Abstract
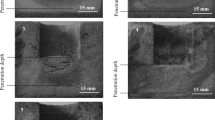
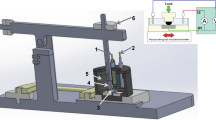
The reactions between MgAlON and MgAlON-BN composites and synthetic CaO-SiO2-Al2O3-MgO-“FeO” slag at different temperatures were investigated under stagnant condition using the ‘‘finger’’ experiment as well as X-ray sessile drop methods. The corrosion rate was denoted by the radius difference between the initial radius of the specimen rod and the unreacted core at definite time intervals. The experimental results showed that the radius difference is linear with the square root of time. This indicated that the diffusion of ions in the slag through the product layer is the rate-determining step. One product layer was observed between the unreacted core and slag. X-ray images showed that gas bubbles were generated during the slag penetration. The slag penetration process depends strongly on the temperature. The apparent activation energy was evaluated to be 376.4 kJ/mol. The FeO addition into slag increased the slag corrosion rate. This is most probably due to the decrease of the slag viscosity, because the Fe+2 generally behaves as a network breaker. Furthermore, MgAlON and boron nitride (BN) can be oxidized by FeO, which also increased the slag corrosion rate. The slag corrosion rate decreased with increasing BN content. This can be explained by the fact that the grain boundary interfacial energy decreases with the increase of BN content and nonwetting of BN by molten slag compared to pure MgAlON.















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
PHILIPS is a trademark of Philips Electronic Instruments Corp., Mahwah, NJ.
REFERENCES
W.E. Lee, S. Zhang: Int. Mater. Rev., 1999, vol. 44 (3), pp. 77–104
N.N. Tripathi, M. Nzotta, A. Sandberg, S.C. Du: Ironmaking Steelmaking, 2004, vol. 31 (6), pp. 235–40
C.F. Chan, B.B. Argent, W.E. Le: J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1998, vol. 81, pp. 3177–88
R.T. Edwards, B. Derby, J. Webster: Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter, 1998, vol. 248, pp. 316–21
K. Goto, B.B. Argent, W.E. Lee: J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1997, vol. 80, pp. 461–71
C.J. Deng, Y.R. Hong, X.C. Zhong, J.L. Sun: Refractories, 2001, vol. 35 (3), pp. 135–37
C.J. Deng, Y.R. Hong, X.C. Zhong, J.L. Sun: Miner. Metall. Mater., 2000, vol.7 (2), pp. 96–98
X.Y. Luo, J.L. Sun, J.X. Wang, Y.R. Hong: Refractories, 2000, vol. 34 (3), pp. 147–50 (in Chinese)
X.T. Wang, B.G. Zhang, H.Z. Wang, J.L. Sun, Y.R. Hong: Refractories, 2004, vol. 38 (2), pp. 66–69 (in Chinese)
G.J. Zhang, J.F. Yang, A. Motohide, O. Tatsuki: J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2002, vol. 22, pp. 2551–54
Z.T. Zhang, T. Matsushita, W.C. Li, S. Seetharaman: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2006, vol. 37B, pp. 421–29
Z.T. Zhang, X.D. Wang, W.C. Li, S. Seetharaman: J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 27, pp. 319–26
Z.T. Zhang, X.D. Wang, W.C. Li, and S. Seetharaman: Z. Metallkd., 2007, vol. 1, pp.64–71
X.D. Wang, S.C. Du, W.C. Li, S. Seetharaman: Steel Res., 2002, vol. 73 (3), pp. 91–96
J. Bygden: Ph.D. Thesis, KTH, Stockholm, 1993, Suppl. IV, pp. 1–10
J. Sune, B. Voicu, and P. Jonsson: Licentiate Thesis, KTH, Stockholm, 2005, Suppl. II, pp. 1–9
Z.S. Li, K. Mukai, Z.N. Tao: ISIJ Int., 2000, vol. 40, pp. S101–S105
H.X. Willems, G. de With, R. Metselaar: J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 1993, vol. 12 (1), pp. 43–49
Emest M. Levin and Howard F. McMurdie: Phase Diagrams for Ceramics, The American Ceramic Society, Ohio, USA, vol. III, p. 4626
O. Matsumoto, T. Isobe, T. Nishitani, and T. Genba: U.S. Patent 4,990,475, 1991
Z. Yu, K. Mukai, K. Kawasaki, I. Furusato: J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn., 1993, vol. 101, pp. 533–39
Y. Kuromitsu, H. Yoshida, H. Takebe, K. Morinaga: J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1997, vol. 80, pp. 1583–87
R. Eriksson, M. Hayashi, S. Seetharaman: Int. J. Thermophys., 2003, vol. 24 (3), pp. 785–97
S.C. Du, J. Bygden, S. Seetharaman: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1994, vol. 25B, pp. 519–25
S. Seetharaman, S.C. Du: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1994, vol. 25B, pp. 589–95
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors thank Drs. Lidong Teng and Era Kapilashrami for their helpful suggestions and contributions during the course of the present investigation. The sample preparation was financially supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China, Grant Nos. 50332010, 50272010, and 50372004.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted January 12, 2006.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Matsushita, T., Li, W. et al. Reactions between MgAlON-BN Composites and CaO-SiO2-Al2O3-MgO-“FeO” Slag. Metall Mater Trans B 38, 231–241 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-007-9038-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-007-9038-1