Abstract
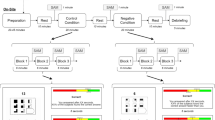
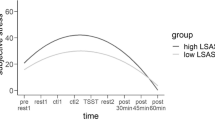
It is a generally accepted observation that individuals act differently under stress. Recent task-based neuroimaging studies have shown that individuals under stress favor the intuitive and fast system over the deliberative and reflective system. In the present study, using a within-subjects design in thirty young adults, we examined whether and how acute social stress impacts regional neural activity in resting state. The results showed that stress induced lower coherence regional homogeneity (Cohe-ReHo) values in left hippocampus and right superior frontal gyrus, both of which are regions associated with deliberative decision making. Stress-induced cortisol change was significantly and positively correlated with the change in Cohe-ReHo value in the right midbrain, a region involved in habitual decision making. These results extend previous findings by demonstrating that stress modulates local synchrony in brain regions implicated in deliberative and intuitive decision making. Our findings might be useful in understanding the neural mechanisms underlying stress-related mental disorders.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, J. K., Hillier, A., Smith, R. M., Tivarus, M. E., & Beversdorf, D. Q. (2007). Beta-adrenergic modulation of cognitive flexibility during stress. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 19(3), 468–478.
Alfarez, D., Wiegert, O., Joels, M., & Krugers, H. (2002). Corticosterone and stress reduce synaptic potentiation in mouse hippocampal slices with mild stimulation. Neuroscience, 115(4), 1119–1126.
Amunts, K., Kedo, O., Kindler, M., Pieperhoff, P., Mohlberg, H., Shah, N. J., Habel, U., Schneider, F., & Zilles, K. (2005). Cytoarchitectonic mapping of the human amygdala, hippocampal region and entorhinal cortex: Intersubject variability and probability maps. Anatomy and Embryology, 210(5–6), 343–352.
Ances, B. M., Leontiev, O., Perthen, J. E., Liang, C., Lansing, A. E., & Buxton, R. B. (2008). Regional differences in the coupling of cerebral blood flow and oxygen metabolism changes in response to activation: Implications for BOLD-fMRI. NeuroImage, 39(4), 1510–1521.
Arnold Anteraper, S., Triantafyllou, C., Sawyer, A. T., Hofmann, S. G., Gabrieli, J. D., & Whitfield-Gabrieli, S. (2014). Hyper-connectivity of subcortical resting-state networks in social anxiety disorder. Brain Connectivity, 4(2), 81–90.
Arnsten, A. F. (2009). Stress signalling pathways that impair prefrontal cortex structure and function. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 10(6), 410–422.
Ashburner, J. (2007). A fast diffeomorphic image registration algorithm. NeuroImage, 38(1), 95–113.
Atsak, P., Guenzel, F. M., Kantar-Gok, D., Zalachoras, I., Yargicoglu, P., Meijer, O. C., Quirarte, G. L., Wolf, O. T., Schwabe, L., & Roozendaal, B. (2016). Glucocorticoids mediate stress-induced impairment of retrieval of stimulus-response memory. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 67, 207–215.
Bomyea, J., & Lang, A. J. (2016). Accounting for intrusive thoughts in PTSD: Contributions of cognitive control and deliberate regulation strategies. Journal of Affecitive Disorder, 192, 184–190.
Brown, S. M., Henning, S., & Wellman, C. L. (2005). Mild, short-term stress alters dendritic morphology in rat medial prefrontal cortex. Cerebral Cortex, 15(11), 1714–1722.
Brunson, K. L. (2005). Mechanisms of late-onset cognitive decline after early-life stress. Journal of Neuroscience, 25(41), 9328–9338.
Buckner, R. L., & Wheeler, M. E. (2001). The cognitive neuroscience of remembering. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 2(9), 624–634.
Diamond, D. M., Campbell, A. M., Park, C. R., Halonen, J., & Zoladz, P. R. (2007). The temporal dynamics model of emotional memory processing: A synthesis on the neurobiological basis of stress-induced amnesia, flashbulb and traumatic memories, and the yerkes-Dodson law. Neural Plasticity, 2007, 1–33.
Evans, J. S. B., & Frankish, K. E. (2009). In two minds: Dual processes and beyond. Oxford University Press.
Evans, J. S. B., & Stanovich, K. E. (2013). Dual-process theories of higher cognition: Advancing the debate. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 8(3), 223–241.
