Abstract
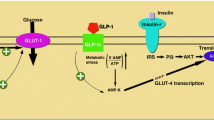
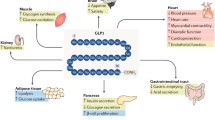
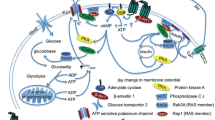
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) stimulates insulin secretion and inhibits glucagon secretion in the pancreatic islets of Langerhans under hyperglycaemia. In type 2 diabetes (T2DM), GLP-1 improves glycaemic control without a hypoglycaemia risk. GLP-1 receptors have also been found in extra-pancreatic tissues, e.g., the cardiovascular system, the gastrointestinal system, and the central nervous system. Since cardiovascular comorbidities and degenerative neurological changes are associated with T2DM, the interest in the extrapancreatic effects of GLP-1 has increased. GLP-1-based therapies with either GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RA) or DPP-4 inhibitors (that delay the degradation of endogenous GLP-1) have become widely used therapeutic options in T2DM. In clinical studies, GLP-1 RA have demonstrated a significant lowering of blood pressure that is independent of body weight changes. Preclinical data and small short-term studies with GLP-1 and GLP-1 RA have shown cardioprotective effects in ischaemia models. GLP-1 as well as a treatment with GLP-1 RA also induces a stable body weight loss by affecting GLP-1 signaling in the hypothalamus and by slowing gastric emptying. Regarding neuroprotective actions in degenerative neurological disease models for Parkinson’s- or Alzheimer’s disease or neurovascular complications like stroke, animal studies have shown positive results. In this article, a summary of the extrapancreatic effects of GLP-1 and GLP-1-based therapies is presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
International Diabetes Federation (IDF): Diabetes Atlas, 6th edition 2013. http://www.idf.org/diabetesatlas. Accessed 15 Jan 2014
N.J. Morrish, S.L. Wang, L.K. Stevens, J.H. Fuller, H. Keen, Mortality and causes of death in the WHO Multinational Study of Vascular Disease in Diabetes. Diabetologia 44(Suppl. 2), S14–S21 (2001)
R. Donnelly, A.M. Emslie-Smith, I.D. Gardner, A.D. Morris, Vascular compli-cations of diabetes. Brit. Med. J. 320, 1062–1066 (2000)
W.P.T. James, Overweight and obesity (high body mass index), in Comparative Quantification of Health Risks: Global and Regional Burden of Disease Attributable to Selected Major Risk Factors, ed. by Ezzati (World Health Organization, Geneva, 2004), pp. 497–596
B. Ahrén, Incretin dysfunction in type 2 diabetes: clinical impact and future perspectives. Diabetes Metab. 39, 195–201 (2013)
J.J. Holst, The physiology of glucagon-like peptide 1. Physiol. Rev. 87, 1409–1439 (2007)
R. Mentlein, B. Gallwitz, W.E. Schmidt, Dipeptidyl-peptidase IV hydrolyses gastric inhibitory polypeptide, glucagon-like peptide-1(7-36)amide, peptide histidine methionine and is responsible for their degradation in human serum. Eur. J. Biochem. 214, 829–835 (1993)
C.F. Deacon, M.A. Nauck, M. Toft-Nielsen, L. Pridal, B. Willms, J.J. Holst, Both subcutaneously and intravenously administered glucagon-like peptide I are rapidly degraded from the NH2-terminus in type II diabetic patients and in healthy subjects. Diabetes 44, 1126–1131 (1995)
M.A. Nauck, T. Vilsbøll, B. Gallwitz, A. Garber, S. Madsbad, Incretin-based therapies: viewpoints on the way to consensus. Diabetes Care 32(Suppl 2), S223–S231 (2009)
M.J. Davies, R. Kela, K. Khunti, Liraglutide - overview of the preclinical and clinical data and its role in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 13, 207–220 (2011)
J. Seufert, B. Gallwitz, The extra-pancreatic effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists: a focus on the cardiovascular, gastrointestinal and central nervous systems. Diabetes Obes. Metab. (2013). doi: 10.1111/dom.12251
M.H. Muskiet, M.M. Smits, L.M. Morsink, M. Diamant, The gut-renal axis: do incretin-based agents confer renoprotection in diabetes? Nat Rev Nephrol. (2013). doi:10.1038/nrneph.2013.272
R. Ritzel, C. Orskov, J.J. Holst, M.A. Nauck, Pharmacokinetic, insulino-tropic, and glucagonostatic properties of GLP-1 [7-36 amide] after subcutaneous injection in healthy volunteers. Dose–response-relationships. Diabetologia 38, 720–725 (1995)
