Abstract
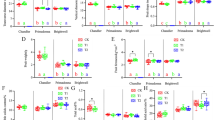
To assess the effects of both development and environment on apple fruit quality, skin color and flavor/taste characteristics were compared between shaded (bagged) and sun-exposed (without bagging) apple fruit. Field experiments were conducted during the middle-to-late fruit development, using three cultivars (non-red ‘Golden Delicious’, pale-red ‘Cripps Pink’, and deep-red ‘Qinguan’) at 830.9 m altitude, and two cultivars (‘Qinguan’ and ‘Golden Delicious’) at three different altitudes (519.8, 830.9, and 1072.5 m). The chromaticity values L*, C*, and h° differed between non-red and both red cultivars over time. Sun-exposed fruits contained more chlorophyll and carotenoids than shaded fruits. Trace amounts of anthocyanin accumulated in the skin of sun-exposed ‘Golden Delicious’, while shading prevented anthocyanin accumulation in red cultivars. The sugar contents of all three tested cultivars increased over time, while the organic acid contents decreased. Shading reduced the sugar and organic acid contents but did not affect their variation trends over time. The growing environments affected both the h° values and pigment contents of ‘Qinguan’, and the maximum fructose and sucrose proportions and the minimum glucose proportion were detected at the lowest altitude. Although red peel color, sugars, and organic acid proportion were determined via genetic cues under natural conditions, the growing environment is centrally important for these traits. Both the temperature and light of the planting region influenced each other and impacted the contents of sugars and organic acids in the tested apple fruit.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackermann J, Fischer M, Amado R (1992) Changes in sugars, acids, and amino acids during ripening and storage of apples (cv. Glockenapfel). J Agric Food Chem 40:1131–1134. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf00019a008
An X-H et al (2015) MdMYB9 and MdMYB11 are Involved in the Regulation of the JA-Induced Biosynthesis of Anthocyanin and Proanthocyanidin in Apples. Plant Cell Physiol 56:650–662. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcu205
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphen Beat Vulg Plant Physiol 24:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.24.1.1
Aslantaş R, Karakurt H (2009) The effects of altitude on stomata number and some vegetative growth parameters of some apple cultivars. Res J Agric Biol Sci 5:853–857
Bai S et al (2017) Transcriptome analysis of bagging-treated red Chinese sand pear peels reveals light-responsive pathway functions in anthocyanin accumulation. Sci Rep 7:63. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-00069-z
Chagné D et al (2016) A functional genetic marker for apple red skin coloration across different environments. Tree Genet Genomes 12:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-016-1025-8
Chen C-S, Zhang D, Wang Y-Q, Li P-M, Ma F-W (2012) Effects of fruit bagging on the contents of phenolic compounds in the peel and flesh of ‘Golden Delicious’, ‘Red Delicious’, and ‘Royal Gala’ apples. Sci Hortic 142:68–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2012.05.001
Crespo P, Bordonaba JG, Terry LA, Carlen C (2010) Characterisation of major taste and health-related compounds of four strawberry genotypes grown at different Swiss production sites. Food Chem 122:16–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.02.010
Feng F, Li M, Ma F, Cheng L (2014) The effects of bagging and debagging on external fruit quality, metabolites, and the expression of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes in ‘Jonagold’ apple (Malus domestica Borkh.). Sci Hortic 165:123–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2013.11.008
Fernandes de Oliveira A, Mercenaro L, Del Caro A, Pretti L, Nieddu G (2015) Distinctive anthocyanin accumulation responses to temperature and natural UV radiation of two field-grown (Vitis vinifera L.) Cultivars. Molecules 20:2061–2080. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20022061
Fischer G, Ebert G, Lüdders P (2007) Production, seeds and carbohydrate contents of cape gooseberry (Physalis peruviana L.) fruits grown at two contrasting Colombian altitudes. J Aappl Bot Food Qual 81:29–35
Hampson CR, Kemp H (2003) Characteristics of important commercial apple cultivars. CABI Publishing, New York. https://doi.org/10.1079/9780851995922.0061
Hecke K et al (2006) Sugar-, acid- and phenol contents in apple cultivars from organic and integrated fruit cultivation. Eur J Clin Nutr 60:1136–1140. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602430
Henry-Kirk RA, Plunkett B, Hall M, Mcghie T, Allan AC, Wargent JJ, Espley RV (2018) Solar UV light regulates flavonoid metabolism in apple (Malus x domestica). Plant Cell Environ. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.13125
Huang C, Yu B, Teng Y, Su J, Shu Q, Cheng Z, Zeng L (2009) Effects of fruit bagging on coloring and related physiology, and qualities of red Chinese sand pears during fruit maturation. Sci Hortic 121:149–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2009.01.031
Iglesias I, Echeverría G, Lopez ML (2012) Fruit color development, anthocyanin content, standard quality, volatile compound emissions and consumer acceptability of several ‘Fuji’ apple strains. Sci Hortic 137:138–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2012.01.029
Iglesias I, Echeverría G, Soria Y (2008) Differences in fruit colour development, anthocyanin content, fruit quality and consumer acceptability of eight ‘Gala’ apple strains. Sci Hortic 119:32–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2008.07.004
Irani NG, Grotewold E (2005) Light-induced morphological alteration in anthocyanin-accumulating vacuoles of maize cells. BMC Plant Biol 5:7. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-5-7