Fleisher, A. S., Podraza, K. M., Bangen, K. J., Taylor, C., Sherzai, A., Sidhar, K., Liu, T. T., Dale, A. M., & Buxton, R. B. (2009a). Cerebral perfusion and oxygenation differences in Alzheimer's disease risk. Neurobiology of Aging, 30(11), 1737–1748.
Fleisher, A. S., Sherzai, A., Taylor, C., Langbaum, J. B., Chen, K., & Buxton, R. B. (2009b). Resting-state BOLD networks versus task-associated functional MRI for distinguishing Alzheimer's disease risk groups. NeuroImage, 47(4), 1678–1690.
Friston, K. J., Williams, S., Howard, R., Frackowiak, R. S., & Turner, R. (1996). Movement-related effects in fMRI time-series. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 35(3), 346–355.
Gray, J. D., Rubin, T. G., Hunter, R. G., & McEwen, B. S. (2014). Hippocampal gene expression changes underlying stress sensitization and recovery. Molecular Psychiatry, 19(11), 1171–1178.
Haeffel, G. J., Abramson, L. Y., Brazy, P. C., Shah, J. Y., Teachman, B. A., & Nosek, B. A. (2007). Explicit and implicit cognition: A preliminary test of a dual-process theory of cognitive vulnerability to depression. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 45(6), 1155–1167.
Hamilton, J. P., Furman, D. J., Chang, C., Thomason, M. E., Dennis, E., & Gotlib, I. H. (2011). Default-mode and task-positive network activity in major depressive disorder: Implications for adaptive and maladaptive rumination. Biological Psychiatry, 70(4), 327–333.
Hermans, E. J., Henckens, M. J., Joels, M., & Fernandez, G. (2014). Dynamic adaptation of large-scale brain networks in response to acute stressors. Trends in Neuroscience, 37(6), 304–314.
Hu, J., Lee, D., Hu, S., Zhang, S., Chao, H., & Li, C. S. (2016). Individual variation in the neural processes of motor decisions in the stop signal task: The influence of novelty seeking and harm avoidance personality traits. Brain Structure and Function, 221(5), 2607–2618.
Kirschbaum, C., Pirke, K.-M., & Hellhammer, D. H. (1993). The 'Trier social stress Test' - a tool for investigating psychobiological stress responses in a laboratory setting. Neuropsychobiology, 28, 76–81.
de Kloet, E. R., Sibug, R. M., Helmerhorst, F. M., & Schmidt, M. V. (2005). Stress, genes and the mechanism of programming the brain for later life. Neuroscience and Biobehavior Review, 29(2), 271–281.
Kruse, O., León, I. T., Stalder, T., Stark, R., & Klucken, T. (2017). Altered reward learning and hippocampal connectivity following psychosocial stress. NeuroImage, 171, 15–25.
Lee, T., Jarome, T., Li, S.-J., Kim, J. J., & Helmstetter, F. J. (2009). Chronic stress selectively reduces hippocampal volume in rats: A longitudinal magnetic resonance imaging study. Neuroreport, 20(17), 1554–1558.
Liu, D., Yan, C., Ren, J., Yao, L., Kiviniemi, V. j., & Zang, Y. (2010). Using coherence to measure regional homogeneity of resting-state fMRI signal. Frontier in Systems Neuroscience, 4, 24.
Liu, F., Hu, M., Wang, S., Guo, W., Zhao, J., Li, J., et al. (2012). Abnormal regional spontaneous neural activity in first-episode, treatment-naive patients with late-life depression: A resting-state fMRI study. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry, 39(2), 326–331.
Liu, Y., Zhao, X., Cheng, Z., Zhang, F., Chang, J., Wang, H., Xie, R., Wang, Z., Cao, L., & Wang, G. (2017). Regional homogeneity associated with overgeneral autobiographical memory of first-episode treatment-naive patients with major depressive disorder in the orbitofrontal cortex: Aresting-state fMRI study. Journal of Affective Disorder, 209, 163–168.
Lovallo, W. R., Robinson, J. L., Glahn, D. C., & Fox, P. T. (2010). Acute effects of hydrocortisone on the human brain: An fMRI study. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 35(1), 15–20.
Luethi, M., Meier, B., & Sandi, C. (2009). Stress effects on working memory, explicit memory, and implicit memory for neutral and emotional stimuli in healthy men. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 2, 5.
Maier, S. U., Makwana, A. B., & Hare, T. A. (2015). Acute stress impairs self-control in goal-directed choice by altering multiple functional connections within the brain's decision circuits. Neuron, 87(3), 621–631.
McEwen, B. S. (1999). Stress and the aging hippocampus. Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology, 20(1), 49–70.
