Abstract
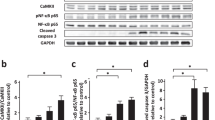
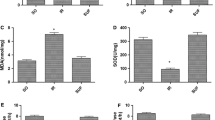
The goals of this study were to investigate the effects of lipid emulsion (LE) on apoptosis induced by a toxic dose of verapamil in H9c2 cells and to elucidate the associated cellular mechanism. The effects of LE alone and combined with an inhibitor on the decreases in cell counts and viability induced by verapamil and diltiazem were examined using the MTT assay. The effects of verapamil alone, combined LE and verapamil treatment, and combined inhibitor, LE and verapamil treatment on cleaved caspase-3, caspase-8 and Bax expression, were examined using Western blotting. The effects of verapamil alone and combined with LE on the number of TUNEL-positive H9c2 cells were also examined. LE attenuated the decreases in cell counts and viability induced by verapamil and diltiazem. However, the magnitude of the LE-mediated attenuation of decreased cell viability was enhanced by verapamil compared with diltiazem treatment. Naloxone, naltrindole hydrochloride, LY294002 and MK-2206 inhibited the LE-mediated attenuation of increased cleaved caspase-3 and caspase-8 expression induced by verapamil. LE attenuated the increase in the number of TUNEL-positive cell induced by verapamil. These results suggest that LE attenuates apoptosis induced by verapamil via activation of the delta-opioid receptor, phosphoinositide 3-kinase and Akt.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weinberg, G. L. (2012). Lipid emulsion infusion: resuscitation for local anesthetic and other drug overdose. Anesthesiology, 117, 180–187.
Cao, D., Heard, K., Foran, M., & Koyfman, A. (2015). Intravenous lipid emulsion in the emergency department: A systematic review of recent literature. Journal of Emergency Medicine, 48, 387–397.
Fettiplace, M. R., & Weinberg, G. (2015). Past, present, and future of lipid resuscitation therapy. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition, 39(1 Suppl), 72S–83S.
St-Onge, M., Dubé, P. A., Gosselin, S., Guimont, C., Godwin, J., Archambault, P. M., et al. (2014). Treatment for calcium channel blocker poisoning: A systematic review. Clinical Toxicology (Phila), 52, 926–944.
Presley, J. D., & Chyka, P. A. (2013). Intravenous lipid emulsion to reverse acute drug toxicity in pediatric patients. Annals of Pharmacotherapy, 47, 735–743.
Ok, S. H., Yu, J., Lee, Y., Cho, H., Shin, I. W., & Sohn, J. T. (2016). Lipid emulsion attenuates apoptosis induced by a toxic dose of bupivacaine in H9c2 rat cardiomyoblast cells. Human and Experimental Toxicology, 35, 929–937.
Pang, D. C., & Sperelakis, N. (1984). Uptake of calcium antagonistic drugs into muscles as related to their lipid solubilities. Biochemical Pharmacology, 33, 821–826.
Pang, D. C., & Sperelakis, N. (1983). Nifedipine, diltiazem, bepridil and verapamil uptakes into cardiac and smooth muscles. European Journal of Pharmacology, 87, 199–207.
Kryshtal, D. O., Dawling, S., Seger, D., & Knollmann, B. C. (2016). In vitro studies indicate intravenous lipid emulsion acts as lipid sink in verapamil poisoning. Journal of Medical Toxicology, 12, 165–171.
French, D., Armenian, P., Ruan, W., Wong, A., Drasner, K., Olson, K. R., et al. (2011). Serum verapamil concentrations before and after Intralipid® therapy during treatment of an overdose. Clinical Toxicology (Phila), 49, 340–344.
Partownavid, P., Sharma, S., Li, J., Umar, S., Rahman, S., & Eghbali, M. (2015). Involvement of opioid receptors in the lipid rescue of bupivacaine-induced cardiotoxicity. Anesthesia and Analgesia, 121, 340–347.
Rahman, S., Li, J., Bopassa, J. C., Umar, S., Iorga, A., Partownavid, P., et al. (2011). Phosphorylation of GSK-3β mediates intralipid-induced cardioprotection against ischemia/reperfusion injury. Anesthesiology, 115, 242–253.
Lv, D., Bai, Z., Yang, L., Li, X., & Chen, X. (2016). Lipid emulsion reverses bupivacaine-induced apoptosis of h9c2 cardiomyocytes: PI3 K/Akt/GSK-3β signaling pathway. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 42, 85–91.
Anderson, P., Bondesson, U., Sylvén, C., & Aström, H. (1982). Plasma concentration–response relationship of verapamil in the treatment of angina pectoris. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology, 4, 609–614.
Zhu, L., Gao, J., Wang, Y., Zhao, X. N., & Zhang, Z. X. (1997). Neuron degeneration induced by verapamil and attenuated by EGb761. Journal of Basic and Clinical Physiology and Pharmacology, 8, 301–314.
Pang, D. B., & Hong, J. (2010). [Ca2+]i homeostasis and caspase-3 gene expression in verapamil-induced retinal pigment epithelium cells apoptosis in vitro. International Journal of Ophthalmology, 3, 288–290.
Chaube, S. K., Dubey, P. K., Mishra, S. K., & Shrivastav, T. G. (2007). Verapamil reversibly inhibits spontaneous parthenogenetic activation in aged rat eggs cultured in vitro. Cloning and Stem Cells, 9, 608–617.
