Abstract
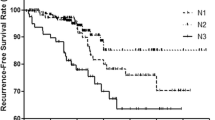
Tumor multifocality is not an unusual finding in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC), but its clinical significance is controversial. In this study, we aimed to evaluate impact of multifocality, tumor number, and total tumor diameter on clinicopathological features of PTC. Medical records of 912 patients who underwent thyroidectomy and diagnosed with PTC were reviewed retrospectively. Patients were grouped into four according to number of tumoral foci: N1 (1 focus), N2 (2 foci), N3 (3 foci), and N4 (≥4 foci). The diameter of the largest tumor was considered the primary tumor diameter (PTD), and total tumor diameter (TTD) was calculated as the sum of the maximal diameter of each lesion in multicentric tumors. Patients were further classified into subgroups according to PTD and TTD. Multifocal PTC was found in 308 (33.8 %) patients. Capsular invasion, extrathyroidal extension, and lymph node metastasis were significantly higher in patients with multifocal tumors compared to patients with unifocal PTC. As the number of tumor increased, extrathyroidal extension and lymph node metastasis also increased (p = 0.034 and p = 0.004, respectively). The risk of lymph node metastasis was 2.287 (OR = 2.287, p = 0.036) times higher in N3 and 3.449 (OR = 3.449, p = 0.001) times higher in N4 compared to N1. Capsular invasion, extrathyroidal extension, and lymph node metastasis were significantly higher in multifocal patients with PTD ≤10 mm and TTD >10 mm than unifocal patients with tumor diameter ≤10 mm (p < 0.001, p < 0.001 and p = 0.001, respectively). There was no significant difference in terms of these parameters in multifocal patients with PTD ≤10 mm and TTD >10 mm and unifocal patients with tumor diameter >10 mm. In this study, increased tumor number was associated with higher rates of capsular invasion, extrathyroidal extension, and lymph node metastasis. In a patient with multifocal papillary microcarcinoma, TTD >10 mm confers a similar risk of aggressive histopathological behavior with unifocal PTC greater than 10 mm.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Ito, M. Fukushima, M. Kihara, Y. Takamura, K. Kobayashi, A. Miya, A. Miyauchi, Investigation of the prognosis of patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma by tumor size. Endocr. J. 59, 457–464 (2012)
K.J. Kim, S.M. Kim, Y.S. Lee, W.Y. Chung, H.S. Chang, C.S. Park, Prognostic significance of tumor multifocality in papillary thyroid carcinoma and its relationship with primary tumor size: a retrospective study of 2309 consecutive patients. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 22, 125–131 (2015)
M. Iacobone, S. Jansson, M. Barczynski, P. Goretzki, Multifocal papillary thyroid carcinoma: a consensus report of the European Society of Endocrine Surgeons (ESES). Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 399, 141–154 (2014)
Y.K. So, M.W. Kim, Y.I. Son, Multifocality and bilaterality of papillary thyroid microcarcinoma. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 8, 174–178 (2015)
H.J. Kim, H.K. Park, D.W. Byun, K. Suh, M.H. Yoo, Y.K. Min, S.W. Kim, J.H. Chung, Number of tumor foci as predictor of lateral lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Head Neck 37, 650–654 (2015)
A. Al Afif, B.A. Williams, M.H. Rigby, M.J. Bullock, S.M. Taylor, J. Trites, R.D. Hart, Multifocal papillary thyroid cancer increases the risk of central lymph node metastasis. Thyroid 25, 1008–1012 (2015)
J.S. Pyo, J.H. Sohn, G. Kang, D.H. Kim, J. Yun, Total surface area is useful for differentiating between aggressive and favorable multifocal papillary thyroid carcinomas. Yonsei. Med. J. 56, 355–361 (2015)
