Abstract
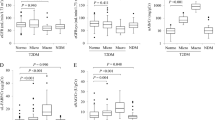
The purpose of this study was to investigate the prevalence of tubular damage in short-term (less than five years) type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients and to explore the correlation between tubular markers and their relationship with renal indices at different stages of diabetic nephropathy. A group of 101 short-term T2DM patients and 28 control subjects were recruited. Tubular markers, such as neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL), N-acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase (NAG), and kidney injury molecule 1 (KIM-1), as well as urinary albumin excretion were measured in voided urine. Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) was estimated via Macisaac’s formula. The patients were further categorized into three groups, namely, the normoalbuminuria, microalbuminuria, and macroalbuminuria groups, according to their urine albumin/creatinine ratio (UACR). Urinary tubular markers were compared and their correlations with renal indices [UACR and estimated GFR (eGFR)] were analyzed among the different diabetic groups. Compared with the control group, Urinary NGAL [median (IQR)][83.6(41.4−138.7) μg/gcr vs. 32.9(26.1−64.5) μg/gcr], NAG [13.5(8.7−17.9) U/gcr vs. 7.6(6.5−13.0) U/gcr] and KIM-1 [120.0(98.4−139.9) ng/gcr vs. 103.1(86.8−106.2) ng/gcr] in the T2DM were all markedly increased. For all patients, urinary NGAL had stronger positive correlations with UACR than NAG (R = 0.556 vs. 0.305, both P < 0.05). In addition, only urinary NGAL showed a negative correlation with eGFR (R = −0.215, P < 0.05). Urinary KIM-1, however, showed no significant difference among the three T2DM groups and did not correlate with either UACR or eGFR. As UACR increased from the normoalbuminuria to the last macroalbuminuria group, all of the markers increased. However, only the concentrations of NGAL were statistically different among the three diabetic groups. The correlation between the tubular markers and their relationships with the renal indices differed markedly among the three T2DM groups. In conclusion, these results suggest that tubular damage is common in short-term T2DM patients. Urinary NGAL may be a promising early marker for monitoring renal impairment in short-term T2DM patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Krolewski, P.W. Eggers, J.H. Warram, Magnitude of end-stage renal disease in IDDM: a 35 year follow-up study. Kidney Int. 50, 2041–2046 (1996)
M. Bojestig, H.J. Arnqvist, G. Hermansson et al., Declining incidence of nephropathy in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 330, 15–18 (1994)
P.A. Sarafidis, P.C. Stafylas, P.I. Georgianos et al., Effect of thiazolidinediones on albuminuria and proteinuria in diabetes: a meta-analysis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 55, 835–847 (2010)
J.L. Gross, M.J. de Azevedo, S.P. Silveiro et al., Diabetic nephropathy: diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. Diabetes Care 28, 164–176 (2005)
V.S. Vaidya, M.A. Niewczas, L.H. Ficociello et al., Regression of microalbuminuria in type 1 diabetes is associated with lower levels of urinary tubular injury biomarkers, kidney injury molecule-1, and N-acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase. Kidney Int. 79, 464–470 (2011)
G. Jerums, S. Panagiotopoulos, E. Premaratne et al., Integrating albuminuria and GFR in the assessment of diabetic nephropathy. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 5, 397–406 (2009)
A. Phillips, U. Janssen, J. Floege, Progression of diabetic nephropathy, Insights from cell culture studies and animal models. Kidney Blood Press Res. 22, 81–97 (1999)
R.E. Gilbert, M.E. Cooper, The tubulointerstitium in progressive diabetic kidney disease: more than an aftermath of glomerular injury? Kidney Int. 56, 1627–1637 (1999)
M. von Eynatten, M. Baumann, U. Heemann et al., Urinary L-FABP and anaemia: distinct roles of urinary markers in type diabetes. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 40, 95–102 (2010)
S.E. Nielsen, T. Sugaya, L. Tarnow et al., Tubular and glomerular injury in diabetes and the impact of ACE inhibition. Diabetes Care 32, 1684–1688 (2009)
K. Damman, D.J. Van Veldhuisen, G. Navis et al., Tubular damage in chronic systolic heart failure is associated with reduced survival independent of glomerular filtration rate. Heart 96, 1297–1302 (2010)
D. Bolignano, V. Donato, G. Coppolino et al., Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a marker of kidney damage. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 52, 595–605 (2008)