J.J. Meier, B. Gallwitz, S. Salmen, O. Goetze, J.J. Holst, W.E. Schmidt, M.A. Nauck, Normalization of glucose concentrations and deceleration of gastric emptying after solid meals during intravenous glucagon-like peptide 1 in patients with type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 88, 2719–2725 (2003)
J.J. Meier, GLP-1 receptor agonists for individualized treatment of type 2 dia-betes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 8, 728–742 (2012)
J. Jelsing, N. Vrang, G. Hansen, K. Raun, M. Tang-Christensen, L.B. Knudsen, Liraglutide: Short lived effect on gastric emptying—long lasting effects on body-weight. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 14, 531–538 (2012)
M. Horowitz, A. Flint, K.L. Jones, C. Hindsberger, M.F. Rasmussen, C. Kapitza, S. Doran, T. Jax, M. Zdravkovic, I.M. Chapman, Effect of the once-daily human GLP-1 analogue liraglutide on appetite, energy intake, energy expenditure and gastric emptying in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 97, 258–266 (2012)
D.J. Drucker, J.B. Buse, K. Taylor, D.M. Kendall, M. Trautmann, D. Zhuang, L. Porter, DURATION-1 Study Group, Exenatide once weekly versus twice daily for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: a randomised, open-label, non-inferiority study. Lancet 372(9645), 1240–1250 (2008)
M. Lorenz, C. Pfeiffer, A. Steinsträßer, R.H. Becker, H. Rütten, P. Ruus, M. Horowitz, Effects of lixisenatide once daily on gastric emptying in type 2 diabetes—relationship to postprandial glycemia. Regul. Pept. 185, 1–8 (2013)
S.E. Kanoski, L.E. Rupprecht, S.M. Fortin, B.C. De Jonghe, M.R. Hayes, The role of nausea in food intake and body weight suppression by peripheral GLP-1 receptor agonists, exendin-4 and liraglutide. Neuropharmacology 62, 1916–1927 (2012)
M.E. Lean, R. Carraro, N. Finer, H. Hartvig, M.L. Lindegaard, S. Rössner, L. Van Gaal, A. Astrup, Tolerability of nausea and vomiting and associations with weight loss in a randomized trial of liraglutide in obese, non-diabetic adults. Int J Obes (Lond). (2013). doi:10.1038/ijo.2013.149
K. Niswender, X. Pi-Sunyer, J. Buse, K.H. Jensen, A.D. Toft, D. Russell-Jones, B. Zinman, Weight change with liraglutide and comparator therapies: an analysis of seven phase 3 trials from the liraglutide diabetes development programme. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 15, 42–54 (2013)
H. Linnebjerg, S. Park, P.A. Kothare, M.E. Trautmann, K. Mace, M. Fineman, I. Wilding, M. Nauck, M. Horowitz, Effect of exenatide on gastric empty-ing and relationship to postprandial glycemia in type 2 diabetes. Regul. Pept. 151, 123–129 (2008)
C.F. Deacon, J.J. Holst, Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: comparison, efficacy and safety. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 14, 2047–2058 (2013)
M.A. Nauck, Incretin-based therapies for type 2 diabetes mellitus: properties, functions, and clinical implications. Am. J. Med. 124(1 Suppl), S3–S18 (2011)
M.D. Turton, D. O’Shea, I. Gunn, S.A. Beak, C.M. Edwards, K. Meeran, S.J. Choi, G.M. Taylor, M.M. Heath, P.D. Lambert, J.P. Wilding, D.M. Smith, M.A. Ghatei, J. Herbert, S.R. Bloom, A role for glucagon-like peptide-1 in the central regulation of feeding. Nature 379(6560), 69–72 (1996)
B. Gallwitz, Anorexigenic effects of GLP-1 and its analogues. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 209, 185–207 (2012)
A.J. Kastin, V. Akerstrom, Entry of exendin-4 into brain is rapid but may be limited at high doses. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 27, 313–318 (2003)
M. Punjabi, M. Arnold, N. Geary, W. Langhans, G. Pacheco-López, Peripheral glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and satiation. Physiol. Behav. 105, 71–76 (2011)
K. Hunter, C. Hölscher, Drugs developed to treat diabetes, liraglutide and lixisenatide, cross the blood brain barrier and enhance neurogenesis. BMC Neurosci. 13, 33 (2012)
S.E. Kanoski, S.M. Fortin, M. Arnold, H.J. Grill, M.R. Hayes, Peripheral and central GLP-1 receptor populations mediate the anorectic effects of peripherally administered GLP-1 receptor agonists, liraglutide and exendin-4. Endocrinology 152, 3103–3112 (2011)
A. Stonehouse, B. Walsh, R. Cuddihy, Exenatide once-weekly clinical development: safety and efficacy across a range of background therapies. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 13, 1063–1069 (2011)
