Abstract
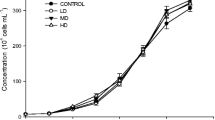
The effect of ultraviolet-B (UV-B) radiation on Antarctic phytoplankton has become an attractive ecological issue as a result of annual springtime ozone depletion. The effects of UV-B radiation on the growth and antioxidant enzymes were investigated using Antarctic sea ice microalgae Chlamydomonas sp. ICE-L as the material in this study. The results demonstrated that UV-B radiation could notably inhibit the growth, especially at high UV-B radiation intensity (70 μW cm−2). Malondialdehyde and O2 ·− content in ICE-L increased rapidly in early days (1–3 days) exposed to UV-B radiation enhancement, then decreased rapidly. In the stress of UV-B radiation enhancement, the superoxide dismutase, peroxidase and Catalase activities of 1–4 days in ICE-L were obviously higher than those in the control, and their activities became higher at high UV-B radiation intensity (70 μW cm−2). These enzymes activity of 7 days would kept stable at low UV-B radiation intensity (35 μW cm−2), but kept high level at high UV-B radiation intensity (70 μW cm−2). However, the ascorbate peroxidase activity in ICE-L kept stable under the stress of UV-B radiation enhancement. The above experimental results indicated that the antioxidant enzyme system played an important role in the adaptation of Antarctic ice microalgae under the UV-B radiation change of Antarctic ecosystems.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- APX:
-
Ascorbate peroxidase
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- DTT:
-
Dithiothreitol
- EDTA:
-
Ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid
- H2O2 :
-
Hydrogen peroxide
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- POD:
-
Peroxidase
- PVP:
-
Polyvinylpyrrolidone
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- TBA:
-
Thiobarbituric acid
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126. doi:10.1016/S0076-6879(84)05016-3
Azzi A, Montecucco C, Richter C (1975) The use of acetylated ferricytochrome c for the detection of superoxide radicals produced in biological membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 65:597–603. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(75)80188-4
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein–dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Campbell D (1998) The cyanobacterium Synechococcus resists UV-B by exchanging photosystem II reaction center D1 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:364–369. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.1.364
Dai Q, Yan B, Huang S et al (1997) Response of oxidative stress defense systems in rice (Oryza sativa) leaves with supplemental UV-B radiation. Physiol Plant 101:301–308. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.1997.tb01000.x
Dawes IW (2000) Response of eukaryotic cells to oxidative stress. Agric Chem Biotechnol 43:211–217
Giannopolitis CN, Ries SK (1977) Superoxide dismutase: 1. Occurrence in higher plants. Plant Physiol 59:309–314
Guillard RL, Ryther JH (1962) Studies of marine planktonic diatoms. I. Cyclotella nana Hustedt and Detonula confervacea Cleve. Can J Microbiol 8:229–239
Heath RI, Packer I (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated choroplasts. I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 125:189–190. doi:10.1016/0003-9861(68)90654-1
Hernandez E, Ferreyra GA, MacCormack WP (2002) Effect of solar radiation on two Antarctic marine bacterial strains. Polar Biol 25:453–459
Hughes KA, Lawley B, Newsham KK (2003) Solar UV-B radiation inhibits the growth of Antarctic terrestrial fungi. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:1488–1491. doi:10.1128/AEM.69.3.1488-1491.2003
Janknegt PJ, van de Poll WH, Visser RJW et al (2008) Oxidative stress responses in the marine Antarctic diatom Chaetoceros brevis (Bacillariophyceae) during photoacclimation. J Phycol 44:957–966. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8817.2008.00553.x
Jordan BR (1996) The effects of ultraviolet-B radiation on plants: a molecular perspective. Adv Bot Res 22:97–162. doi:10.1016/S0065-2296(08)60057-9
Liu P, Miao JL, Kan GF et al (2004) Effect of UV-B on the morphology and ultrastructure of a strain of Antarctic cyanophyceae. Mar Sci 28:21–25
Lizotte MP, Sullivan CW (1991) Rates of photoadaptation in sea ice diatoms from McMurdo Sound, Antarctica. J Phycol 27:367–373. doi:10.1111/j.0022-3646.1991.00367.x
Maehly AC (1955) Plant peroxidases [M]. In: Colowick PS, Kaplan NO (eds) Methods in enzymology. Academic, New York, pp 271–285
Miao JL, Jiang YH, Wang B et al (2002) Study on induced synthesis of anti-UV substances in the Antarctic alga. High Technol Lett 4:92–96
Miao JL, Kan GF, Jiang YH et al (2004) Responses of biochemical compositions of four Antarctic ice microalgae to UV-B irradiation enhancement. Mar Sci 28:26–31
Nakano Y, Asada K (1981) Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 22:867–880
Norgaard MA, Andersen CB, Pettersson G et al (1998) Changes in biologically active ultraviolet radiation reaching the Earth’s surface. J Photochem Photobiol B 46:5–19. doi:10.1016/S1011-1344(98)00182-1
Qian JG, Mopper K, Kieber DJ (2001) Photochemical production of the hydroxyl radical in Antarctic water deep-sea res. Deep Sea Res Part I Oceanogr Res Pap 48:741–759. doi:10.1016/S0967-0637(00)00068-6
Rao MV, Paliyath G, Ormrod DP (1996) Ultraviolet-B and ozone-induced biochemical changes in antioxidant enzymes of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol 110:125–136. doi:10.1104/pp.110.1.125
Skerratt JH, Davidson AT, Nichols PD et al (1998) Effect of UV-B on lipid content of three Antarctic marine phytoplankton. Phytochemistry 49:999–1007
Smith RC, Prezelin BB, Baker KS et al (1992) Ozone depletion: ultraviolet radiation and phytoplankton biology in Antarctic waters. Science 255:952–959. doi:10.1126/science.1546292
Staehelin J, Harris NRP, Appenzeller C et al (2001) Ozone trends: a review. Rev Geophys 39:231–290. doi:10.1029/1999RG000059
Wang GH, Hu CX, Li DH et al (2007) The response of antioxidant systems in Nostoc sphaeroides against UV-B radiation and the protective effects of exogenous antioxidants. Adv Space Res 39:1034–1042. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2007.03.022
Zhang PY, Yu J, Tang XX (2005) UV-B radiation suppresses the growth and antioxidant systems of two marine microalgae, Platymonas subcordiformis (Wille) Hazen and Nitzschia closterium (Ehrenb.) W. Sm. J Integr Plant Biol 47:683–691
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the natural scientific research innovation foundation in Harbin Institute of Technology (No. 2008-067), the Key Lab of Marine Bioactive Substances, SOA (No. MBS-2007-01), the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No. Y2007D58), Science and Technology Development Project of Weihai (No. 2008087) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 40876107).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by J. Zwiazek.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Qf., Hou, Yh., Miao, Jl. et al. Effect of UV-B radiation on the growth and antioxidant enzymes of Antarctic sea ice microalgae Chlamydomonas sp. ICE-L. Acta Physiol Plant 31, 1097–1102 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-009-0271-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-009-0271-x