Abstract
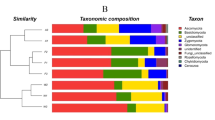
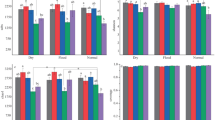
This study assessed the effects of changes in organic carbon content on soil bacterial community composition and diversity in the Antarctic Fildes Peninsula. 16S rRNA gene sequencing was performed to investigate bacterial community composition. Firstly, we found that organic carbon (OrC) and nutrients showed an increasing trend in the lake area. Secondly, soil geochemistry changes affected microbial composition in the soil. Specifically, we found 3416 operational taxonomical units (OTUs) in 300 genera in five main phyla: Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria, Acidobacteria, Chloroflexi, and Bacteroidetes. Although the diversity was similar among the four sites, the composition was different. Among them, Hungateii content changed very significantly, from 16.67% to 33.33%. Canonical correspondence analysis showed that most measured geochemical factors were relevant in structuring microbiomes, and organic carbon concentration showed the highest correlation, followed by NO3−-N. Hungateii was significantly correlated with the content of organic carbon. Our finding suggested organic carbon played an important role in soil bacterial communities of the Antarctic coastal lake region.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrian, R., O’Reilly, C. M., Zagarese, H., Baines, S. B., Hessen, D. O., Keller, W., Livingstone, D. M., Sommaruga, R., Straile, D., and Donk, E. V., 2009. Lakes as sentinels of climate change. Limnology & Oceanography, 54 (6 part 2): 2283–2297.
Berg, G., and Smalla, K., 2009. Plant species and soil type cooperatively shape the structure and function of microbial communities in the rhizosphere. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 68 (1): 1–13.
Bölter, M., 2011. Soil development and soil biology on King George Island, Maritime Antarctic. Polish Polar Research, 32 (2): 105–116.
Caporaso, J. G., Kuczynski, J., Stombaugh, J., Bittinger, K., Bushman, F. D., Costello, E. K., Fierer, N., Peña, A. G., Goodrich, J. K., Gordon, J. I., Huttley, G. A., Kelley, S. T., Knights, D., Koenig, J. E., Ley, R. E., Lozupone, C. A., McDonald, D., Muegge, B. D., Pirrung, M., Reeder, J., Sevinsky, J. R., Turnbaugh, P. J., Walters, W. A., Widmann, J., Yatsunenko, T., Zaneveld, J., and Knight, R., 2010a. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nature Methods, 7 (5): 335–336.
Caruso, T., Trokhymets, V., Bargagli, R., and Convey, P., 2013. Biotic interactions as a structuring force in soil communities: Evidence from the micro-arthropods of an Antarctic moss model system. Oecologia, 172 (2): 495–503.
Chotte, J. L., Ladd, J. N., and Amato, M., 1998. Sites of microbial assimilation, and turnover of soluble and particulate 14C-labelled substrates decomposing in a clay soil. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 30 (2): 205–218.
Edgar, R. C., 2013. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nature Methods, 10: 996–998.
Edgar, R. C., Haas, B. J., Clemente, J. C., Quince, C., and Knight, R., 2011. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics, 27 (16): 2194–2200.
Edwards, A. C., Scalenghe, R., and Freppaz, M., 2007. Changes in the seasonal snow cover of alpine regions and its effect on soil processes: A review. Quaternary International, 162 (1): 172–181.
Goldfarb, K. C., Karaoz, U., Hanson, C. A., Santee, C. A., Bradford, M. A., Treseder, K. K., Wallenstein, M. D., and Brodie, E. L., 2011. Differential growth responses of soil bacterial taxa to carbon substrates of varying chemical recalcitrance. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2 (1): 94.
Haas, B. J., Gevers, D., Earl, A. M., Feldgarden, M., Ward, D. V., Giannoukos, G., Ciulla, D., Tabbaa, D., Highlander, S. K., Sodergren, E., Methé, B., DeSantis, T. Z., Petrosino, J. F.
Knight, R., and Birren, B. W., 2011. Chimeric 16S rRNA sequence formation and detection in Sanger and 454-pyrose-quenced PCR amplicons. Genome Research, 21 (3): 494–504.
Hogg, I. D., Cary, S. C., Convey, P., Newsham, K. K., O’Donnell, A. G., Adams, B. J., Aislabie, J., Frati, F., Stevens, M. I., and Wall, D. H., 2006. Biotic interactions in Antarctic terrestrial ecosystems: Are they a factor. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 38 (10): 3035–3040.