H.J. Kim, S.Y. Sohn, H.W. Jang, S.W. Kim, J.H. Chung, Multifocality, but not bilaterality, is a predictor of disease recurrence/persistence of papillary thyroid carcinoma. World J. Surg. 37, 376–384 (2013)
N. Qu, L. Zhang, Q.H. Ji, Y.X. Zhu, Z.Y. Wang, Q. Shen, Y. Wang, D.S. Li, Number of tumor foci predicts prognosis in papillary thyroid cancer. BMC Cancer 14, 914 (2014)
D.S. Cooper, G.M. Doherty, B.R. Haugen, R.T. Kloos, S.L. Lee, S.J. Mandel, E.L. Mazzaferri, B. McIver, S.I. Sherman, R.M. Tuttle, Management guidelines for patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid 16, 109–142 (2006)
F. Pacini, M. Schlumberger, H. Dralle, R. Elisei, J.W. Smit, W. Wiersinga, European consensus for the management of patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma of the follicular epithelium. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 154, 787–803 (2006)
J.D. Lin, T.C. Chao, C. Hsueh, S.F. Kuo, High recurrent rate of multicentric papillary thyroid carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 16, 2609–2616 (2009)
D.W. Hosmer, S. Lemeshow, R.X. Sturdivant, Applied logistic regression, 3rd edn. (Wiley, New York, 2013)
M.R. Haymart, M. Cayo, H. Chen, Papillary thyroid microcarcinomas: big decisions for a small tumor. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 16, 3132–3139 (2009)
S.F. Kuo, S.F. Lin, T.C. Chao, C. Hsueh, K.J. Lin, J.D. Lin, Prognosis of multifocal papillary thyroid carcinoma. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 809382 (2013)
B.H. Lang, C.Y. Lo, W.F. Chan, K.Y. Lam, K.Y. Wan, Staging systems for papillary thyroid carcinoma: a review and comparison. Ann. Surg. 245, 366–378 (2007)
S.B. Edge, American joint committee on cancer: AJCC cancer staging manual, 7th edn. (Springer, New York, 2010)
W. Wang, H. Wang, X. Teng, H. Wang, C. Mao, R. Teng, W. Zhao, J. Cao, TJ 3rd Fahey, L Teng, Clonal analysis of bilateral, recurrent, and metastatic papillary thyroid carcinomas. Hum. Pathol. 41, 1299–1309 (2010)
T.M. Shattuck, W.H. Westra, P.W. Ladenson, A. Arnold, Independent clonal origins of distinct tumor foci in multifocal papillary thyroid carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 352, 2406–2412 (2005)
M. Bansal, M. Gandhi, R.L. Ferris, M.N. Nikiforova, L. Yip, S. Carty, Y. Nikiforov, Molecular and histopathologic characteristics of multifocal papillary thyroid carcinoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 37, 1586–1591 (2013)
G. Tallini, D. Biase, C. Durante, G. Acquaviva, M. Bisceglia, R. Bruno, M.L.B. Reggiani, G.P. Casadei, G. Costante, N. Cremonini, L. Lamartina, D. Meringolo, F. Nardi, A. Pession, K.J. Rhoden, G. Ronga, M. Torlontano, A. Verrienti, M. Visani, S. Filetti, BRAF V600E and risk stratification of thyroid microcarcinoma: a multicenter pathological and clinical study. Mod. Pathol. 28, 1343–1359 (2015)
Q. Zhao, J. Ming, C. Liu, L. Shi, X. Xu, X. Nie, T. Huang, Multifocality and total tumor diameter predict central neck lymph node metastases in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 20, 746–752 (2013)
H. Qu, G.R. Sun, Y. Liu, Q.S. He, Clinical risk factors for central lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Endocrinol. 83, 124–132 (2015)
M. Mustafa, T. Kuwert, K. Weber, P. Knesewitsch, T. Negele, A. Haug, R. Linke, P. Bartenstein, D. Schmidt, Regional lymph node involvement in T1 papillary thyroid carcinoma: a bicentric prospective SPECT/CT study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 37, 1462–1466 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tam, A.A., Özdemir, D., Çuhacı, N. et al. Association of multifocality, tumor number, and total tumor diameter with clinicopathological features in papillary thyroid cancer. Endocrine 53, 774–783 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-016-0955-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-016-0955-0