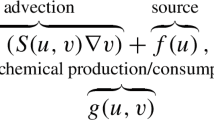Abstract
We propose a deterministic continuum model for mixed-culture biofilms. A crucial aspect is that movement of one species is affected by the presence of the other. This leads to a degenerate cross-diffusion system that generalizes an earlier single-species biofilm model. Two derivations of this new model are given. One, like cellular automata biofilm models, starts from a discrete in space lattice differential equation where the spatial interaction is described by microscopic rules. The other one starts from the same continuous mass balances that are the basis of other deterministic biofilm models, but it gives up a simplifying assumption of these models that has recently been criticized as being too restrictive in terms of ecological structure. We show that both model derivations lead to the same PDE model, if corresponding closure assumptions are introduced. To investigate the role of cross-diffusion, we conduct numerical simulations of three biofilm systems: competition, allelopathy and a mixed system formed by an aerobic and an anaerobic species. In all cases, we find that accounting for cross-diffusion affects local distribution of biomass, but it does not affect overall lumped quantities such as the total amount of biomass in the system.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida C, Azevedo NF, Santos S, Keevil CW, Vieira MJ (2011) Discriminating multi-species populations in biofilms with peptide nucleic acid fluorescence in situ hybridization (PNA FISH). Plos ONE 6(3):e14786
Alpkvist E, Klapper I (2007) A multidimensional multispecies continuum model for heterogeneous biofilm development. Bull Math Biol 69(2):765789
Anguige K, King JR, Ward JP (2005) Modelling antibiotic- and anti-quorum sensing treatment of a spatially-structured Pseudomonas aeruginosa population. J Math Biol 51:557–594
Anguige K, Schmeiser C (2009) A one-dimensional model of cell-diffusion and aggregation, incorporating volume filling and cell-to-cell adhesion. J Math Biol 58:395–427
Bryers JD, Drummond F (1998) Local macromolecule diffusion coefficients in structurally non-uniform bacterial biofilms using fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP). Biotechnol Bioeng 60(4):462–473
Chambless JD, Hunt SM, Stewart PS (2006) A three-dimensional computer model of four hypothetical mechanisms protecting biofilms from antimicrobials. Appl Environ Mivrobiol 72(3):2005–2013
Clarelli F, Di Russo C, Natalini R, Ribot M (2013) A fluid dynamics model of the growth of phototrophic biofilms. J Math Biol 66(7):1387–1408
Cogan NG (2008) Two-fluid model of biofilm disinfection. Bull Math Biol 70:800–819
Costerton JW, Stewart PS, Greenberg EP (1999) Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections. Science 248(5418):13181322
Cumsille P, Asenjoc JA, Concad C (2014) A novel model for biofilm growth and its resolution by using the hybrid immersed interface-level set method. Comput Math Appl 67(1):34–51
Dockery J, Klapper I (2001) Finger formation in biofilm layers. SIAM J Appl Math 62(3):853–869
Duddu R, Chopp DL, Moran B (2009) A two-dimensional continuum model of biofilm growth incorporating fluid flow and shear stress based detachment. Biotechnol Bioeng 103(1):92–104
Eberl HJ, Demaret L (2007) A finite difference scheme for a doubly degenerate diffusion–reaction equation arising in microbial ecology. J Differ Equ CS15:77–95
Eberl HJ, Sudarsan R (2008) Exposure of biofilms to slow flow fields: the convective contribution to growth and disinfection. J Theor Biol 253(4):788–807
Eberl HJ, Collinson MS (2009) A modeling and simulation study of siderophore mediated antagonism in dual-species biofilms. Theor Biol Med Mod 6:30
Eberl H, Parker DF, van Loosdrecht MCM (2001) A new deterministic spatio-temporal continuum model for biofilm development. J Theor Med 3:161–175
Eberl HJ, Khassekhan H, Demaret L (2010) A mixed-culture model of a probiotic biofilm control system. Comput Math Methods Med 11(2):99–118
Efendiev MA, Eberl HJ, Zelik SV (2002) Existence and longtime behavior of solutions of a nonlinear reaction–diffusion system arising in the modeling of biofilms. RIMS Kyoto Kokyuroko 1258:49–71
Efendiev MA, Zelik SV, Eberl HJ (2009) Existence and longtime behavior of a biofilm Model. Commun Pure Appl Math 8(2):509–531
Emerenini BO, Hense BA, Kuttler C, Eberl HJ (2015) A mathematical model of quorum sensing induced biofilm detachment. Plos ONE 10(7):e0132385
Fratamico PM, Annous BA, Gunther NW IV (eds) (2009) Biofilms in the food and beverage industries. Woodhead Publishing, CRC Press, Boca Raton
