectively) versus patients with HBsAg 1,500–20,000 IU/mL (32.3 and 26.1%, respectively) or HBsAg < 20,000 IU/mL (16.3 and 15.4%, respectively) (all p < 0.0001 and <0.0001).
Conclusions
HBsAg levels at baseline strongly associated with posttreatment response were not identified. Low HBsAg levels during peginterferon alfa-2a therapy were associated with high rates of posttreatment response. On-treatment HBsAg quantification may, therefore, help guide patient management in the future.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marcellin P. Hepatitis B and hepatitis C in 2009. Liver Int 2009;29:1–8
Fattovich G, Giustina G, Sanchez-Tapias J, et al. Delayed clearance of serum HBsAg in compensated cirrhosis B: relation to interferon alfa therapy and disease prognosis. European Concerted Action on Viral Hepatitis (EUROHEP). Am J Gastroenterol 1998;93:896–900
Moucari R, Korevaar A, Lada O, et al. High rates of HBsAg seroconversion in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B patients responding to interferon: a long-term follow-up. J Hepatol 2009;50:1084–1092
European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines: management of chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol 2009;50:227–242
Lok A, McMahon B. Chronic hepatitis B: update 2009. Hepatology 2009;50:1–36.
Liaw YF, Leung N, Kao JH, et al. Asian-Pacific consensus statement on the management of chronic hepatitis B: a 2008 update. Hepatol Int 2008;2:263–283
Lau GK, Piratvisuth T, Luo KX, et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a, lamivudine and the combination for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med 2005;352:2682–2695
Buster EH, Flink HJ, Cakaloglu Y, et al. Sustained HBeAg and HBsAg loss after long-term follow-up of HBeAg-positive patients treated with peginterferon alfa-2b. Gastroenterology 2008;135:459–467.
van Zonneveld M, Honkoop P, Hansen BE, et al. Long-term follow-up of alpha-interferon treatment of patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2004;39:804–810.
Liaw Y-F, Chu C-M. Hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet 2009;373:582–592
Buster EH, Flink HJ, Simsek H, et al. Early HBeAg loss during peginterferon alfa-2b predicts HBsAg loss: results of a long-term follow-up study in chronic hepatitis B patients. Am J Gastroenterol 2009;104:2449–2457
Buster EH, Hansen BE, Lau GK, et al. Factors that predict response of patients with hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B to pegylated interferon alfa. Gastroenterology 2009;137:2002–2009
Fried MW, Piratvisuth T, Lau GK, et al. HBeAg and hepatitis B virus DNA as outcome predictors during therapy with peginterferon alfa-2a for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2008;47:428–434
Brunetto MR, Moriconi F, Bonino F, et al. Hepatitis B virus surface antigen levels: a guide to sustained response to peginterferon alfa-2a in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2009;49:1141–1150
Wong VW, Wong GL, Yan KK, Chim AM, Chan HY, Tse CH, Choi PC, Chan AW, Sung JJ, Chan HL. Durability of peginterferon alfa-2b treatment at 5 years in patients with hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2010;51:1945–1953
Kuhns MC, Kleinman SH, McNamara AL, Rawal B, Glynn S, Busch MP. Lack of correlation between HBsAg and HBV DNA levels in blood donors who test positive for HBsAg and anti-HBc: implications for future HBV screening policy. Transfusion 2004;44:1332–1339.