McEwen, B. S., Bowles, N. P., Gray, J. D., Hill, M. N., Hunter, R. G., Karatsoreos, I. N., & Nasca, C. (2015). Mechanisms of stress in the brain. Nature Neuroscience, 18(10), 1353–1363.
McEwen, B. S., Nasca, C., & Gray, J. D. (2016). Stress effects on neuronal structure: Hippocampus, amygdala, and prefrontal cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology, 41(1), 3–23.
Mobbs, D., Petrovic, P., Marchant, J. L., Hassabis, D., Weiskopf, N., Seymour, B., Dolan, R. J., & Frith, C. D. (2007). When fear is near: Threat imminence elicits prefrontal-periaqueductal gray shifts in humans. Science, 317(5841), 1079–1083.
Mobbs, D., Marchant, J. L., Hassabis, D., Seymour, B., Tan, G., Gray, M., Petrovic, P., Dolan, R. J., & Frith, C. D. (2009). From threat to fear: The neural organization of defensive fear systems in humans. Journal of Neuroscience, 29(39), 12236–12243.
Mobbs, D., Hagan, C. C., Dalgleish, T., Silston, B., & Prévost, C. (2015). The ecology of human fear: Survival optimization and the nervous system. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 9.
Nguyen, E. T., Streicher, J., Berman, S., Caldwell, J. L., Ghisays, V., Estrada, C. M., Wulsin, A. C., & Solomon, M. B. (2017). A mixed glucocorticoid/mineralocorticoid receptor modulator dampens endocrine and hippocampal stress responsivity in male rats. Physiology & Behavior, 178, 82–92.
Oei, N. Y. L., Elzinga, B. M., Wolf, O. T., de Ruiter, M. B., Damoiseaux, J. S., Kuijer, J. P. A., Veltman, D. J., Scheltens, P., & Rombouts, S. A. R. B. (2007). Glucocorticoids decrease hippocampal and prefrontal activation during declarative memory retrieval in young men. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 1(1–2), 31–41.
Olver, J. S., Pinney, M., Maruff, P., & Norman, T. R. (2015). Impairments of spatial working memory and attention following acute psychosocial stress. Stress and Health, 31(2), 115–123.
Pittenger, C., & Duman, R. S. (2008). Stress, depression, and neuroplasticity: A convergence of mechanisms. Neuropsychopharmacology, 33(1), 88–109.
Power, J. D., Mitra, A., Laumann, T. O., Snyder, A. Z., Schlaggar, B. L., & Petersen, S. E. (2014). Methods to detect, characterize, and remove motion artifact in resting state fMRI. NeuroImage, 84, 320–341.
Radley, J. J., Rocher, A. B., Miller, M., Janssen, W. G., Liston, C., Hof, P. R., McEwen, B., & Morrison, J. H. (2005). Repeated stress induces dendritic spine loss in the rat medial prefrontal cortex. Cerebral Cortex, 16(3), 313–320.
Roley, M. E., Claycomb, M. A., Contractor, A. A., Dranger, P., Armour, C., & Elhai, J. D. (2015). The relationship between rumination, PTSD, and depression symptoms. Journal of Affective Disorder, 180, 116–121.
Rubin, L. H., Meyer, V. J., J. Conant, R., Sundermann, E. E., Wu, M., Weber, K. M., et al. (2016). Prefrontal cortical volume loss is associated with stress-related deficits in verbal learning and memory in HIV-infected women. Neurobiology of Disease, 92, 166–174.
Sandi, C. (2013). Stress and cognition. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Cognitive Science, 4(3), 245–261.
Sapolsky, R. M. (2000). The possibility of neurotoxicity in the hippocampus in major depression: A primer on neuron death. Biological Psychiatry, 48, 755–765.
Schwabe, L., & Bolam, P. (2017). Memory under stress: From single systems to network changes. European Journal of Neuroscience, 45(4), 478–489.
Schwabe, L., & Wolf, O. T. (2012). Stress modulates the engagement of multiple memory systems in classification learning. Journal of Neuroscience, 32(32), 11042–11049.
Schwabe, L., & Wolf, O. T. (2013). Stress and multiple memory systems: From ‘thinking’ to ‘doing’. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 17(2), 60–68.
Schwabe, L., Dalm, S., Schächinger, H., & Oitzl, M. S. (2008). Chronic stress modulates the use of spatial and stimulus-response learning strategies in mice and man. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 90(3), 495–503.