Hu, L., Shi, X., Yu, Z., Lin, T., Wang, H., Ma, D., Guo, Z., and Yang, Z., 2012. Distribution of sedimentary organic matter in estuarine-inner shelf regions of the East China Sea: Implications for hydrodynamic forces and anthropogenic impact. Marine Chemistry, 142–144 (11): 29–40.
Hughes, K. A., Convey, P., Ziska, L. H., and Dukes, J. S., 2014. Non-native species in Antarctic terrestrial environments: The impacts of climate change and human activity. In: Invasive Species & Global Climate Change, Ziska, L., ed., 81–100, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1079/9781780641645.0081.
Jeanette, B., Brandt, K. K., Al-Soud, W. A., Holm, P. E., Hansen, L. H., Srensen, S. R. J., and Ole, N., 2012. Selection for Cutolerant bacterial communities with altered composition, but unaltered richness, via long-term Cu exposure. Applied & Environmental Microbiology, 78 (20): 7438–7446.
Jones, H. G., 1991. Snow chemistry and biological activity: A particular perspective on nutrient cycling. NATO ASI Series, 28: 173–228.
Jones, H. G., 2010. The ecology of snow-covered systems: A brief overview of nutrient cycling and life in the cold. Hydrological Processes, 13 (14–15): 2135–2147.
Kuramae, E. E., Yergeau, E., Wong, L. C., Pijl, A. S., van Veen, J. A., and Kowalchuk, G. A., 2015. Soil characteristics more strongly influence soil bacterial communities than land-use type. Fems Microbiology Ecology, 79 (1): 12–24.
Ladd, J. N., Gestel, M. V., Monrozier, L. J., and Amato, M., 1996. Distribution of organic 14C and 15N in particle-size fractions of soils incubated with 14C, 15N-labelled glucose/NH4, and legume and wheat straw residues. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 28 (7): 893–905.
Lagomarsino, A., Grego, S., and Kandeler, E., 2012. Soil organic carbon distribution drives microbial activity and functional diversity in particle and aggregate-size fractions. Pedobiologia, 55 (2): 101–110.
Lavian, I. L., Vishnevetsky, S., Barness, G., and Steinberger, Y., 2001. Soil microbial community and bacterial functional diversity at Machu Picchu, King George Island, Antarctica. Polar Biology, 24 (6): 411–416.
Liu, J., Zang, J., Zhao, C., Yu, Z., Xu, B., Li, J., and Ran, X., 2016. Phosphorus speciation, transformation, and preservation in the coastal area of Rushan Bay. Science of the Total Environment, 565: 258–270.
Magoä, T., and Salzberg, S. L., 2011. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics, 27 (21): 2957–2963.
Marilley, L., Vogt, G., Blanc, M., and Aragno, M., 1998. Bacterial diversity in the bulk soil and rhizosphere fractions of Lolium perenne and Trifolium repens as revealed by PCR restriction analysis of 16S rDNA. Plant & Soil, 198 (2): 219–224.
Michelsen, C. F., Pedas, P., Glaring, M. A., Schjoerring, J. K., and Stougaard, P., 2014. Bacterial diversity in Greenlandic soils as affected by potato cropping and inorganic versus organic fertilization. Polar Biology, 37 (1): 61–71.
Monserrate, E., Leschine, S. B., and Canale-Parola, E., 2001. Clostridium hungatei sp. nov., a mesophilic, N2-fixing celluolytic bacterium isolated from soil. International Journal of Systematic & Evolutionary Microbiology, 51 (1): 123–132.
Nicolas, J. P., Vogelmann, A. M., Scott, R. C., Wilson, A. B., Cadeddu, M. P., Bromwich, D. H., Verlinde, J., Lubin, D., Russell, L. M., Jenkinson, C., Powers, H. H., Ryczek, M., Stone, G., and Wille, J. D., 2017. January 2016 extensive summer melt in West Antarctica favoured by strong El Niño. 8: 15799.
Oksanen, J., Blanchet, F. G., Kindt, R., Legendre, P., Minchin, P. R., O’Hara, R. B., and Wagner, H., 2016. Vegan: Community Ecology Package [Software].
Oyugi, J. O., Qiu, H., and Safronetz, D., 2007. Global warming and the emergence of ancient pathogens in Canada’s Arctic regions. Medical Hypotheses, 68 (3): 709.
Parsons, A. N., Barrett, J. E., Wall, D. H., and Virginia, R. A., 2004. Soil carbon dioxide flux in antarctic dry valley ecosystems. Ecosystems, 7 (3): 286–295.
Pritchard, H. D., Ligtenberg, S. R. M., Fricker, H. A., Vaughan, D. G., van den Broeke, M. R., and Padman, L., 2012. Antarctic ice-sheet loss driven by basal melting of ice shelves. Nature, 484 (7395): 502–505.