D. Russell-Jones, R.M. Cuddihy, M. Hanefeld, A. Kumar, J.G. González, M. Chan, A.M. Wolka, M.K. Boardman, DURATION-4 Study Group, Efficacy and safety of exenatide once weekly versus metformin, pioglitazone, and sitagliptin used as monotherapy in drug-naive patients with type 2 diabetes (DURATION-4): a 26-week double-blind study. Diabetes Care 35, 252–258 (2012)
J.B. Buse, R.R. Henry, J. Han, D.D. Kim, M.S. Fineman, A.D. Baron, Ex-enatide-113 Clinical Study Group, Effects of exenatide (exendin-4) on glyce-mic control over 30 weeks in sulfonylurea-treated patients with type 2 diabe-tes. Diabetes Care 27, 2628–2635 (2004)
R.A. DeFronzo, R.E. Ratner, J. Han, D.D. Kim, M.S. Fineman, A.D. Baron, Effects of exenatide (exendin-4) on glycemic control and weight over 30 weeks in metformin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 28, 1092–1100 (2005)
D.M. Kendall, M.C. Riddle, J. Rosenstock, D. Zhuang, D.D. Kim, M.S. Fineman, A.D. Baron, Effects of exenatide (exendin-4) on glycemic control over 30 weeks in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with metformin and a sul-fonylurea. Diabetes Care 28, 1083–1091 (2005)
J.B. Buse, M. Nauck, T. Forst, W.H. Sheu, S.K. Shenouda, C.R. Heilmann, B.J. Hoogwerf, A. Gao, M.K. Boardman, M. Fineman, L. Porter, G. Schernthaner, Exenatide once weekly versus liraglutide once daily in patients with type 2 diabetes (DURATION-6): a randomised, open-label study. Lancet 381(9861), 117–124 (2013)
L.J. Scott, Lixisenatide: a review of its use in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. BioDrugs 27, 509–523 (2013)
A. Astrup, S. Rossner, L. Van Gaal, A. Rissanen, L. Niskanen, M. Al Hakim, J. Madsen, M.F. Rasmussen, M.E. Lean, NN8022-1807 Study Group, Effects of liraglutide in the treatment of obesity: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Lancet 374, 1606–1616 (2009)
A. Astrup, R. Carraro, N. Finer, A. Harper, M. Kunesova, M.E. Lean, L. Niskanen, M.F. Rasmussen, A. Rissanen, S. Rössner, M.J. Savolainen, L. Van Gaal, NN8022-1807 Investigators, Safety, tolerability and sustained weight loss over 2 years with the once-daily human GLP-1 analog, liraglutide. Int J Obes (Lond) 36, 843–854 (2012)
K. Elkind-Hirsch, O. Marrioneaux, M. Bhushan, D. Vernor, R. Bhushan, Comparison of single and combined treatment with exenatide and metformin on menstrual cyclicity in overweight women with polycystic ovary syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 93, 2670–2678 (2008)
J. Rosenstock, L.J. Klaff, S. Schwartz, J. Northrup, J.H. Holcombe, K. Wilhelm, M. Trautmann, Effects of exenatide and lifestyle modification on body weight and glucose tolerance in obese subjects with and without pre-diabetes. Diabetes Care 33, 1173–1175 (2010)
A.S. Kelly, A.M. Metzig, K.D. Rudser, A.K. Fitch, C.K. Fox, B.M. Nathan, M.M. Deering, B.L. Schwartz, M.J. Abuzzahab, L.M. Gandrud, A. Moran, C.J. Billington, S.J. Schwarzenberg, Exenatide as a weight-loss therapy in extreme pediatric obesity: a randomized, controlled pilot study. Obesity 20, 364–370 (2012)
F. Irie, A.L. Fitzpatrick, O.L. Lopez, L.H. Kuller, R. Peila, A.B. Newman, L.J. Launer, Enhanced risk for Alzheimer disease in persons with type 2 dia-betes and APOE epsilon4: the Cardiovascular Health Study Cognition Study. Arch. Neurol. 65, 89–93 (2008)
J.A. Driver, A. Smith, J.E. Buring, J.M. Gaziano, T. Kurth, G. Logroscino, Prospective cohort study of type 2 diabetes and the risk of Parkinson’s disease. Diabetes Care 31, 2003–2005 (2008)
T. Perry, N.J. Haughey, M.P. Mattson, J.M. Egan, N.H. Greig, Protection and reversal of excitotoxic neuronal damage by glucagon-like peptide-1 and exendin-4. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 302, 881–888 (2002)
T. Perry, D.K. Lahiri, K. Sambamurti, D. Chen, M.P. Mattson, J.M. Egan, N.H. Greig, Glucagon-like peptide-1 decreases endogenous amyloid-β pep-tide (Aβ) levels and protects hippocampal neurons from death induced by Aβ and iron. J. Neurosci. Res. 72, 603–612 (2003)
T. Himeno, H. Kamiya, K. Naruse, N. Harada, N. Ozaki, Y. Seino, T. Shibata, M. Kondo, J. Kato, T. Okawa, A. Fukami, Y. Hamada, N. Inagaki, Y. Seino, D.J. Drucker, Y. Oiso, J. Nakamura, Beneficial effects of exendin-4 on experimental polyneuropathy in diabetic mice. Diabetes 60, 2397–2406 (2011)
