Summary
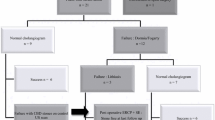
In order to investigate the safety and efficacy of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatograpy (ERCP) in liver cirrhosis patients with common bile duct stones, we retrospectively analyzed data of 46 common bile duct stones patients with liver cirrhosis who underwent ERCP between 2000 and 2008. There were 12 cases of Child-Pugh A, 26 cases of Child-Pugh B, and 8 cases of Child-Pugh C. 100 common bile duct stones patients without liver cirrhosis were randomly selected. All the patients were subjected to ERCP for biliary stones extraction. The rates of bile duct clearance and complications were compared between cirrhotic and non-cirrhotic patients. The success rate of selective biliary cannulation was 95.6% in liver cirrhotic patients versus 97% in non-cirrhotic patients (P>0.05). The bile duct clearance rate was 87% in cirrhotic patients versus 96% in non-cirrhotic patients, but the difference was not statistically significant. Two liver cirrhotic patients (4.35%, 2/46) who were scored Child-Pugh C had hematemesis and melena 24 h after ERCP. The hemorrhage rate after ERCP in non-cirrhotic patients was 3%. The hemorrhage rate associated with ERCP in Child-Pugh C patients was significantly higher (25%, 2/8) than that (3%, 3/100) in non-cirrhotic patients (P<0.01%). There was no significant difference between these two groups in the rate of post-ERCP pancreatitis (PEP) and cholangitis. ERCP is safe and effective for Child-Pugh A and B cirrhotic patients with common bile duct stones. Hemorrhage risk in ERCP is higher in Child-Pugh C patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tanaka R, Itoshima T, Nagashima H. Follow-up study of 582 liver cirrhosis patients for 26 years in Japan. Liver, 1987,7(6):316–324
Del Olmo JA, García F, Serra MA, et al. Prevalence and incidence of gallstones in liver cirrhosis. Scand J Gastroenterol, 1997,32(10):1061–1065
Acaloversuschi M, Badea R, Pascu M. Incidence of gallstones in liver cirrhosis. Am J Gastroenterol, 1991,86(9):1179–1181
Acaloversuschi M, Badea R, Dumitraşcu D, et al. Prevalence of gallstones in liver cirrhosis: a sonographic survey. Am J Gastroenterol, 1988,83(9):954–956
Vanhuyse F, Maureira P, Portocarrero E, et al. Cardiac surgery in cirrhotic patients: results and evaluation of risk factors. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg, 2012,42(2):293–299
Mansour A, Watson W, Shayani V, et al. Abdominal operations in patients with cirrhosis: still a major surgical challenge. Surgery, 1997,122(4):730–736
O’Leary JG, Yachimski PS, Friedman LS. Surgery in the patient with liver disease. Clin Liver Dis, 2009,13(2):211–231
Freitas ML, Bell RL, Duffy AJ. Choledocholithiasis: evolving standards for diagnosis and management. World J Gastroenterol, 2006,12(20):3162–3167
Williams EJ, Green J, Beckingham I, et al. Guidelines on the management of common bile duct stones (CBDS). Gut, 2008,57(7):1004–1021
Itoi T, Wang HP. Endoscopic management of bile duct stones. Dig Endosc, 2010,22(Suppl 1):S69–75
Baron TH, Harewood GC. Endoscopic balloon dilation of the biliary sphincter compared to endoscopic biliary sphincterotomy for removal of common bile duct stones during ERCP: a meta analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Am J Gastroenterol, 2004,99(8):1455–1460
Watanabe H, Yoneda M, Tominaga K, et al. Comparison between endoscopic papillary balloon dilatation and endoscopic sphincterotomy for the treatment of common bile duct stones. J Gastroenterol, 2007,42(1):56–62
Toda N, Saito K, Wada R, et al. Endoscopic sphincterotomy and papillary balloon dilation for bile duct stones. Hepatogastroenterology, 2005,52(63):700–704
Zhao HC, He L, Zhou DC, et al. Meta-analysis comparison of endoscopic papillary balloon dilatation and endoscopic sphincteropapillotomy. World J Gastroenterol, 2013,19(24):3883–3891
Prat F, Tennenbaum R, Ponsot P, et al. Endoscopic sphincterotomy in patients with liver cirrhosis. Gastrointest Endosc, 1996,43(2 Pt 1):127–131
Kawabe T, Komatsu Y, Tada M, et al. Endoscopic papillary balloon dilation in cirrhotic patients: removal of common bile duct stones without sphincterotomy. Endoscopy, 1996,28(8):694–698
Park DH, Kim MH, Lee SK, et al. Endoscopic sphincterotomy versus endoscopic papillary balloon dilation for choledocholithiasis in patients with liver cirrhosis and coagulopathy. Gastrointest Endosc, 2004,60(2):180–185
Child CG, Turcotte JG. Surgery and portal hypertension. Major Probl Clin Surg, 1964;1:1–85
Kamath PS, Wiesner RH, Malinchoc M, et al. A model to predict survival in patients with end-stage liver disease. Hepatology, 2001,33(2):464–470
Cotton PB, Lehman G, Vennes J, et al. Endoscopic sphincterotomy complications and their management: an attempt at consensus. Gastrointest Endosc, 1991,37(3):383–393
Freeman ML, Nelson DB, Sherman S, et al. Complications of endoscopic biliary sphincterotomy. N Engl J Med, 1996,335(13):909–918
Andriulli A, Loperfido S, Napolitano G, et al. Incidence rates of post-ERCP complications: a systematic survey of prospective studies. Am J Gastroenterol, 2007,102(8):1781–1788
Staritz M, Ewe K, Meyer zum Büschenfelde KH. Endoscopic papillary dilation (EPD) for the treatment of common bile duct stones and papillary stenosis. Endoscopy, 1983,15(Suppl 1):197–198
May GR, Cotton PB, Edmunds SE, et al. Removal of stones from the bile duct at ERCP without sphincterotomy. Gastrointest Endosc, 1993,39(6):749–754
Mac Mathuna P, White P, Clarke E, et al. Endoscopic sphincteroplasty: a novel and safe alternative to papillotomy in the management of bile duct stones. Gut, 1994,35(1):127–129
Freeman ML. Adverse outcomes of ERCP. Gastrointest Endosc, 2002,56(6 Suppl):S273–S282
ASGE Standards of Practice Committee, Anderson MA, Fisher L, Jain R, et al. Complications of ERCP. Gastrointest Endosc, 2012,75(3):467–473
Thalheimer U, Triantos CK, Samonakis DN, et al. Infection, coagulation, and variceal bleeding in cirrhosis. Gut, 2005,54(4):556–563
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Dm., Zhao, J., Zhao, Q. et al. Safety and efficacy of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography for common bile duct stones in liver cirrhotic patients. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 34, 612–615 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-014-1325-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-014-1325-x