J. Mishra, Q. Ma, C. Kelly et al., Kidney NGAL is a novel early marker of acute injury following transplantation. Pediatr. Nephrol. 21, 856–863 (2006)
C. Bazzi, C. Petrini, V. Rizza et al., Urinary N-acetyl-beta-glucosaminidase excretion is a marker of tubular cell dysfunction and a predictor of outcome in primary glomerulonephritis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 17, 1890–1896 (2002)
O. Liangos, M.C. Perianayagam, V.S. Vaidya et al., Urinary N-acetyl-beta-(d)- glucosaminidase activity and kidney injury molecule-1 level are associated with adverse outcomes in acute renal failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 18, 904–912 (2007)
H.K. Kang, D.K. Kim, B.H. Lee et al., Urinary N-acetyl-beta-d-glucosaminidase and malondialdehyde as a markers of renal damage in burned patients. J. Korean Med. Sci. 16, 598–602 (2001)
F. Waanders, M.M. van Timmeren, C.A. Stegeman et al., Kidney injury molecule-1 in renal disease. J. Pathol. 220, 7–16 (2010)
T. Ichimura, J.V. Bonventre, V. Bailly et al., Kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), a putative epithelial cell adhesion molecule containing a novel immunoglobulin domain, is up-regulated in renal cells after injury. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 4135–4142 (1998)
T. Ichimura, C.C. Hung, S.A. Yang et al., Kidney injury molecule-1: a tissue and urinary biomarker for nephrotoxicant-induced renal injury. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 286, F552–F563 (2004)
E.W. Kuehn, K.M. Park, S. Somlo et al., Kidney injury molecule-1 expression in murine polycystic kidney disease. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 283, F1326–F1336 (2002)
V.S. Vaidya, V. Ramirez, T. Ichimura et al., Urinary kidney injury molecule-1: a sensitive quantitative biomarker for early detection of kidney tubular injury. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 290(2), F517–F529 (2006)
J. Surendar, S. Anuradha, B. Ashley et al., Cystatin C and cystatin glomerular filtration rate as markers of early renal disease in Asian Indian subjects with glucose intolerance (CURES-32). Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 7, 419–425 (2009)
R.J. Macisaac, C. Tsalamandris, M.C. Thomas et al., Estimating glomerular filtration rate in diabetes: a comparison of cystatin-C- and creatinine-based methods. Diabetologia 49, 1686–1689 (2006)
E. Brocco, P. Fioretto, M. Mauer et al., Renal structure and function in non-insulin dependent diabetic patients with microalbuminuria. Kidney Int. 63, S40–S44 (1997)
M. Dalla, Vestra, A. Saller, E. Bortoloso et al., Structural involvement in type 1 and type 2 diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes. Metab. 26(Suppl), 8–14 (2000)
Y. Yu, H. Jin, D. Holder et al., Biomarkers of kidney tubule injury: urinary trefoil factor 3 and albumin. Nat. Biotechnol. 28, 470–477 (2010)
L.M. Russo, R.M. Sandoval, S.B. Campos et al., Impaired tubular uptake explains albuminuria in early diabetic nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 20, 489–494 (2009)
Y.C. Ma, L. Zuo, J.H. Chen et al., Modified glomerular filtration rate estimating equation for Chinese patients with chronic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 17, 2937–2944 (2006)
P. Devarajan, Emerging urinary biomarkers in the diagnosis of acute kidney injury. Expert. Opin. Med. Diagn. 2(4), 387–398 (2008)
S.E. Nielsen, K.J. Schjoedt, A.S. Astrup et al., Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) and kidney injury molecule 1 (KIM1) in patients with diabetic nephropathy: a cross-sectional study and the effects of lisinopril. Diabet. Med. 27, 1144–1150 (2010)
S.E. Nielsen, S. Andersen, D. Zdunek et al., Tubular markers do not predict the decline in glomerular filtration rate in type 1 diabetic patients with overt nephropathy. Kidney Int. 79, 1113–1118 (2011)
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the funds from the Scientific and Technological Projects of Dongguan city (200910515000104), Guangdong province, china, P. R.
Conflict of interest
Nothing to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Shi-long Xiong and Wen-jin Fu contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, Wj., Xiong, Sl., Fang, Yg. et al. Urinary tubular biomarkers in short-term type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: a cross-sectional study. Endocrine 41, 82–88 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-011-9509-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-011-9509-7