Fgaier H, Kalmokoff M, Ells T, Eberl HJ (2014) An allelopathy based model for the Listeria overgrowth phenomenon. Math Biosci 247:13–26
Frederick MR, Kuttler C, Hense BA, Eberl HJ (2011) A mathematical model of quorum sensing regulated EPS production in biofilm communities. Theor Biol Med Model 8:8
Frederick MR, Kuttler C, Hense BA, Müller J, Eberl HJ (2010) A mathematical model of quorum sensing in patchy biofilm communities with slow background flow. Can Appl Math Q 18(3):267–298
Friedman A, Hu B, Xue C (2014) On a multiphase multicomponent model of biofilm growth. Arch Ration Mech Anal 211(1):257–300
Hunt SM, Werner EM, Huang B, Hamilton MA, Stewart PS (2004) Hypothesis for the role of nutrient starvation in biofilm detachment. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:7418–7425
Hunt SM, Hamilton MA, Stewart PS (2005) A 3D model of antimicrobial action on biofilms. Water Sci Technol 52(7):143–148
Jalbert E, Eberl HJ (2014) Numerical computation of sharp travelling waves of a degenerate diffusion-reaction equation arising in biofilm modelling. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Sim 19(7):2181–2190
Kepka G (2008) Interaction of Pseudomonas putida and Listeria monocytogenes in mixed culture biofilms. M.Sc. thesis, Lakehead University
Khassehkhan H, Efendiev MA, Eberl HJ (2009a) A degenerate diffusion reaction model of an amensalistic probiotic biofilm control system: existence and simulation of solutions. Discrete Contin Dyn Syst B 12(2):371–388
Khassehkhan H, Hillen T, Eberl HJ (2009b) A nonlinear master equation for a degenerate diffusion model of biofilm growth. LNCS, vol. 5544, pp. 735–744
Klapper I, Dockery J (2010) Mathematical description of microbial biofilms. SIAM J Appl Math 52(2):221265
Klapper I, Szomolay B (2011) An exclusion principle and the importance of mobility for a class of biofilm models. Bull Math Biol 73(9):2213–2230
Koza A, Hallett PD, Moon CD, Spiers AJ (2009) Characterization of a novel air–liquid interface biofilm of Pseudomonas fluorescens SBW25. Microbiology 155(5):1397–1406
Kreft J-U (2004) Biofilms promote altruism. Microbiology 150(8):2751–2760
Lewandowski Z (2011) Biofilms in water and wastewater treatment. In: Wilderer P (ed) Treatise on water science. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 529–570
Lewandowski Z, Beyenal H (2007) Fundamentals of biofilm research. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Lizavan M, Padorn V (1999) A spatially discrete model of aggregating populations. J Math Biol 38:79–102
Logan BE, Hamelers B, Rozendal R, Schroder U, Keller J, Freguia S, Aelterman P, Verstraete W, Rabaey K (2006) Microbial fuel cells: methodology and technology. Environ Sci Technol 40(17):51815192
Lindley B, Wang Q, Zhang T (2011) A multicomponent model for biofilm–drug interaction. DCDS-B 15(2):417–456
Merkey BV, Chopp DL (2014) Modeling the impact of interspecies competition on performance of a microbial fuel cell. Bull Math Biol 76(6):1429–1453
Merkey BV, Rittman BE, Chopp DL (2009) Modeling how soluble microbial products (SMP) support heterotrophic bacteria in autotroph-based biofilms. J Theor Biol 259(4):670–683
Muhammad N, Eberl HJ (2010) OpenMP parallelization of a Mickens time-integration scheme for a mixed-culture biofilm model and its performance on multi-core and multi-processor computers. LNCS, vol. 5976, pp. 180–195
Muhammad N, Eberl HJ (2011) Model parameter uncertainties in a dual-species biofilm competition model affect ecological output parameters much stronger than morphological ones. Math Biosci 233(1):1–18
Nielsen AT, Tolker-Nielsen T, Barken KB, Molin S (2000) Role of commensal relationships on the spatial structure of a surface-attached microbial consortium. Environ Microbiol 2(1):59–68
Noguera DR, Pizarro G, Stahl DA, Rittmann BE (1999) Simulation of multispecies biofilm development in three dimensions. Water Sci Technol 39(7):123–130
Okubo A, Levin SA (1980) Diffusion in ecological problems: modern perspectives, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin
Ostrander S (2011) Macroscopic cross-diffusion models derived from spatially discrete continuous time microscopic models. SIAM SIURO. doi:10.1137/10S010818
Painter K, Hillen T (2002) Volume-filling and quorum sensing in models for chemosensitive movement. Can Appl Math Q 10:501–543
Picioreanu C, van Loosdrecht MCM, Heijnen JJ (1998) A new combined differential-discrete cellular automaton approach for biofilm modeling: application for growth in gel beads. Biotechnol Bioeng 57(6):718–731
Picioreanu C, Kreft J, van Loosdrecht MCM (2004) Particle-based multidimensional multispecies biofilm model. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(5):3024–3040
