Abstract
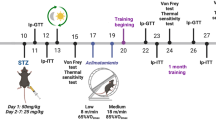
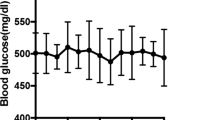
The exact effectiveness of supportive care activities, such as exercise, in diabetes patients has yet to be elucidated in the diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) field. Therefore, this study was designed to investigate the effect of regular exercise on the peripheral nerves of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. The animals were divided as follows into six groups according to exercise combination and glucose control: Normal group, normal group with exercise (EXE), diabetic group (DM), DM group with EXE, DM + glucose control with insulin (INS), and DM + INS + EXE. Animals in the exercise groups were made to walk on a treadmill machine everyday for 30 min at a setting of 8 m/min without inclination. After 8 weeks, sensory parameters were evaluated, and after 16 weeks, biochemicals and peripheral nerves were quantified by immunohistochemistry and compared among experimental groups. The resulting data showed that fasting blood glucose levels and HbA1c levels were not influenced significantly by exercise in normal and DM groups. However, the current perception threshold and the von Frey stimulation test revealed higher thresholds in the DM + INS + EXE group than in the DM + INS group (P < 0.05). Significantly lower thresholds were observed in untreated DM groups (DM or DM + EXE) compared to the normal and insulin-treated DM groups (P < 0.05). Intra-epidermal nerve fiber density was reduced in a lesser degree in the DM + INS + EXE group than in the DM + INS group (9.8 ± 0.4 vs. 9.1 ± 0.5, P < 0.05). Exercise alone was not associated with a significant protective effect on the peripheral nerve in the normal or DM groups; however, a beneficial effect from exercise was observed when hyperglycemia was controlled with insulin in the DM group. These findings suggest that exercise has a potential protective effect against DPN based on the preferential effort for glucose control, although exercise alone cannot prevent peripheral nerve damage from hyperglycemia.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CPT:
-
Current perception threshold
- DM:
-
Diabetes mellitus
- DPN:
-
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy
- IENFD:
-
Intra-epidermal nerve fiber density
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
References
A.J. Boulton, Malik RA diabetic neuropathy. Med. Clin. North Am. 82, 909–929 (1998)
J.L. Edwards, A.M. Vincent, H.T. Cheng, E.L. Feldman, Diabetic neuropathy: mechanisms to management. Pharmacol. Ther. 120, 1–34 (2008)
J.W. Baynes, S.R. Thorpe, Role of oxidative stress in diabetic complications: a new perspective on an old paradigm. Diabetes 48, 1–9 (1999)
J.W. Baynes, Role of oxidative stress in development of complications in diabetes. Diabetes 40, 405–412 (1991)
O. Coskun, A. Ocakci, T. Bayraktaroglu, M. Kanter, Exercise training prevents and protects streptozotocin-induced oxidative stress and beta-cell damage in rat pancreas. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 203, 145–154 (2004)
A.S. Veras-Silva, K.C. Mattos, N.S. Gava, P.C. Brum, C.E. Negrao et al., Low-intensity exercise training decreases cardiac output and hypertension in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am. J. Physiol. 273, H2627–H2631 (1997)
H.H. Lee, M.S. Shin, Y.S. Kim, H.Y. Yang, H.K. Chang et al., Early treadmill exercise decreases intrastriatal hemorrhage-induced neuronal cell death and increases cell proliferation in the dentate gyrus of streptozotocin-induced hyperglycemic rats. J. Diabetes Complicat. 19, 339–346 (2005)
H.Y. Jin, K.A. Lee, S.K. Song, W.J. Liu, J.H. Choi et al., Sulodexide prevents peripheral nerve damage in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 674, 217–226 (2012)
H.Y. Jin, S.H. Kim, H.M. Yu, H.S. Baek, T.S. Park, Therapeutic potential of dioscorea extract (DA-9801) in comparison with alpha lipoic acid on the peripheral nerves in experimental diabetes. J. Diabetes Res. 2013, 631218 (2013)
H.M. Rathur, A.J. Boulton, Recent advances in the diagnosis and management of diabetic neuropathy. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 87, 1605–1610 (2005)
K.B. Muller, L.C. Galdieri, V.G. Pereira, A.M. Martins, V. D’Almeida, Evaluation of oxidative stress markers and cardiovascular risk factors in Fabry Disease patients. Genet. Mol. Biol. 35, 418–423 (2012)
J. Kasznicki, M. Kosmalski, A. Sliwinska, M. Mrowicka, M. Stanczyk et al., Evaluation of oxidative stress markers in pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy. Mol. Biol. Rep. 39, 8669–8678 (2012)
A.A. Tahrani, T. Askwith, M.J. Stevens, Emerging drugs for diabetic neuropathy. Expert Opin. Emerg. Drugs 15, 661–683 (2010)