W.J. Liu, H.Y. Jin, K.A. Lee, S.H. Xie, H.S. Baek, T.S. Park, Neuroprotec-tive effect of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, synthetic exendin-4, in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 164, 1410–1420 (2011)
W.N. Han, C. Hölscher, L. Yuan, W. Yang, X.H. Wang, M.N. Wu, J.S. Qi, Liraglutide protects against amyloid-β protein-induced impairment of spatial learning and memory in rats. Neurobiol. Aging 34, 576–588 (2013)
H.J. Huang, Y.H. Chen, K.C. Liang, Y.S. Jheng, J.J. Jhao, M.T. Su, G.J. Lee-Chen, H.M. Hsieh-Li, Exendin-4 protected against cognitive dysfunction in hyperglycemic mice receiving an intrahippocampal lipopolysaccharide injection. PLoS One 7(7), e39656 (2012)
C. Hölscher, L. Li, New roles for insulin-like hormones in neuronal signalling and protection: new hopes for novel treatments of Alzheimer’s disease? Neurobiol. Aging 31, 1495–1502 (2010)
A. Hamilton, S. Patterson, D. Porter, V.A. Gault, C. Hölscher, Novel GLP-1 mimetics developed to treat type 2 diabetes promote progenitor cell prolifera-tion in the brain. J. Neurosci. Res. 89, 481–489 (2011)
P.L. McClean, V. Parthsarathy, E. Faivre, C. Hölscher, The diabetes drug li-raglutide prevents degenerative processes in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci. 31, 6587–6594 (2011)
S. Kim, M. Moon, S. Park, Exendin-4 protects dopaminergic neurons by in-hibition of microglial activation and matrix metalloproteinase-3 expression in an animal model of Parkinson’s disease. J. Endocrinol. 202, 431–439 (2009)
Y. Li, T. Perry, M.S. Kindy, B.K. Harvey, D. Tweedie, H.W. Holloway, K. Powers, H. Shen, J.M. Egan, K. Sambamurti, A. Brossi, D.K. Lahiri, M.P. Mattson, B.J. Hoffer, Y. Wang, N.H. Greig, GLP-1 receptor stimulation preserves primary cortical and dopaminergic neurons in cellular and rodent models of stroke and Parkinsonism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106, 1285–1289 (2009)
V. Darsalia, H. Ortsäter, A. Olverling, E. Darlöf, P. Wolbert, T. Nyström, T. Klein, Å. Sjöholm, C. Patrone, The DPP-4 inhibitor linagliptin counteracts stroke in the normal and diabetic mouse brain: a comparison with glimepiride. Diabetes 62, 1289–1296 (2013)
R.P. Shannon, DPP-4 inhibition and neuroprotection: do mechanisms matter? Diabetes 62, 1029–1031 (2013)
R.C. Turner, H. Millns, H.A. Neil, I.M. Stratton, S.E. Manley, D.R. Matthews, R.R. Holman, Risk factors for coronary artery disease in non-insulin de-pendent diabetes mellitus: United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS: 23). BMJ 316, 823–828 (1998)
Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration, S.R. Seshasai, S. Kaptoge, A. Thompson, E. Di Angelantonio, P. Gao, N. Sarwar, P.H. Whincup, K.J. Mukamal, R.F. Gillum, I. Holme, I. Njølstad, A. Fletcher, P. Nilsson, S. Lewington, R. Collins, V. Gudnason, S.G. Thompson, N. Sattar, E. Selvin, F.B. Hu, J. Danesh, Diabetes mellitus, fasting glucose, and risk of cause-specific death. N Engl J Med 364, 829–841 (2011)
ADVANCE Collaborative Group, A. Patel, S. MacMahon, J. Chalmers, B. Neal, L. Billot, M. Woodward, M. Marre, M. Cooper, P. Glasziou, D. Grobbee, P. Hamet, S. Harrap, S. Heller, L. Liu, G. Mancia, C.E. Mogensen, C. Pan, N. Poulter, A. Rodgers, B. Williams, S. Bompoint, B.E. de Galan, R. Joshi, F. Travert, Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 358, 2560–2572 (2008)
Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Study Group, H.C. Gerstein, M.E. Miller, R.P. Byington, D.C. Goff Jr, J.T. Bigger, J.B. Buse, W.C. Cushman, S. Genuth, F. Ismail-Beigi, R.H. Grimm Jr, J.L. Probstfield, D.G. Simons-Morton, W.T. Friedewald, Effects of intensive glucose lowering in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 358, 2545–2559 (2008)
L.A. Nikolaidis, S. Mankad, G.G. Sokos, G. Miske, A. Shah, D. Elahi, R.P. Shannon, Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 in patients with acute myocardial infarction and left ventricular dysfunction after successful reperfusion. Circulation 109, 962–965 (2004)
