Abstract
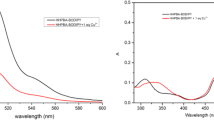
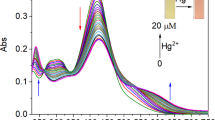
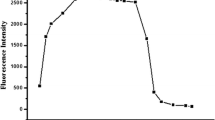
The excessive accumulation of Cu2+ in the human body and the natural environment will endanger human health and break the balance of the ecosystem. Therefore, the development of a low-cost and rapid method to detect Cu2+ is of great significance to protect human health and the environment. In this study, we used electron-rich triphenylamine as the electron donor and AIE active core, coupled with the electron acceptor imine nitrogen, and further connected to the ESIPT active salicylaldimine unit, detection based on the ESIPT system a new AIE fluorescent probe 5-(diethylamino)-2-((E)-(((E)-4-(diphenylamino)benzylidene)hydrazono)methyl)phenol (DDP) was synthesized. DDP has strong fluorescence and can coordinate specifically with Cu2+ to form a copper complex and cause fluorescence quenching, thereby achieving the purpose of detecting Cu2+. The EDTA titration experiment was carried out on the DDP–Cu2+ solution, and the experimental results proved that the combination of DDP and Cu2+ is reversible. The interaction between DDP and Cu2+ rapidly forms a copper complex, which is approximately completed within 6 s. The detection limit of the probe is as low as 5.7 × 10–8 M and it shows good stability in a weakly alkaline and weakly acidic environment, which provides necessary conditions for the detection of Cu2+ in a living environment. It is applied to the detection of Cu2+ in river water and lake water, showing a good linear relationship, indicating that DDP has the ability to detect Cu2+ in real water samples. Therefore, DDP is expected to become an effective tool for detecting Cu2+ in the environment and organisms.
Graphic abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews NC (2002) Metal transporters and disease. Curr Opin Chem Biol 2(6):181–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1367-5931(02)00307-1
Backes GL, Neumann DM, Jursic BS (2014) Synthesis and antifungal activity of substituted salicylaldehyde hydrazones, hydrazides and sulfohydrazides. Bioorg Med Chem 22(17):4629–4636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2014.07.022
Chen J, Ying GG, Deng WJ (2019) Antibiotic residues in food: extraction, analysis, and human health concerns. J Agric Food Chem 67(27):7569–7586. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b01334
Demchenko AP, Tomin VI, Chou PT (2017) Breaking the Kasha rule for more efficient photochemistry. Chem Rev 117:13353–13381. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00110
Goswami S, Manna A, Paul AK, Das AK, Chakraborty S (2013) Dual channel selective fluorescence detection of Al(III) and PPi in aqueous media with an ‘off–on–off’ switch which mimics molecular logic gates (INHIBIT and EXOR gates). Dalton Trans 42(22):8078–8085. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3dt50621e
Gu B, Huang L, Huang L, Tan Z, Hu M, Yang Z, Chen Z, Peng C, Xiao W, Yu D, Li H (2018) A reaction-based, colorimetric and near-infrared fluorescent probe for Cu2+ and its applications. Sens Actuators B 273:118–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.06.032
He L, Dong B, Liu Y, Lin W (2016) Fluorescent chemosensors manipulated by dual/triple interplaying sensing mechanisms. Chem Soc Rev 23(45):6449–6461. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6cs00413j
Hu Z, Zhang H, Chen Y, Wang Q, Elsegood MRJ, Teat SJ, Feng X, Islam MM, Wu F, Tang BZ (2020) Tetraphenylethylene-based color-tunable AIE-ESIPT chromophores. Dyes Pigments 175:108175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2019.108175
Kwon N, Hu Y, Yoon J (2018) Fluorescent chemosensors for various analytes including reactive oxygen species, biothiol, metal ions, and toxic gases. ACS Omega 3:13731–13751. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b01717
Li DY, Tian XW, Li Z, Zhang JH, Yang XB (2019) Preparation of a near-infrared fluorescent probe based on IR-780 for highly selective and sensitive detection of bisulfite−sulfite in food, living cells, and mice. J Agric Food Chem 67(10):3062–3067. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b00822
Li XY, Guo YF, Xu TT, Fang M, Xu Q, Zhang F, Wu ZY, Li C, Zhu WJ (2020) A highly sensitive naphthalimide-based fluorescent probe for detection of Cu2+ via selective hydrolysis reaction and its application in practical samples. J Chin Chem Soc 67(6):1070–1077. https://doi.org/10.1002/jccs.201900315
Linder MC, Maryam HA (1996) Copper biochemistry and molecular biology. Am J Clin Nutr 63(5):797S. https://doi.org/10.1016/0163-7827(96)00005-7
Luo JD, Xie ZL, Lam JWY, Cheng L, Chen H, Qiu C, Kwok HS, Zhan X, Liu Y, Zhu D, Tang BZ (2001) Aggregation-induced emission of 1-methyl-1,2,3,4,5-pentaphenylsilole. Chem Commun 18:1740–1741. https://doi.org/10.1039/B105159H
Madsen E, Gitlin JD (2007) Copper and iron disorders of the brain. Annu Rev Neurosci 30(1):317–337. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.neuro.30.051606.094252
Maity D, Kumar V, Govindaraju T (2012) Reactive probes for ratiometric detection of Co2+ and Cu2+ based on excited-state intramolecular proton transfer mechanism. Org Lett 14:6008–6011. https://doi.org/10.1021/ol302904c
