Abstract
Introduction
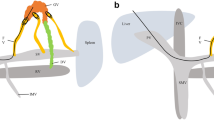
Stomal varices can develop in patients with ostomy in the setting of portal hypertension. Bleeding from the stomal varices is uncommon, but the consequences can be disastrous. Haemorrhage control measures that have been described in the literature include pressure dressings, stomal revision, mucocutaneous disconnection, variceal suture ligation and sclerotherapy. These methods may only serve to temporise the stomal bleeding and have a high risk of recurrent bleed. While transjugular intrahepatic porto-systemic shunting has been advocated as the treatment of choice in patients with underlying liver cirrhosis, histoacryl glue or coil embolisation has been successfully employed in patients who are not suitable candidates for TIPS.
Methods and Results
Direct percutaneous embolisation of the dominant varices was performed successfully under ultrasound and fluoroscopic guidance in two patients using a combination of coils and histoacryl glue.
Results
While transjugular intrahepatic porto-systemic shunting has been advocated as the treatment of choice in patients with underlying liver cirrhosis, histoacryl glue or coil embolisation has been successfully employed in patients who are not suitable candidates for TIPS.
Conclusion
Direct percutaneous embolisation is a safe and effective treatment for stomal varices in selected patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johnson PA, Laurin J. Transjugular portosystemic shunt for treatment of bleeding stomal varices. Digestive diseases and sciences. Feb 1997;42(2):440–442.
Norton ID, Andrews JC, Kamath PS. Management of ectopic varices. Hepatology. Oct 1998;28(4):1154–1158.
Ryu RK, Nemcek AA, Jr., Chrisman HB, et al. Treatment of stomal variceal hemorrhage with TIPS: case report and review of the literature. Cardiovascular and interventional radiology. Jul-Aug 2000;23(4):301–303.
Vidal V, Joly L, Perreault P, Bouchard L, Lafortune M, Pomier-Layrargues G. Usefulness of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in the management of bleeding ectopic varices in cirrhotic patients. Cardiovascular and interventional radiology. Mar-Apr 2006;29(2):216–219.
Medina CA, Caridi JG, Wajsman Z. Massive bleeding from ileal conduit peristomal varices: successful treatment with the transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. The Journal of urology. Jan 1998;159(1):200–201.
Conte JV, Arcomano TA, Naficy MA, Holt RW. Treatment of bleeding stomal varices. Report of a case and review of the literature. Diseases of the colon and rectum. Apr 1990;33(4):308–314.
Han SG, Han KJ, Cho HG, et al. A case of successful treatment of stomal variceal bleeding with transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt and coil embolization. Journal of Korean medical science. Jun 2007;22(3):583–587.
Kishimoto K, Hara A, Arita T, et al. Stomal varices: treatment by percutaneous transhepatic coil embolization. Cardiovascular and interventional radiology. Nov-Dec 1999;22(6):523–525.
Naidu SG, Castle EP, Kriegshauser JS, Huettl EA. Direct percutaneous embolization of bleeding stomal varices. Cardiovascular and interventional radiology. Feb 2010;33(1):201–204.
Hedaya MS, El Moghazy WM, Uemoto S. Living-related liver transplantation in patients with variceal bleeding: outcome and prognostic factors. Hepatobiliary & pancreatic diseases international: HBPD INT. Aug 2009;8(4):358–362.
Kochar N, Tripathi D, McAvoy NC, Ireland H, Redhead DN, Hayes PC (2008) Bleeding ectopic varices in cirrhosis: the role of TIPSS. Alimentary pharmacology & therapeutics, 28(3):294-303.
Alkari B, Shaath NM, El-Dhuwaib Y, et al. Transjugular intrahepatic porto-systemic shunt and variceal embolisation in the management of bleeding stomal varices. International journal of colorectal disease. Sep 2005;20(5):457–462.
Arulraj R, Mangat KS, Tripathi D. Embolization of bleeding stomal varices by direct percutaneous approach. Cardiovascular and interventional radiology. Feb 2011;34 Suppl 2:S210–S213.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwok, A.C.H., Wang, F., Maher, R. et al. The Role of Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Embolisation Technique in the Management of Bleeding Stomal Varices. J Gastrointest Surg 17, 1327–1330 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-013-2180-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-013-2180-y