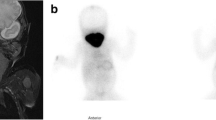
Abstract
Mutations in the thyroglobulin (TG) gene have been reported to cause congenital hypothyroidism (CH) and we have been investigating the genetic architecture of CH in a large cohort of consanguineous/multi-case families. Our aim in this study was to determine the genetic basis of CH in four affected individuals coming from two separate consanguineous families. Since CH is usually inherited in autosomal recessive manner in consanguineous/multi-case families, we adopted a two-stage strategy of genetic linkage studies and targeted sequencing of the TG gene. First we investigated the potential genetic linkage of families to any known CH locus using microsatellite markers and then determined the pathogenic mutations in linked-genes by Sanger sequencing. Both families showed potential linkage to TG locus and we detected two previously unreported nonsense TG mutations (p.Q630X and p.W637X) that segregated with the disease status in both families. This study highlights the importance of molecular genetic studies in the definitive diagnosis and classification of CH, and also adds up to the limited number of nonsense TG mutations in the literature. It also suggests a new clinical testing strategy using next-generation sequencing in all primary CH cases.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Medeiros-Neto, M. Knobel, L.J. DeGroot, Genetic disorders of the thyroid hormone system, in Genetics in Endocrinology, ed. by J.D. Baxter (Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, 2002), pp. 375–402
M. Caputo, C.M. Rivolta, S.A. Esperante et al., Congenital hypothyroidism with goitre caused by new mutations in the thyroglobulin gene. Clin. Endocrinol. 67, 35–351 (2007)
L. Lamas, P.C. Anderson, J.W. Fox et al., Consensus sequences for early iodination and hormonogenesis in human thyroglobulin. J. Biol. Chem. 264, 13541–13545 (1989)
J.T. Dunn, A.D. Dunn, Thyroglobulin chemistry, biosynthesis proteolysis, in Werner and Ingbar’s The Thyroid: A Fundamental and Clinical Text, ed. by L.E. Braverman, R. Utiger (Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, 2000), pp. 91–104
G. Medeiros-Neto, H.M. Targovnik, G. Vassart, Defective thyroglobulin synthesis and secretion causing goiter and hypothyroidism. Endocr. Rev. 14, 165–183 (1993)
H.M. Targovnik, S.A. Esperante, C.M. Rivolta, Genetics and phenomics of hypothyroidism and goiter due to thyroglobulin mutations. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 322, 44–55 (2010)
F.M. Mendive, C.M. Rivolta, C.M. Moya, Genomic organization of the human thyroglobulin gene: the complete intron–exon structure. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 145, 485–496 (2001)
J. Corral, C. Martín, R. Pe’rez et al., Thyroglobulin gene point mutation associated with non-endemic simple goitre. Lancet 341, 462–464 (1993)
C. Pe’rez-Centeno, R. Gonza’lez-Sarmiento, M.T. Mories et al., Thyroglobulin exon 10 gene point mutation in a patient with endemic goiter. Thyroid 6, 423–427 (1996)
A.S. Alzahrani, E.Y. Baitei, M. Zou et al., Metastatic follicular thyroid carcinoma arising from congenital goiter as a result of a novel splice donor site mutation in the thyroglobulin gene. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 91, 740–746 (2006)
A. Hishinuma, S. Fukata, K. Kakudo et al., High incidence of thyroid cancer in long-standing goiters with thyroglobulin mutations. Thyroid 15, 1079–1084 (2005)
A. Hishinuma, S. Fukata, S. Nishiyama et al., Haplotype analysis reveals founder effects of thyroglobulin gene mutations C1058R and C1977S in Japan. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 91, 3100–3104 (2006)
Y. Ban, D.A. Greenberg, E. Concepcion et al., Amino acid substitutions in the thyroglobulin gene are associated with susceptibility to human and murine autoimmune thyroid disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 15119–15124 (2003)
S.A. van de Graaf, M. Cammenga, N.J. Ponne et al., The screening for mutations in the thyroglobulin cDNAfrom six patients with congenital hypothyroidism. Biochimie (Paris) 81, 425–432 (1999)
H. Cangul, N.V. Morgan, J.R. Forman et al., Novel TSHR mutations in consanguineous families with congenital non-goitrous hypothyroidism. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf) 73, 671–677 (2010)
H. Cangul, Z. Aycan, H. Saglam et al., TSHR is the main causative-locus in autosomal recessively inherited thyroid dysgenesis. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metabol. 25, 419–426 (2012)
V.N. Baş, H. Cangül, S.Y. Ağladıoğlu et al., Mild and severe congenital primary hypothyroidism in two patients by thyrotropine receptor (TSHR) gene mutation. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metabol. 25, 1153–1156 (2012)
Cangul, H., Aycan, Z., Olivera-Nappa, A., et al.: Thyroid dyshormonogenesis is primarily caused by TPO mutations in consanguineous community. Clin. Endocrinol. (2012). doi:10.1111/cen.12127
S.A.R. van de Graaf, C. Ris-Stalpers, G.J.M. Veenboer et al., A premature stopcodon in thyroglobulin mRNA results in familial goiter and moderate hypothyroidism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 84, 2537–2542 (1999)
D.M. Niu, J.H. Hsu, K.W. Chong et al., Six new mutations of the thyroglobulin gene discovered in Taiwanese children presenting with thyroid dyshormonogenesis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 94, 5045–5052 (2009)
H.M. Targovnik, G. Medeiros-Neto, V.P. Varela et al., A nonsense mutation causes human hereditary congenital goiter with preferential production of a 171-nucleotide-deleted thyroglobulin ribonucleic acid messenger. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 77, 210–215 (1993)
C.E. Citterio, G.A. Machiavelli, M.B. Miras et al., New insights into thyroglobulin gene: molecular analysis of seven novel mutations associated with goiter and hypothyroidism. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 365(2), 277–291 (2013)
V. Pardo, J. Vono-Toniolo, I.G. Rubio et al., The p.A2215D thyroglobulin gene mutation leads to deficient synthesis and secretion of the mutated protein and congenital hypothyroidism with wide phenotype variation. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 94, 2938–2944 (2009)
G.A. Machiavelli, M. Caputo, C.M. Rivolta et al., Molecular analysis of congenital goitres with hypothyroidism caused by defective thyroglobulin synthesis. Identification of a novel c. 7006C>T [p. R2317X] mutation and expression of minigenes containing nonsense mutations in exon 7. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 72, 112–121 (2010)
M.H. Ricketts, M.J. Simons, J. Parma et al., A nonsense mutation causes hereditary goitre in the Afrikander cattle and unmasks alternative splicing of thyroglobulin transcripts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84, 3181–3184 (1987)
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by European Union under its Framework 7 programme, FP7-PEOPLE-2009-Marie Curie-IEF, and by Queen Elisabeth Hospital Birmingham Foundation Trust. We also thank the families for their participation in this study.
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cangul, H., Boelaert, K., Dogan, M. et al. Novel truncating thyroglobulin gene mutations associated with congenital hypothyroidism. Endocrine 45, 206–212 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-013-0027-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-013-0027-7