Vilpo, J., Koski, T., & Vilpo, L. (2000). Calcium antagonists potentiate P-glycoprotein-independent anticancer drugs in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells in vitro. Haematologica, 85, 806–813.
Mangiardi, L. M., Hariman, R. J., McAllister, R. G., Jr., Bhargava, V., Surawicz, B., & Shabetai, R. (1978). Electrophysiologic and hemodynamic effects of verapamin. Correlation with plasma drug concentrations. Circulation, 57, 366–372.
Kline, J. A., Tomaszewski, C. A., Schroeder, J. D., & Raymond, R. M. (1993). Insulin is a superior antidote for cardiovascular toxicity induced by verapamil in the anesthetized canine. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 267, 744–750.
Baines, C. P. (2011). How and when do myocytes die during ischemia and reperfusion: The late phase. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 16, 239–243.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72, 248–254.
Liang, C. W., Diamond, S. J., & Hagg, D. S. (2011). Lipid rescue of massive verapamil overdose: A case report. Journal of Medical Case Reports, 5, 399.
Young, A. C., Velez, L. I., & Kleinschmidt, K. C. (2009). Intravenous fat emulsion therapy for intentional sustained-release verapamil overdose. Resuscitation, 80, 591–593.
Montiel, V., Gougnard, T., & Hantson, P. (2011). Diltiazem poisoning treated with hyperinsulinemic euglycemia therapy and intravenous lipid emulsion. European Journal of Emergency Medicine, 18, 121–123.
Oerlemans, M. I., Koudstaal, S., Chamuleau, S. A., de Kleijn, D. P., Doevendans, P. A., & Sluijter, J. P. (2013). Targeting cell death in the reperfused heart: Pharmacological approaches for cardioprotection. International Journal of Cardiology, 165, 410–422.
Maslov, L. N., Lishmanov, Iu B, Headrick, J. P., Pei, J., Hanus, L., Krylatov, A. V., et al. (2012). Perspective of creation of drugs on basis of opioids increasing cardiac tolerance to pathogenic impact of ischemia reperfusion. Eksperimentalnaia I Klinicheskaia Farmakologiia, 75, 22–28.
Shen, H., Ben, Q., Zhang, Y., Jiang, G., Yao, C., Shi, D., et al. (2012). Role of δ2 opioid receptor in cardioprotection against hypoxia-reoxygenation injury. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology, 60, 253–261.
Tong, G., Sun, Z., Wei, X., Gu, C., Kaye, A. D., Wang, Y., et al. (2011). U50,488H postconditioning reduces apoptosis after myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Life Sciences, 88, 31–38.
Schultz, J. E., & Gross, G. J. (2011). Opioids and cardioprotection. Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 89, 123–137.
Partownavid, P., Umar, S., Li, J., Rahman, S., & Eghbali, M. (2012). Fatty-acid oxidation and calcium homeostasis are involved in the rescue of bupivacaine-induced cardiotoxicity by lipid emulsion in rats. Critical Care Medicine, 40, 2431–2437.
Fettiplace, M. R., Ripper, R., Lis, K., Lin, B., Lang, J., Zider, B., et al. (2013). Rapid cardiotonic effects of lipid emulsion infusion. Critical Care Medicine, 41, e156–e162.
Fettiplace, M. R., Lis, K., Ripper, R., Kowal, K., Pichurko, A., Vitello, D., et al. (2015). Multi-modal contributions to detoxification of acute pharmacotoxicity by a triglyceride micro-emulsion. Journal of Controlled Release, 198, 62–70.
Kline, J. A., Leonova, E., Williams, T. C., Schroeder, J. D., & Watts, J. A. (1996). Myocardial metabolism during graded intraportal verapamil infusion in awake dogs. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology, 27, 719–726.
Walker, D. B. (2006). Serum chemical biomarkers of cardiac injury for nonclinical safety testing. Toxicologic Pathology, 34, 94–104.
Tebbutt, S., Harvey, M., Nicholson, T., & Cave, G. (2006). Intralipid prolongs survival in a rat model of verapamil toxicity. Academic Emergency Medicine, 13, 134–139.
Bania, T. C., Chu, J., Perez, E., Su, M., & Hahn, I. H. (2007). Hemodynamic effects of intravenous fat emulsion in an animal model of severe verapamil toxicity resuscitated with atropine, calcium, and saline. Academic Emergency Medicine, 14, 105–111.
DeWitt, C. R., & Waksman, J. C. (2004). Pharmacology, pathophysiology and management of calcium channel blocker and beta-blocker toxicity. Toxicol. Rev., 23, 223–238.
Kimes, B. W., & Brandt, B. L. (1976). Properties of a clonal muscle cell line from rat heart. Experimental Cell Research, 98, 367–381.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (2015R1C1A1A01054105).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Seong-Ho Ok is currently receiving a Grant from National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (2015R1C1A1A01054105). The remaining authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ok, SH., Choi, M.H., Shin, IW. et al. Lipid Emulsion Inhibits Apoptosis Induced by a Toxic Dose of Verapamil via the Delta-Opioid Receptor in H9c2 Rat Cardiomyoblasts. Cardiovasc Toxicol 17, 344–354 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-016-9392-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-016-9392-9