D.C. Klonoff, J.B. Buse, L.L. Nielsen, X. Guan, C.L. Bowlus, J.H. Holcombe, M.E. Wintle, D.G. Maggs, Exenatide effects on diabetes, obesity, cardiovascular risk factors and hepatic biomarkers in patients with type 2 diabetes treated for at least 3 years. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 24, 275–286 (2008)
T. Forst, G. Michelson, F. Ratter, M.M. Weber, S. Anders, M. Mitry, B. Wilhelm, A. Pfützner, Addition of liraglutide in patients with Type 2 diabetes well controlled on metformin monotherapy improves several markers of vascular function. Diabet. Med. 29, 1115–1118 (2012)
R. Simo, B. Guerci, G. Schernthaner, B. Gallwitz, J. Guzman, F. Dotta, A. Festa, H. Sapin, S. Chen, J. Kiljanski, Long-term administration of ex-enatide and changes in body weight and markers of cardiovascular risk: a comparative study with glimepiride. Diabetologia 55(Suppl. 1), S332 (2012). (Abstract 781)
J. Buse, J. Rosenstock, G. Sesti, W.E. Schmidt, E. Montanya, J.H. Brett, M. Zychma, L. Blonde, LEAD-6 Study Group, Liraglutide once a day versus exenatide twice a day for type 2 diabetes: a 26-week randomised, parallel-group, multinational, open-label trial (LEAD-6). Lancet 374, 39–47 (2009)
M. Monami, V. Vitale, M.L. Ambrosio, N. Bartoli, G. Toffanello, B. Ragghianti, F. Monami, N. Marchionni, E. Mannucci, Effects on lipid profile of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors, pioglitazone, acarbose, and sulfonylureas: meta-analysis of placebo-controlled trials. Adv. Ther. 29, 736–746 (2012)
M. Monami, C. Lamanna, C.M. Desideri, E. Mannucci, DPP-4 inhibitors and lipids: systematic review and meta-analysis. Adv. Ther. 29, 14–25 (2012)
N. Satoh-Asahara, Y. Sasaki, H. Wada, M. Tochiya, A. Iguchi, R. Nakagawachi, S. Odori, S. Kono, K. Hasegawa, A. Shimatsu, A dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, sitagliptin, exerts anti-inflammatory effects in type 2 diabetic patients. Metabolism 62, 347–351 (2013)
B. Gallwitz, J. Guzman, F. Dotta, B. Guerci, R. Simó, B.R. Basson, A. Festa, J. Kiljański, H. Sapin, M. Trautmann, G. Schernthaner, Exenatide twice daily versus glimepiride for prevention of glycaemic deterioration in patients with type 2 diabetes with metformin failure (EUREXA): an open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 379, 2270–2278 (2012)
T. Vilsbøll, M. Christensen, A.E. Junker, F.K. Knop, L.L. Gluud, Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on weight loss: systematic review and meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 344, d7771 (2012)
B. Gallwitz, Glucagon-like peptide-1 analogues for type 2 diabetes mellitus: current and emerging agents. Drugs 71, 1675–1688 (2011)
M. Diamant, L. Van Gaal, S. Stranks, J. Northrup, D. Cao, K. Taylor, M. Trautmann, Once weekly exenatide compared with insulin glargine titrated to target in patients with type 2 diabetes (DURATION-3): an open-label randomised trial. Lancet 375, 2234–2243 (2010)
P. Valensi, S. Chiheb, M. Fysekidis, Insulin- and glucagon-like peptide-1-induced changes in heart rate and vagosympathetic activity: why they matter. Diabetologia 56, 1196–1200 (2013)
D. Nathanson, B. Ullman, U. Löfström, A. Hedman, M. Frick, A. Sjöholm, T. Nyström, Effects of intravenous exenatide in type 2 diabetic patients with congestive heart failure: a double-blind, randomised controlled clinical trial of efficacy and safety. Diabetologia 55, 926–935 (2012)
H. Linnebjerg, M. Seger, P.A. Kothare, T. Hunt, A.M. Wolka, M.I. Mitchell, A thorough QT study to evaluate the effects of single dose exenatide 10 μg on cardiac repolarization in healthy subjects. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 49, 594–604 (2011)
B. Darpö, P. Sager, L. Macconell, B. Cirincione, M. Mitchell, J. Han, W. Huang, J. Malloy, C. Schulteis, L. Shen, L. Porter, Exenatide at therapeutic and supratherapeutic concentrations does not prolong the QTc interval in healthy subjects. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 75, 979–989 (2013)
D.J. Chatterjee, N. Khutoryansky, M. Zdravkovic, C.R. Sprenger, J.S. Litwin, Absence of QTc prolongation in a thorough QT study with subcutaneous liraglutide, a once-daily human GLP-1 analog for treatment of type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 11, 1353–1362 (2009)
A. Sheikh, Direct cardiovascular effects of glucagon like peptide-1. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 5, 47 (2013)
