Abstract
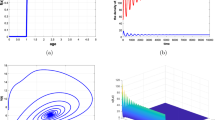
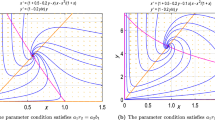
In this paper, we study a predator–prey system with random predator dispersal over two habitat patches. We show that in most cases the dispersal delay does not affect the stability and instability of the coexistence equilibrium. However, if the mean time that the predator spent in one patch is much shorter than the timescale of reproduction of the prey and is larger than the double mean time of capture of prey, the dispersal delay can induce stability switches such that an otherwise unstable coexistence equilibrium can be stabilized over a finite number of stability intervals.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cooke KL, Grossman Z (1982) Discrete delay, distributed delay and stability switches. J Math Anal Appl 86(2):592–627
Edwards R, van den Driessche P, Wang L (2007) Periodicity in piecewise-linear switching networks with delay. J Math Biol 55(2):271–298
El Abdllaoui A, Auger P, Kooi BW, De la Parra RB, Mchich R (2007) Effects of density-dependent migrations on stability of a two-patch predator-prey model. Math Biosci 210(1):335–354
Feng W, Hinson J (2005) Stability and pattern in two-patch predator-prey population dynamics. Discrete Contin Dyn Syst Suppl 2005:268–279
Feng W, Rock B, Hinson J (2011) On a new model of two-patch predator prey system with migration of both species. J Appl Anal Comput 1(2):193–203
Freedman HI (1987) Single species migration in two habitats: persistence and extinction. Math Model 8:778–780
Hale JK, Verduyn Lunel SM (1993) Introduction to Functional differential equations, vol 99. Springer, Berlin
Hauzy C, Gauduchon M, Hulot FD, Loreau M (2010) Density-dependent dispersal and relative dispersal affect the stability of predator-prey metacommunities. J Theor Biol 266(3):458–469
Holyoak M, Lawler SP (1996) The role of dispersal in predator-prey metapopulation dynamics. J Anim Ecol 65(5):640–652
Hsu S-B (1978) On global stability of a predator-prey system. Math Biosci 39(1–2):1–10
Huffaker CB, Kennett CE (1956) Experimental studies on predation: predation and cyclamen-mite populations on strawberries in california. Hilgardia 26(4):191–222
Jansen VAA (2001) The dynamics of two diffusively coupled predator-prey populations. Theor Popul Biol 59(2):119–131
Kang Y, Sourav KS, Komi M (2017) A two-patch prey-predator model with predator dispersal driven by the predation strength. Math Biosci Eng 14(4):843–880
Klepac P, Neubert MG, van den Driessche P (2007) Dispersal delays, predator-prey stability, and the paradox of enrichment. Theor Popul Biol 71(4):436–444
Kot M (2001) Elements of mathematical ecology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Kuang Y (1993) Delay differential equations: with applications in population dynamics, vol 191. Academic Press, New York
Kuang Y, Takeuchi Y (1994) Predator-prey dynamics in models of prey dispersal in two-patch environments. Math Biosci 120(1):77–98
Levin SA (1974) Dispersion and population interactions. Am Nat 108(960):207–228
Liao K-L, Lou Y (2014) The effect of time delay in a two-patch model with random dispersal. Bull Math Biol 76(2):335–376
Mai A, Sun G, Zhang F, Wang L (2019) The joint impacts of dispersal delay and dispersal patterns on the stability of predator-prey metacommunities. J Theor Biol 462:455–465
Mchich R, Auger P, Poggiale J-C (2007) Effect of predator density dependent dispersal of prey on stability of a predator-prey system. Math Biosci 206(2):343–356
Nathan R, Giuggioli L (2013) A milestone for movement ecology research. Mov Ecol 1:1–1
Neubert MG, Klepac P, van den Driessche P (2002) Stabilizing dispersal delays in predator-prey metapopulation models. Theor Popul Biol 61(3):339–347
Pillai P, Gonzalez A, Loreau M (2011) Evolution of dispersal in a predator-prey metacommunity. Am Nat 179(2):204–216
Wall E, Guichard F, Humphries AR (2013) Synchronization in ecological systems by weak dispersal coupling with time delay. Theor Ecol 6(4):405–418
Wang W, Takeuchi Y (2009) Adaptation of prey and predators between patches. J Theor Biol 258(4):603–613
Wang X, Zou X (2016) On a two-patch predator-prey model with adaptive habitancy of predators. Discrete Contin Dyn Syst Ser B 21(2):677–697
Whitten KR, Garner GW (1992) Productivity and early calf survival in the porcupine caribou herd. J Wildl Manag 56(2):201
Zhang Y, Lutscher F, Guichard F (2015) The effect of predator avoidance and travel time delay on the stability of predator-prey metacommunities. Theor Ecol 8(3):273–283
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the anonymous referee for his/her valuable comments and suggestions, which greatly helped us improve the presentation of this paper. This work is partially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11526183), China Scholarship Council (201608140214), Foundation of Yuncheng University (YQ-2017003), Biomathematics Laboratory of Yuncheng University (SWSX201502, SWSX201602) and by a discovery grant from NSERC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mai, A., Sun, G. & Wang, L. Impacts of the Dispersal Delay on the Stability of the Coexistence Equilibrium of a Two-Patch Predator–Prey Model with Random Predator Dispersal. Bull Math Biol 81, 1337–1351 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-018-00568-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-018-00568-8