Laperche S, Thibault V, Bouchardeau F, et al. Expertise of laboratories in viral load quantification, genotyping and precore mutation determination for hepatitis B virus in a multicenter study. J Clin Microbiol 2006;44:3600–3607
Pawlotsky JM, Bastie A, Hézode C, et al. Routine detection and quantification of hepatitis B virus DNA in clinical laboratories: performance of three commercial assays. J Virol Methods 2000;85:11–21
Pawlotsky JM. Molecular diagnosis of viral hepatitis. Gastroenterology 2002;122:1554–1568
Deguchi M, Yamashita N, Kagita M, et al. Quantitation of hepatitis B surface antigen by an automated chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay. J Virol Methods 2004;115:217–222
Rodella A, Galli C, Terlenghi L, Perandin F, Bonfanti C, Manca N. Quantitative analysis of HBsAg, IgM anti-HBc and anti-HBc avidity in acute and chronic hepatitis B. J Clin Virol 2006;37:206–212
Werle-Lapostolle B, Bowden S, Locarnini S, et al. Persistence of cccDNA during the natural history of chronic hepatitis B and decline during adefovir dipivoxil therapy. Gastroenterology 2004;126:1750–1758
Chan HL, Wong VW, Tse AM, et al. Serum hepatitis B surface antigen quantitation can reflect hepatitis B virus in the liver and predict treatment response. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2007;5:1462–1468
Volz T, Lutgehetmann M, Wachtler P, Jacob A, et al. Impaired intrahepatic hepatitis B virus productivity contributes to low viremia in most HBeAg-negative patients. Gastroenterology 2007;133:843–852
Zoulim F. Assessment of treatment efficacy in HBV infection and disease. J Hepatol 2006;44:S95–S99.
Peters M. Actions of cytokines on the immune response and viral interactions: an overview. Hepatology 1996;23:909–916
Thimme R, Wieland S, Steiger C, et al. CD8 (+) T cells mediate viral clearance and disease pathogenesis during acute hepatitis B virus infection. J Virol 2003;77:68–76
Tangkijvanich P, Komolmit P, Mahachai V, Sa-Nguanmoo P, Theamboonlers A, Poovorawan Y. Comparison between quantitative hepatitis surface antigen, hepatitis B e antigen and hepatitis B virus DNA levels for predicting virological response to pegylated interferon alfa-2b therapy in hepatitis B e-antigen positive chronic hepatitis B. Hepatol Res 2010;40:269–277
Sonneveld MJ, Rijckborst V, Boucher CA, Hansen BE, Janssen HL. Prediction of sustained response to peginterferon alfa-2b for hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B using on-treatment hepatitis B surface antigen decline. Hepatology 2010;52:1251–1257
Piratvisuth T, Marcellin P. Further analysis is required to identify an early stopping rule for peginterferon therapy that is valid for all HBeAg-positive patients. Hepatology. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.24136.
Lampertico P, Vigano M, Bhoori S, et al. Extended (2 years) treatment with peginterferon alfa-2a [40 KD] improves sustained response rates in genotype D patients with HBeAg negative chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol 2010;52:S45
Moucari R, Mackiewicz V, Lada O, et al. Early serum HBsAg drop: a strong predictor of sustained virological response to pegylated interferon alfa-2a in HBeAg-negative patients. Hepatology 2009;49:1151–1157
Hansen BE, Buster EH, Steyerberg EW, Lesaffre E, Janssen HL. Prediction of the response to peg-interferon-alfa in patients with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B using decline of HBV DNA during treatment. J Med Virol 2010;82:1135–1142
Acknowledgements
Research grant was provided by F. Hoffmann-La Roche, Basel, Switzerland. Editorial support was provided by Dr Liesje Thomas of Elements Communications Ltd., Westerham, UK.
Conflict of interest
TP has participated in advisory boards for Roche, Novartis, MSD and GSK, in Speaker’s Bureau for Roche, Novartis, MSD, GSK and BMS, and has received research grants from Roche and Novartis. PM has acted as a speaker for Roche, Schering-Plough, Gilead, BMS, Novartis, Tibotec, and Intermune; has acted as an expert for Roche, Schering-Plough, Gilead, BMS, Verex, Novartis, Pharmasset, Tibotec, MSD, Biolex, Zymogenetics and Intermune; as an investigator for Roche, Schering-Plough, Gilead, BMS, Verex, Novartis, Tibotec, MSD, Biolex and Intermune; and has received grant support from Roche, Schering-Plough and Gilead. EBM is an employee of Genentech. H-PK is an employee of Abbott GmbH and Company. All other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Piratvisuth, T., Marcellin, P., Popescu, M. et al. Hepatitis B surface antigen: association with sustained response to peginterferon alfa-2a in hepatitis B e antigen-positive patients. Hepatol Int 7, 429–436 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-011-9280-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-011-9280-0