T. Shigeta, M. Aoyama, Y.K. Bando, A. Monji, T. Mitsui, M. Takatsu, X.W. Cheng, T. Okumura, A. Hirashiki, K. Nagata, T. Murohara, Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 modulates left ventricular dysfunction in chronic heart failure via angiogenesis-dependent and -independent actions. Circulation 126, 1838–1851 (2012)
N. Gomez, K. Touihri, V. Matheeussen, A. Mendes Da Costa, M. Mahmoudabady, M. Mathieu, L. Baerts, A. Peace, P. Lybaert, S. Scharpe, I. De Meester, J. Bartunek, M. Vanderheyden, K. Mc Entee, Dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibition improves cardiorenal function in overpacing-induced heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail 14, 14–21 (2012)
H. Yanai, H. Adachi, H. Hamasaki, Y. Masui, R. Yoshikawa, S. Moriyama, S. Mishima, A. Sako, Effects of 6-month sitagliptin treatment on glucose and lipid metabolism, blood pressure, body weight and renal function in type 2 diabetic patients: a chart-based analysis. J. Clin. Med. Res. 4, 251–258 (2012)
S. Ogawa, M. Ishiki, K. Nako, M. Okamura, M. Senda, T. Mori, S. Ito, Sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, decreases systolic blood pressure in Japanese hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 223, 133–135 (2011)
N. Chhabra, Endothelial dysfunction—a predictor of atherosclerosis. Internet J. Med. Updat 4, 33–41 (2009)
A.S. Kelly, R.M. Bergenstal, J.M. Gonzalez-Campoy, H. Katz, A.J. Bank, Effects of exenatide vs. metformin on endothelial function in obese patients with pre-diabetes: a randomized trial. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 11, 64 (2012)
T. Gaspari, H. Liu, I. Welungoda, Y. Hu, R.E. Widdop, L.B. Knudsen, R.W. Simpson, A.E. Dear, A GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide inhibits endothelial cell dysfunction and vascular adhesion molecule expression in an Ap-oE−/− mouse model. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 8, 117–124 (2011)
A. Shiraki, J. Oyama, H. Komoda, M. Asaka, A. Komatsu, M. Sakuma, K. Kodama, Y. Sakamoto, N. Kotooka, T. Hirase, K. Node, The glucagon-like peptide 1 analog liraglutide reduces TNF-α-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis 221, 375–382 (2012)
Ö. Erdogdu, L. Eriksson, T. Nyström, Å. Sjöholm, Q. Zhang, Exendin-4 restores glucolipotoxicity-induced gene expression in human coronary artery endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 419, 790–795 (2012)
L. Han, Y. Yu, X. Sun, B. Wang, Exendin-4 directly improves endothelial dysfunction in isolated aortas from obese rats through the cAMP or AMPK-eNOS pathways. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 97, 453–460 (2012)
C. Irace, S. De Luca, E. Shehaj, C. Carallo, A. Loprete, F. Scavelli, A. Gnasso, Exenatide improves endothelial function assessed by flow mediated dilation technique in subjects with type 2 diabetes: results from an observational research. Diab. Vasc. Dis. Res. 10, 72–77 (2013)
R.W. Simpson, T. Gaspari, I. Welungoda, R.E. Widdop, L.B. Knudsen, A.E. Dear, The GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide attenuates atherosclerotic lesion development and potentially enhances plaque stability in an ApoE−/− mouse model. Diabetes 61(Suppl 1), A486 (2012). (Abstract 1896-P)
M. Rizzo, A. Maria Patti, V. Di Bartolo, R. Vincenza Giglio, G. Montalto, A.A. Rizvi, Effect of liraglutide on carotid intima-media thickness in patients with type-2 diabetes: a 4-month prospective study. Diabetes 61(Suppl 1), A109 (2012). (Abstract 418-P)
M.H. Noyan-Ashraf, M.A. Momen, K. Ban, A.M. Sadi, Y.Q. Zhou, A.M. Riazi, L.L. Baggio, R.M. Henkelman, M. Husain, D.J. Drucker, GLP-1R agonist liraglutide activates cytoprotective pathways and improves outcomes after experimental myocardial infarction in mice. Diabetes 58, 975–983 (2009)
L. Timmers, J.P. Henriques, D.P. de Kleijn, J.H. Devries, H. Kemperman, P. Steendijk, C.W. Verlaan, M. Kerver, J.J. Piek, P.A. Doevendans, G. Pasterkamp, I.E. Hoefer, Exenatide reduces infarct size and improves cardiac function in a porcine model of ischemia and reperfusion injury. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 53, 501–510 (2009)