Quast, C., Pruesse, E., Yilmaz, P., Gerken, J., Schweer, T., Yarza, P., Peplies, J., and Glöckner, F. O., 2013. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Research, 41 (Database issue): 590–596.
Santamans, A. C., Boluda, R., Picazo, A., Gil, C., Ramosmiras, J., Tejedo, P., Pertierra, L. R., Benayas, J., and Camacho, A., 2017. Soil features in rookeries of Antarctic penguins reveal sea to land biotransport of chemical pollutants. PLoS One, 12 (8): e0181901.
Schaefer, K., Lantuit, H., Romanovsky, V. E., Schuur, E. A. G., and Witt, R., 2014. The impact of the permafrost carbon feedback on global climate. Environmental Research Letters, 9 (8): 085003.
Schmidt, I. K., Jonasson, S., and Michelsen, A., 1999. Mineralization and microbial immobilization of N and P in arctic soils in relation to season, temperature and nutrient amendment. Applied Soil Ecology, 11 (2–3): 147–160.
Segata, N., Izard, J., Waldron, L., Gevers, D., Miropolsky, L., Garrett, W. S., and Huttenhower, C., 2011. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biology, 12 (6): R60.
Staddon, W. J., Duchesne, L. C., and Trevors, J. T., 1997. Microbial diversity and community structure of postdisturbance forest soils as determined by sole-carbon-source utilization patterns. Microbial Ecology, 34 (2): 125–130.
Staddon, W. J., Trevors, J. T., Duchesne, L. C., and Colombo, C. A., 1998. Soil microbial diversity and community structure across a climatic gradient in western Canada. Biodiversity & Conservation, 7 (8): 1081–1092.
Steig, E. J., Schneider, D. P., Rutherford, S. D., Mann, M. E., Comiso, J. C., and Shindell, D. T., 2009. Warming of the Antarctic ice-sheet surface since the 1957 International Geophysical Year. Nature, 457 (7228): 459–462.
Tierney, L., 2012. The R Statistical Computing Environment. Springer, New York, 1–21.
Turner, J., Colwell, S. R., Marshall, G. J., Lachlan-Cope, T. A., Carleton, A. M., Jones, P. D., Lagun, V., Reid, P. A., and Iagovkina, S., 2005. Antarctic climate change during the last 50 years. International Journal of Climatology, 25 (3): 279–294.
Tytgat, B., Verleyen, E., Sweetlove, M., D’Hondt, S., Clercx, P., Ranst, E. V., Peeters, K., Roberts, S., Namsaraev, Z., and Wilmotte, A., 2016. Bacterial community composition in relation to bedrock type and macrobiota in soils from the Sør Rondane Mountains, East Antarctica. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 92 (9): fiw126.
Van Horn, D. J., Okie, J. G., Buelow, H. N., Gooseff, M. N., Barrett, J. E., and Takacs-Vesbach, C. D., 2014. Soil microbial responses to increased moisture and organic resources along a salinity gradient in a polar desert. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 80 (10): 3034–3043.
Wang, N. F., Zhang, T., Zhang, F., Wang, E. T., He, J. F., Ding, H., Zhang, B. T., Liu, J., Ran, X. B., and Zang, J. Y., 2015. Diversity and structure of soil bacterial communities in the fildes region (maritime Antarctica) as revealed by 454 pyrosequencing. Frontiers in Microbiology, 6: 1188.
Wang, Q., Garrity, G. M., Tiedje, J. M., and Cole, J. R., 2007. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 73 (16): 5261–5267.
You, Y., Wang, J., Huang, X., Tang, Z., Liu, S., and Sun, O. J., 2014. Relating microbial community structure to functioning in forest soil organic carbon transformation and turnover. Ecology & Evolution, 4 (5): 633–647.
Zhang, C., Zhang, X. Y., Zou, H. T., Kou, L., Yang, Y., Wen, X. F., Li, S. G., Wang, H. M., and Sun, X. M., 2017. Contrasting effects of ammonium and nitrate additions on the biomass of soil microbial communities and enzyme activities in subtropical China. Biogeosciences, 14 (20): 4815–4827.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41776198), the Basic Scientific Fund for National Public Research Institutes of China (No. GY0219Q10), and the Development Fund of Marine Bioactive Substances, SOA (No. MBSMAT-2017-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, W., Wang, N., Ma, Y. et al. The Effect of Organic Carbon on Soil Bacterial Diversity in an Antarctic Lake Region. J. Ocean Univ. China 18, 1402–1410 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-019-4097-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-019-4097-x