Jiang M, Ren L, Lian H, Liu Y, Chen H (2016) Novel insight into the mechanism underlying light-controlled anthocyanin accumulation in eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2016.04.001
Jing C, Ma C, Zhang J, Jing S, Jiang X, Yang Y, Zhao Z (2016) Effect of debagging time on pigment patterns in the peel and sugar and organic acid contents in the pulp of ‘Golden Delicious’ and ‘Qinguan’ apple fruit at mid and late stages of development. PLoS ONE 11:e0165050. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0165050
Lakso AN, Robinson TL, Greene DW (2006) Interation of Environment, Physiology and Frut Abscission via Carbon Balance Modeling- Implications for Uuderstanding Growth Regulator Responses. In: 2006. International Society for Horticultural Science (ISHS), Leuven, Belgium, pp 321–326. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2006.727.38
Łata B, Tomala K (2007) Apple peel as a contributor to whole fruit quantity of potentially healthful bioactive compounds. Cultivar and year implication. J Agric Food Chem 55:10795–10802. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf072035p
Li XQ (2009) Developmental and environmental variation in genomes. Heredity 102:323–329
Liu T et al (2015) Improved peach peel color development by fruit bagging. Enhanced expression of anthocyanin biosynthetic and regulatory genes using white non-woven polypropylene as replacement for yellow paper. Sci Hortic 184:142–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2015.01.003
Liu Y, Che F, Wang L, Meng R, Zhang X, Zhao Z (2013) Fruit coloration and anthocyanin biosynthesis after bag removal in non-red and red apples (Malus x domestica Borkh.). Molecules 18:1549–1563. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18021549
Liu Y, Zhang X, Zhao Z (2012) Effects of fruit bagging on anthocyanins, sugars, organic acids, and color properties of ‘Granny Smith’ and ‘Golden Delicious’ during fruit maturation. Eur Food Res Technol 236:329–339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-012-1896-3
Ma B et al (2015) Comparative assessment of sugar and malic acid composition in cultivated and wild apples. Food Chem 172:86–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.09.032
McGuire RG (1992) Reporting of objective color measurements. HortScience 27:1254–1255
Meng R, Zhang J, An L, Zhang B, Jiang X, Yang Y, Zhao Z (2015) Expression profiling of several gene families involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis in apple (Malus domestica Borkh.) skin during fruit development. J Plant Growth Regul. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-015-9552-3
Milosevic N, Milosevic T, Glisic I Productiove and organoleptic traits of recent apple cultuvars. In: 2009. International Society for Horticultural Science (ISHS), Leuven, Belgium, pp 565–570. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2009.825.90
Moing A et al (2000) Role of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase in organic acid accumulation during peach fruit development. Physiol Plantarum 108:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1399-3054.2000.108001001.x
Nguyen CT, Kim J, Yoo KS, Lim S, Lee EJ (2014) Effect of prestorage UV-A, -B, and -C radiation on fruit quality and anthocyanin of 'Duke' blueberries during cold storage. J Agric Food Chem 62:12144–12151. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf504366x
Palapol Y, Ketsa S, Stevenson D, Cooney JM, Allan AC, Ferguson IB (2009) Colour development and quality of mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana L.) fruit during ripening and after harvest. Postharvest Biol Technol 51:349–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2008.08.003
Rokaya PR, Baral DR, Gautam DM, Shrestha AK, Paudyal KP (2016) Effect of altitude and maturity stages on quality attributes of mandarin (Citrus reticulata Blanco). American J Plant Sci 7:958–966. https://doi.org/10.4236/ajps.2016.76091
Saure MC (1990) External control of anthocyanin formation in apple. Sci Hortic 42:181–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4238(90)90082-P
Takos AM, Jaffe FW, Jacob SR, Bogs J, Robinson SP, Walker AR (2006) Light-induced expression of a MYB gene regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis in red apples. Plant Physiol 142:1216–1232. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.106.088104
Usenik V, Stampar F, Veberic R (2009) Anthocyanins and fruit colour in plums (Prunus domestica L.) during ripening. Food Chem 114:529–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.09.083
Wang L-J et al (2014) Variation of anthocyanins and flavonols in Vaccinium uliginosum berry in Lesser Khingan Mountains and its antioxidant activity. Food Chem 160:357–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.03.081
Zheng J, Kallio H, Linderborg K, Yang B (2011) Sugars, sugar alcohols, fruit acids, and ascorbic acid in wild Chinese sea buckthorn (Hippophaë rhamnoides ssp. sinensis) with special reference to influence of latitude and altitude. Food Res Int 44:2018–2026. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2010.10.007
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Xiaoying Qiao and Feifei Chen for assistance with sample collection, and Dr. Chunhui Song and Libo Xing for technical assistance. This research was supported by grants from the Modern Agro-industry Technology Research System, China (CARS-28), the “Twelfth Five-Year-Plan” of the National Science and Technology in Rural Field (2013BAD02B01-2), the National Sci-Tech Support Plan (2014BAD16B06), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31471845).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by P. Wojtaszek.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jing, C., Feng, D., Zhao, Z. et al. Effect of environmental factors on skin pigmentation and taste in three apple cultivars. Acta Physiol Plant 42, 69 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-020-03039-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-020-03039-7