W. Bao, K. Aravindhan, H. Alsaid, T. Chendrimada, M. Szapacs, D.R. Citerone, M.R. Harpel, R.N. Willette, J.J. Lepore, B.M. Jucker, Albiglutide, a long lasting glucagon-like peptide-1 analog, protects the rat heart against is-chemia/reperfusion injury: evidence for improving cardiac metabolic efficiency. PLoS One 6, e23570 (2011)
P. Wohlfart, W. Linz, T. Hübschle, D. Linz, J. Huber, S. Hess, D. Crowther, U. Werner, H. Ruetten, Cardioprotective effects of lixisenatide in rat myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury studies. J. Transl. Med. 11, 84 (2013)
J.R. Ussher, D.J. Drucker, Cardiovascular biology of the incretin system. Endocr. Rev. 33, 187–215 (2012)
J. Lønborg, H. Kelbæk, N. Vejlstrup, H.E. Bøtker, W.Y. Kim, L. Holmvang, E. Jørgensen, S. Helqvist, K. Saunamäki, C.J. Terkelsen, M.M. Schoos, L. Køber, P. Clemmensen, M. Treiman, T. Engstrøm, Exenatide reduces final infarct size in patients with ST-segment-elevation myocardial infarction and short-duration of ischemia. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 5, 288–295 (2012)
J. Lønborg, N. Vejlstrup, H. Kelbæk, H.E. Bøtker, W.Y. Kim, A.B. Mathiasen, E. Jørgensen, S. Helqvist, K. Saunamäki, P. Clemmensen, L. Holmvang, L. Thuesen, L.R. Krusell, J.S. Jensen, L. Køber, M. Treiman, J.J. Holst, T. Engstrøm, Exenatide reduces reperfusion injury in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Eur. Heart J. 33, 1491–1499 (2012)
F.J. Bernink, L. Timmers, M. Diamant, M. Scholte, A.M. Beek, O. Kamp, K.M. Marques, R.N. Denham, W.J. Chen, P.A. Doevendans, A.C. van Rossum, N. van Royen, A.J. Horrevoets, Y. Appelman, Effect of additional treatment with EXenatide in patients with an acute myocardial infarction: the EXAMI study. Int. J. Cardiol. 167, 289–290 (2013)
P.A. Read, F.Z. Khan, P.M. Heck, S.P. Hoole, D.P. Dutka, DPP-4 inhibition by sitagliptin improves the myocardial response to dobutamine stress and mitigates stunning in a pilot study of patients with coronary artery disease/clinical perspective. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging. 3, 195–201 (2010)
H.D. Theiss, C. Brenner, M.G. Engelmann, M.M. Zaruba, B. Huber, V. Henschel, U. Mansmann, B. Wintersperger, M. Reiser, G. Steinbeck, W.M. Franz, Safety and efficacy of SITAgliptin plus GRanulocyte-colony-stimulating factor in patients suffering from acute myocardial infarction (SITAGRAMI-Trial)–rationale, design and first interim analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. 145, 282–284 (2010)
S.P. Marso, J.B. Lindsey, J.M. Stolker, J.A. House, G. Martinez Ravn, K.F. Kennedy, T.M. Jensen, J.B. Buse, Cardiovascular safety of liraglutide assessed in a patient-level pooled analysis of phase 2: 3 liraglutide clinical development studies. Diab. Vasc. Dis. Res. 8, 237–240 (2011)
S.P. Marso, N.R. Poulter, S.E. Nissen, M.A. Nauck, B. Zinman, G.H. Daniels, S. Pocock, W.M. Steinberg, R.M. Bergenstal, J.F. Mann, L.S. Ravn, K.B. Frandsen, A.C. Moses, J.B. Buse, Liraglutide effect and action in diabetes: evaluation of cardiovascular outcome and results (LEADER) trial design and methods. Am. Heart J. 166, 823–830 (2013)
M. Monami, I. Dicembrini, D. Martelli, E. Mannucci, Safety of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 27(Suppl 3), 57–64 (2011)
M. Monami, I. Dicembrini, C. Nardini, I. Fiordelli, E. Mannucci, Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on cardiovascular risk: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 39–47, 109 (2014)
W.B. White, C.P. Cannon, S.R. Heller, Alogliptin after acute coronary syndrome in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl. J. Med. 369, 1327–1335 (2013)
B.M. Scirica, D.L. Bhatt, E. Braunwald, Saxagliptin and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. M N Engl J Med 369, 1317–1326 (2013)
M.E. Cobble, R. Frederich, Saxagliptin for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: assessing cardiovascular data. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 11, 6 (2012)
W.B. White, R. Pratley, P. Fleck, M. Munsaka, M. Hisada, C. Wilson, V. Me-non, Cardiovascular safety of the dipetidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor alogliptin in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 15, 668–673 (2013)
N. Mikhail, Effects of incretin-based therapy in patients with heart failure and myocardial infarction. Endocrine. (2014) [Epub ahead of print]