N.E. Cameron, M.A. Cotter, V. Archibald, K.C. Dines, E.K. Maxfield, Anti-oxidant and pro-oxidant effects on nerve conduction velocity, endoneurial blood flow and oxygen tension in non-diabetic and streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Diabetologia 37, 449–459 (1994)
N.E. Cameron, M.A. Cotter, E.K. Maxfield, Anti-oxidant treatment prevents the development of peripheral nerve dysfunction in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Diabetologia 36, 299–304 (1993)
N.L. van Meeteren, J.H. Brakkee, G.J. Biessels, A.C. Kappelle, P.J. Helders et al., Effect of exercise training on acute (crush lesion) and chronic (diabetes mellitus) peripheral neuropathy in the rat. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 10, 85–93 (1996)
P.M. Kluding, M. Pasnoor, R. Singh, S. Jernigan, K. Farmer et al., The effect of exercise on neuropathic symptoms, nerve function, and cutaneous innervation in people with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J. Diabetes Complicat. 26, 424–429 (2012)
S. Balducci, G. Iacobellis, L. Parisi, N. Di Biase, E. Calandriello et al., Exercise training can modify the natural history of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J. Diabetes Complicat. 20, 216–223 (2006)
Y.W. Chen, P.L. Hsieh, Y.C. Chen, C.H. Hung, J.T. Cheng, Physical exercise induces excess hsp72 expression and delays the development of hyperalgesia and allodynia in painful diabetic neuropathy rats. Anesth. Analg. 116, 482–490 (2013)
C.H. Song, J.S. Petrofsky, S.W. Lee, K.J. Lee, J.E. Yim, Effects of an exercise program on balance and trunk proprioception in older adults with diabetic neuropathies. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 13, 803–811 (2011)
H. Li, Z. Shen, Y. Lu, F. Lin, Y. Wu et al., Muscle NT-3 levels increased by exercise training contribute to the improvement in caudal nerve conduction velocity in diabetic rats. Mol. Med. Rep. 6, 69–74 (2012)
Y.W. Chen, Y.T. Li, Y.C. Chen, Z.Y. Li, C.H. Hung, Exercise training attenuates neuropathic pain and cytokine expression after chronic constriction injury of rat sciatic nerve. Anesth. Analg. 114, 1330–1337 (2012)
A.I. Vinik, T.S. Park, K.B. Stansberry, G.L. Pittenger, Diabetic neuropathies. Diabetologia 43, 957–973 (2000)
M.A. Kiraly, H.E. Bates, N.A. Kaniuk, J.T. Yue, J.H. Brumell et al., Swim training prevents hyperglycemia in ZDF rats: mechanisms involved in the partial maintenance of beta-cell function. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 294, E271–E283 (2008)
B.B. Johansson, A.L. Ohlsson, Environment, social interaction, and physical activity as determinants of functional outcome after cerebral infarction in the rat. Exp. Neurol. 139, 322–327 (1996)
Y.R. Yang, R.Y. Wang, P.S. Wang, Early and late treadmill training after focal brain ischemia in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 339, 91–94 (2003)
S.B. DeBow, M.L. Davies, H.L. Clarke, F. Colbourne, Constraint-induced movement therapy and rehabilitation exercises lessen motor deficits and volume of brain injury after striatal hemorrhagic stroke in rats. Stroke 34, 1021–1026 (2003)
Z. Radak, M. Sasvari, C. Nyakas, T. Kaneko, S. Tahara et al., Single bout of exercise eliminates the immobilization-induced oxidative stress in rat brain. Neurochem. Int. 39, 33–38 (2001)
Z. Radak, T. Kaneko, S. Tahara, H. Nakamoto, J. Pucsok et al., Regular exercise improves cognitive function and decreases oxidative damage in rat brain. Neurochem. Int. 38, 17–23 (2001)
N.C. Berchtold, J.P. Kesslak, C.J. Pike, P.A. Adlard, C.W. Cotman, Estrogen and exercise interact to regulate brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA and protein expression in the hippocampus. Eur. J. Neurosci. 14, 1992–2002 (2001)
E. Carro, J.L. Trejo, S. Busiguina, I. Torres-Aleman, Circulating insulin-like growth factor I mediates the protective effects of physical exercise against brain insults of different etiology and anatomy. J. Neurosci. 21, 5678–5684 (2001)
A.G. Smith, P. Ramachandran, S. Tripp, J.R. Singleton, Epidermal nerve innervation in impaired glucose tolerance and diabetes-associated neuropathy. Neurology 57, 1701–1704 (2001)
Acknowledgments
We thank to the Research Institute of Clinical Medicine of Chonbuk National University—Biomedical Research Institute of Chonbuk National University Hospital for supporting our researches in a grant partly and experimental system.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, H.Y., Lee, K.A. & Park, T.S. The effect of exercise on the peripheral nerve in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats. Endocrine 48, 826–833 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-014-0422-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-014-0422-8