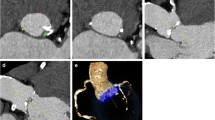
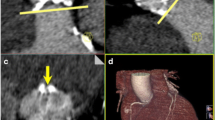
Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the performance of computer-aided evaluation software for a comprehensive workup of patients prior to transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) using low-contrast agent and low radiation dose third-generation dual-source CT angiography.
Methods
We evaluated 30 consecutive patients scheduled for TAVI. All patients underwent ECG-triggered high-pitch dual-source CT angiography of the aortic root and aorta with a standardized contrast agent volume (30 ml Imeron350, flow rate 4 ml/s) and low-dose (100 kv/350 mAs) protocol. An expert (10 years of experience) manually evaluated aortic root and iliac access dimensions (distance between coronary ostia and aortic annulus, minimal/maximal diameters and area-derived diameter of the aortic annulus) and best CT-predicted fluoroscopic projection angle as the reference standard. Utilizing computer-aided software (syngo.via), the same pre-TAVI workup was performed and compared to the reference standard.
Results
Mean CTDI\(_\mathrm{vol}\) was 3.46 mGy and mean DLP 217.6 ± 12.1 mGy cm, corresponding to a mean effective dose of 3.7 ± 0.2 mSv. Computer-aided evaluation was successful in all but one patient. Compared to the reference standard, Bland–Altman analysis indicated very good agreement for the distances between aortic annulus and coronary ostia (RCA: mean difference 0.8 mm; 95 % CI 0.4–1.2 mm; LM: mean difference 0.9 mm; 95 % CI 0.5–1.3 mm); however, we demonstrated a systematic overestimation of annulus- derived diameter using the software (mean difference 44.4 mm\(^{2}\); 95 % CI 30.4–58.3 mm\(^{2}\)). Based on respective annulus dimensions, the recommended prosthesis size (Edwards SAPIEN 3) matched in 26 out of the 29 patients (90 %). CT-derived fluoroscopic projection angles showed an excellent agreement for both methods. Out of 58 iliac arteries, 15 (25 %) arteries could not be segmented by the software. Preprocessing time of the software was 71 ± 11 s (range 51–96 s), and reading time with the software was 118 ± 31 s (range 68–201 s).
Conclusion
In the workup of pre-TAVI CT angiography, computer-aided evaluation of low-contrast, low-dose examinations is feasible with good agreement and quick reading time. However, a systematic overestimation of the aortic annulus area is observed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Webb J, Cribier A (2011) Percutaneous transarterial aortic valve implantation: what do we know? Eur Heart J 32(2):140–147
Kim CA, Rasania SP, Afilalo J, Popma JJ, Lipsitz LA, Kim DH (2014) Functional status and quality of life after transcatheter aortic valve replacement: a systematic review. Ann Intern Med 160(4):243–254
Makkar RR, Fontana GP, Jilaihawi H, Kapadia S, Pichard AD, Douglas PS (2012) Transcatheter aortic-valve replacement for inoperable severe aortic stenosis. N Engl J Med 366(18):1696–1704
Schuhbaeck A, Achenbach S, Pflederer T, Marwan M, Schmid J, Nef H, Rixe J, Hecker F, Schneider C, Lell M, Uder M, Arnold M (2014) Reproducibility of aortic annulus measurements by computed tomography. Eur Radiol 24(8):1878–1888
Blanke P, Schoepf UJ, Leipsic JA (2013) CT in transcatheter aortic valve replacement. Radiology 269(3):650–669
Geyer LL, De Cecco CN, Schoepf UJ, Silverman JR, Krazinski AW, Bamberg F, Steinberg DH (2015) Low-volume contrast medium protocol for comprehensive cardiac and aortoiliac CT assessment in the context of transcatheter aortic valve replacement. Acad Radiol 22(9):1138–1146
Ferro CJ, Chue CD, de Belder MA, Moat N, Wendler O, Trivedi U, Ludman P, Townend JN (2015) Impact of renal function on survival after transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI): an analysis of the UK TAVI registry. Heart 101(7):546–552
Huda W (2015) Radiation risks: what is to be done? AJR Am J Roentgenol 204(1):124–127
Achenbach S, Manolopoulos M, Schuhbäck A, Ropers D, Rixe J, Schneider C, Krombach GA, Uder M, Hamm C, Daniel WG, Lell M (2012) Influence of heart rate and phase of the cardiac cycle on the occurrence of motion artifact in dual-source CT angiography of the coronary arteries. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr 6(2):91–98
McCollough CH, Primak AN, Saba O, Bruder H, Stierstorfer K, Raupach R, Suess C, Schmidt B, Ohnesorge BM, Flohr TG (2007) Dose performance of a 64-channel dual-source CT scanner. Radiology 243(3):775–784
Grbic S, Mansi T, Ionasec R, Voigt I, Houle H, John M, Schoebinger M, Navab N, Comaniciu D (2013) Image-based computational models for TAVI planning: from CT images to implant deployment. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv 16(Pt 2):395–402
Swee JK, Grbić S (2014) Advanced transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) planning from CT with ShapeForest. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv 17(Pt 2):17–24
Bongartz G, Golding SJ, Jurik AG, Leonardi M, van Persijn van Meerten E, Rodriguez R, Schneider K, Calzado A, Geleijens J, Jessen KA, Panzer W, Shrimpton PC, Tosi G (2004) European Guidelines for multislice computed tomography: funded by the European Commission, Contract number FIGM-CT2000-20078-CT-TIP. http://www.msct.eu/CT_Quality_Criteria.htm. Accessed 10 March 2016
Wuest W, Anders K, Schuhbaeck A, May MS, Gauss S, Marwan M, Arnold M, Ensminger S, Muschiol G, Daniel WG, Uder M, Achenbach S (2012) Dual source multidetector CT-angiography before transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) using a high-pitch spiral acquisition mode. Eur Radiol 22(1):51–58
Watanabe Y, Morice MC, Bouvier E, Leong T, Hayashida K, Lefèvre T, Hovasse T, Romano M, Chevalier B, Donzeau-Gouge P, Farge A, Cormier B, Garot P (2013) Automated 3-dimensional aortic annular assessment by multidetector computed tomography in transcatheter aortic valve implantation. JACC Cardiovasc Interv 6(9):955–964
Van Linden A, Kempfert J, Blumenstein J, Möllmann H, Kim WK, Alkaya S, Hamm C, Walther T (2014) Manual versus automatic detection of aortic annulus plane in a computed tomography scan for transcatheter aortic valve implantation screening. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 46(2):207–212
Lou J, Obuchowski NA, Krishnaswamy A, Popovic Z, Flamm SD, Kapadia SR, Svensson LG, Bolen MA, Desai MY, Halliburton SS, Tuzcu EM, Schoenhagen P (2015) Manual, semiautomated, and fully automated measurement of the aortic annulus for planning of transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR/TAVI): analysis of interchangeability. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr 9(1):42–49
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest in the research. Mohamed Marwan received speaker Honoria from Edwards Lifesciences. Michael Uder received speaker Honoria from Bayer Healthcare and Siemens Healthcare. Alexander Cavallaro received speaker Honoria from Siemens Healthcare.
Additional information
Peter Dankerl and Matthias Hammon have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dankerl, P., Hammon, M., Seuss, H. et al. Computer-aided evaluation of low-dose and low-contrast agent third-generation dual-source CT angiography prior to transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI). Int J CARS 12, 795–802 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-016-1470-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-016-1470-8