R. Retnakaran, C.A. Cull, K.I. Thorne, A.I. Adler, R.R. Holman, UKPDS Study Group, Risk factors for renal dysfunction in type 2 diabetes: U.K. Prospective Diabetes Study 74. Diabetes 55, 1832–1839 (2006)
J.A. Davidson, J. Brett, A. Falahati, D. Scott, Mild renal impairment has no effect on the efficacy and safety of liraglutide. Endocr. Pract. 6, 1–31 (2010)
W.J. Weise, M.S. Sivanandy, C.A. Block, R.J. Comi, Exenatide-associated ischemic renal failure. Diabetes Care 32, e22–e23 (2009)
B. Kuehn, Exenatide and kidney function. JAMA 302, 2644 (2009)
C.B. Giorda, E. Nada, B. Tartaglino, Pharmacokinetics, safety, and efficacy of DPP-4 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and renal or hepatic impairment. A systematic review of the literature. Endocrine. (2014) [Epub ahead of print]
A.E. Butler, M. Campbell-Thompson, T. Gurlo, D.W. Dawson, M. Atkin-son, P.C. Butler, Marked expansion of exocrine and endocrine pancreas with incretin therapy in humans with increased exocrine pancreas dysplasia and the potential for glucagon-producing neuroendocrine tumors. Diabetes 62, 2595–2604 (2013)
EMA statement Investigation into GLP-1-based diabetes therapies con-cluded. http://www.ema.europa.eu/ema/index.jsp?curl=pages/news_and_events/news/2013/07/news_detail_001856.jsp&mid=WC0b01ac058004d5c1. Accessed 13 Sept 2013
NIDDK-NCI Workshop on Pancreatitis-Diabetes-Pancreatic Cancer. http://www2.niddk.nih.gov/News/Calendar/PDPC2013.htm. Accessed 13 Sept 2013
S.E. Kahn, Incretin therapy and islet pathology—a time for caution. Diabetes 62, 2178–2180 (2013)
S. Bonner-Weir, P. In’t Veld, G. Weir, Re-analysis of study of pancre-atic effects of incretin therapy: Methodological deficiencies. Diabetes Obes. Metab. (2014). doi:10.1111/dom.12257
A.J. Williams, S.L. Thrower, I.M. Sequeiros, A. Ward, A.S. Bickerton, J.M. Triay, M.P. Callaway, C.M. Dayan, Pancreatic volume is reduced in adult patients with recently diagnosed type 1 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 97, E2109–E2113 (2012)
A.J. Williams, W. Chau, M.P. Callaway, C.M. Dayan, Magnetic resonance imaging: a reliable method for measuring pancreatic volume in type 1 diabetes. Diabet. Med. 24, 35–40 (2007)
S.S. Engel, E. Round, G.T. Golm, K.D. Kaufman, B.J. Goldstein, Safety and tolerability of sitagliptin in type 2 diabetes: pooled analysis of 25 clinical studies. Diabetes Ther. 4, 119–145 (2013)
C. Alves, F. Batel-Marques, A.F. Macedo, A meta-analysis of serious adverse events reported with exenatide and liraglutide: acute pancreatitis and cancer. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 98, 271–284 (2012)
D.D. Dore, J.D. Seegerac, K.A. Chanac, Use of a claims-based active drug safety surveillance system to assess the risk of acute pancreatitis with exenatide or sitagliptin compared to metformin or glyburide. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 25, 1019–1102 (2009)
E. Garg, W. Chen, M. Pendergrass, Acute pancreatitis in type 2 diabetes treated with exenatide or sitagliptin. A retrospective observational pharmacy claims analysis. Diabetes Care 33, 2349–2354 (2010)
M. Wenten, J.A. Gaebler, M. Hussein, E.M. Pelletier, D.B. Smith, P. Girase, R.A. Noel, D.K. Braun, G.L. Bloomgren, Relative risk of acute pancreatitis in initiators of exenatide twice daily compared with other anti-diabetic medication: a follow-up study. Diabet. Med. 29, 1412–1418 (2012)
Conflict of interests
The author has attended Advisory Boards for AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly & Co, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Roche, Merck & Co; has received Research Support from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly & Co, Novartis, Novo Nordisk; has attended Speaker’s Bureaux for AstraZeneca, Berlin Chemie AG, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly & Co, Merck & Co, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Roche, Sanofi, and Takeda.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gallwitz, B. Extra-pancreatic effects of incretin-based therapies. Endocrine 47, 360–371 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-014-0223-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-014-0223-0