Schwabe, L., Oitzl, M. S., Richter, S., & Schächinger, H. (2009). Modulation of spatial and stimulus–response learning strategies by exogenous cortisol in healthy young women. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 34(3), 358–366.
Schwabe, L., Joëls, M., Roozendaal, B., Wolf, O. T., & Oitzl, M. S. (2012). Stress effects on memory: An update and integration. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 36(7), 1740–1749.
Schwabe, L., Tegenthoff, M., Höffken, O., & Wolf, O. T. (2013). Mineralocorticoid receptor blockade prevents stress-induced modulation of multiple memory systems in the human brain. Biological Psychiatry, 74(11), 801–808.
Simonovic, B., Stupple, E. J., Gale, M., & Sheffield, D. (2017). Stress and risky decision making: Cognitive reflection, emotional learning or both. Journal of Behavioral Decision Making, 30(2), 658–665.
Song, X. W., Dong, Z. Y., Long, X. Y., Li, S. F., Zuo, X. N., Zhu, C. Z., He, Y., Yan, C. G., & Zang, Y. F. (2011). REST: A toolkit for resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging data processing. PLoS One, 6(9), e25031.
Sterlemann, V., Ganea, K., Liebl, C., Harbich, D., Alam, S., Holsboer, F., Müller, M. B., & Schmidt, M. V. (2008). Long-term behavioral and neuroendocrine alterations following chronic social stress in mice: Implications for stress-related disorders. Hormones and Behavior, 53(2), 386–394.
Stokes, M. G., Kusunoki, M., Sigala, N., Nili, H., Gaffan, D., & Duncan, J. (2013). Dynamic coding for cognitive control in prefrontal cortex. Neuron, 78(2), 364–375.
Travis, S. G., Coupland, N. J., Hegadoren, K., Silverstone, P. H., Huang, Y., Carter, R., Fujiwara, E., Seres, P., & Malykhin, N. V. (2016). Effects of cortisol on hippocampal subfields volumes and memory performance in healthy control subjects and patients with major depressive disorder. Journal of Affective Disorder, 201, 34–41.
Tzourio-Mazoyer, N., Hervé, P. Y., & Mazoyer, B. (2007). Neuroanatomy: Tool for functional localization, key to brain organization. NeuroImage, 37(4), 1059–1060.
Vinkers, C. H., Joels, M., Milaneschi, Y., Kahn, R. S., Penninx, B. W., & Boks, M. P. (2014). Stress exposure across the life span cumulatively increases depression risk and is moderated by neuroticism. Depression and Anxiety, 31(9), 737–745.
Vogel, S., Fernández, G., Joëls, M., & Schwabe, L. (2016). Cognitive adaptation under stress: A case for the mineralocorticoid receptor. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 20(3), 192–203.
Wellman, C. L. (2001). Dendritic reorganization in pyramidal neurons in medial prefrontal cortex after chronic corticosterone administration. Developmental Neurobiology, 49(3), 245–253.
Yan, C. G., Wang, X. D., Zuo, X. N., & Zang, Y. F. (2016). DPABI: Data processing & analysis for (resting-state) brain imaging. Neuroinformatics, 14(3), 339–351.
Youssef, F. F., Dookeeram, K., Basdeo, V., Francis, E., Doman, M., Mamed, D., Maloo, S., Degannes, J., Dobo, L., Ditshotlo, P., & Legall, G. (2012). Stress alters personal moral decision making. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 37(4), 491–498.
Yu, R. (2016). Stress potentiates decision biases: A stress induced deliberation-to-intuition (SIDI) model. Neurobiology of Stress, 3, 83–95.
Zang, Y., Jiang, T., Lu, Y., He, Y., & Tian, L. (2004). Regional homogeneity approach to fMRI data analysis. NeuroImage, 22(1), 394–400.
Zhong, Y., Zhang, R., Li, K., Qi, R., Zhang, Z., Huang, Q., & Lu, G. (2015). Altered cortical and subcortical local coherence in PTSD: Evidence from resting-state fMRI. Acta Radiologica, 56(6), 746–753.
Acknowledgements
We thank J. Hu for collecting the data.
Funding
This study was funded by Natural Scientific Foundation of China (No. 81771186) and MOE Tier 2 (MOE2016-T2–1-015) to RY, and by the Scientific Research Foundation of School of Psychology at South China Normal University (hsxly2017003) to J. Chang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Both authors have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, J., Yu, R. Acute social stress modulates coherence regional homogeneity. Brain Imaging and Behavior 13, 762–770 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-018-9898-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-018-9898-9