Mathivanan M, Tharmalingam B, Lin C-H, Pandiyan BV, Thiagarajan V, Murugesapandian B (2020) ESIPT-active multi-color aggregation-induced emission features of triphenylamine-salicy-laldehyde-based unsymmetrical azine family. Cryst Eng Comm 2(22):213–228. https://doi.org/10.1021/ol302904c
Prohaska JR (2011) Impact of copper limitation on expression and function of multicopper oxidases (ferroxidases). Adv Nutr 2(2):89–95. https://doi.org/10.3945/an.110.000208
Puangsamlee T, Tachapermpon Y, Kammalun P, Sukrat K, Wainiphithapong C, Sirirak J, Wanichacheva N (2017) Solvent control bifunctional fluorescence probe for selective detection of Cu2+ and Hg2+ via the excimer of pyrenylacetamide subunits. J Lumin 196:227–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2017.11.048
Roland K (1998) Fluorescent chemosensors for Cu2+ ions: fast, selective, and highly sensitive. Angew Chem Int Ed 37(6):772–773. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19980403)37:63.0.CO;2-Z
Tamima U, Singha U, Kim HR, Reo YJ, Jun YW, Das A, Ahn KH (2018) A benzocoumarin based two-photon fluorescent probe for ratiometric detection of bisulfite. Sens Actuators B 277:576–583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.09.052
Udhayakumari D, Velmathi S (2013) Colorimetric and fluorescent sensor for selective sensing of Hg2+ ions in semi aqueous medium. J Lumin 136(4):117–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2012.11.011
Valentine JS, Hart PJ (2003) Misfolded CuZnSOD and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 7(100):3617–3622. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0730423100
Wang L, Jiao S, Zhang W, Liu Y, Yu G (2013) Synthesis, structure, optoelectronic properties of novel zinc schiff-base complexes. Chin Sci Bull 58:2733–2740. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-013-5786-2
Wang H, Chen J, Hong YG, Lv K, Yu ML, Zhang PS, Long YF, Yi PG (2017) Fabrication of water-soluble fluorescent polymeric micelles for selective detection of Hg2+ in blood serum. Anal Sci 5(33):591–597. https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.33.591
Wang L, Wei ZL, Chen ZZ, Liu C, Dong WK, Ding YJ (2020a) A chemical probe capable for fluorescent and colorimetric detection to Cu2+ and CN− based on coordination and nucleophilic addition mechanism. Microchem J 155:104801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2020.104801
Wang Y, Zhou J, Zhao L, Xu B (2020b) A dual-responsive and highly sensitive fluorescent probe for Cu2+ and pH based on a dansyl derivative. Dyes Pigments 180:108513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2020.108513
Wen H, Huang Q, Yang XF, Li H (2013) Spirolactamized benzothiazole-substituted N, N-diethylrhodol: a new platform to construct ratiometric fluorescent probes. Chem Commun 49:4956–4958. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CC41343H
Xiong JW, Li ZZ, Tan JH, Ji SM, Sun JW, Li XW, Huo YP (2018) Two new quinoline-based regenerable fluorescent probes with AIE characteristics for selective recognition of Cu2+ in aqueous solution and test strips. Analyst 143:4870–4886. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8AN00940F
Zhang J, Ma S, Fang H, Xu B, Sun H, Chan I, Tian W (2017) Insights into the origin of aggregation enhanced emission of 9,10-distyrylanthracene derivatives. Mater Chem Front 1:1422–1429. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7QM00032D
Zhang XF, Xu HM, Han L, Li NB, Luo HQ (2018) A thioflavin T-induced G-quadruplex fluorescent biosensor for target DNA detection. Anal Sci 2(34):149–153. https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.34.149
Zhao YH, Li Y, Long Y, Zhou Z, Tang Z, Deng K, Zhang S (2017) Highly selective fluorescence turn-on determination of fluoride ions via chromogenic aggregation of a silyloxy-functionalized salicylaldehyde azine. Tetrahedron Lett 13(58):1351–1355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2017.02.066
Zhao YH, Luo Y, Wang H, Guo T (2018) A new fluorescent probe based on aggregation induced emission for selective and quantitative determination of copper(II) and its further application to cysteine detection. ChemSel 3(5):1521–1526. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201702252
Zhao C, Shang JY, Yang CS, Li ZW, Ning JH, Li HP (2020) A water-soluble fluorescent probe for rapid detection of sulfur dioxide derivatives. Anal Sci 36:329–333. https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.19P314
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Open Fund of Key Laboratory of Road Structure and Material of Ministry of Transport (kfj170301), Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (2019JJ40295), Changsha University of Science and Technology Postgraduate Research and Innovation Project (CX2019SS31), and Key Project of Hunan Provincial Education Department of China (17A002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shang, J.Y., Li, Y., Chen, K. et al. Synthesis and properties of an AIE fluorescent probe for Cu2+ detection based on ESIPT system. Chem. Pap. 75, 1851–1859 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-020-01447-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-020-01447-0