Prieto-Langarica A, Kojouharov HV, Chen-Charpentier BM (2012a) Discrete and continuous approaches to modeling cell movement in the presence of a foreign stimulus. Comput Math Appl 64(3):167–174
Prieto-Langarica A, Kojouharov HV, Chen-Charpentier BM (2012b) Upscaling from discrete to continuous mathematical models of two interacting populations. Comput Math Appl 66(9):1606–1612
Purevdorj-Gage B, Costerton WJ, Stoodley P (2005) Phenotypic differentiation and seeding dispersal in non-mucoid and mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Microbiology 151:1569–1576
Rahman KA, Eberl HJ (2014) Numerical treatment of a cross-diffusion model of biofilm exposure to antimicrobials. LNCS 8384:134–144
Rittmann BE, McCarty PL (2001) Environmental biotechnology: principles and applications. McGraw-Hill, New York
Sauer K, Camper AK, Ehrlich GD, Costerton JW, Davies DG (2002) Pseudomonas aeruginosa displays multiple phenotypes during development as a biofilm. J Bacteriol 184(1140–1154):2001
Seminara A, Angelini TE, Wilking JN, Vlamakis H, Ebrahim S, Kolter R, Weitz DA, Brenner MP (2012) Osmotic spreading of Bacillus subtilis biofilms driven by an extracellular matrix. PNAS 109(4):116–1121
Shigesada N, Kawasaki K, Teramoto E (1979) Spatial segregation of interacting species. J Theor Biol 79(1):83–99
Sonner S, Efendiev MA, Eberl HJ (2011) On the well-posedness of a mathematical model of quorum-sensing in patchy biofilm communities. Math Methods Appl Sci 34(13):1667–1684
Sneddon IA (1961) Special functions of mathematical physics and chemistry. Oliver & Boyd, Edinburgh
Stevens A, Othmer HG (1997) Aggregation, blowup, and collapse: the ABC’s of taxis in reinforced random walks. SIAM J Appl Math 57(4):10441081
Stewart PS (2003) Diffusion in biofilms. J Bacteriol 185:1485–1491
Tan S, Yu T, Shi H-C (2014) Microsensor determination of multiple microbial processes in an oxygen-based membrane aerated biofilm. Water Sci Technol 69(5):909–914
Tang Y, Valocchi AJ (2013) An improved cellular automaton method to model multispecies biofilms. Water Res 47:5729–5742
Terada A, Lackner S, Kristensen K, Smets BF (2010) Inoculum effects on community composition and nitration performance of autotrophic nitrifying biofilm reactors with counter-diffusion geometry. Environ Microbiol 12(10):2858–2872
Tolker-Nielsen T, Molin S (2000) Spatial organization of microbial biofilm communities. Microb Ecol 40(2):75–84
Turner S, Sherratt JA, Painter KJ (2004) From a discrete to a continuous model of biological cell movement. Phys Rev E 69:1–10
van Loosdrecht MCM, Heijnen JJ, Eberl H, Kreft J, Picioreanu C (2002) Mathematical modelling of biofilms structures. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 81:245–256
Vaughan BL, Smith BG, Chopp DL (2010) The influence of fluid flow on modeling quorum sensing in bacterial biofilms. Bull Math Biol 72(5):1143–1165
Visser AW (2008) Lagrangian modelling of plankton motion: from deceptively simple random walks to Fokker–Planck and back again. J Mar Sys 70:287–299
Wang R, Terada A, Lackner S, Smets BF, Henze M, Xia S, Zhao J (2009) Nitration performance and biofilm development of co- and counter-diffusion biofilm reactors: modeling and experimental comparison. Water Res 43:2699–2709
Wanner O, Gujer W (1986) A multispecies biofilm model. Biotechnol Bioeng 28(3):314–328
Wanner O, Eberl H, Morgenroth E, Noguera D, Picioreanu C, Rittmann B, van Loosdrecht M (2006) Mathematical modeling of biofilms. IWA Publishing, London
Ward JP, King JR (2012) Thin-film modelling of biofilm growth and quorum sensing. J Eng Math 73(1):71–92
Wood BD, Whitaker S (1999) Cellular growth in biofilms. Biotechnol Bioeng 64(6):656–670
Xavier JB, Picioreanu C, van Loosdrecht MCM (2005) A framework for multidimensional modelling of activity and structure of multispecies biofilms. Environ Microbiol 7(8):1085–1103
Xavier JB, Picioreanu C, van Loosdrecht MCM (2004) A modelling study of the activity and structure of biofilms in biological reactors. Biofilms 1(4):377–391
Zhang T (2012) Modeling of biocide action against biofilm. Bull Math Biol 74:1427–1447
Zhang T, Cogan NG, Wang Q (2008) Phase-field models for biofilms II. 2-D numerical simulations of biofilm-flow interaction. Commun Comput Phys 4(1):72–101
Acknowledgments
This study was support by the Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) under a Discovery Grant awarded to HJE and by the Canada Research Chairs Program. The computing equipment used in this study was a SGI Altix 450 funded by the Canada Foundation for Innovation through a New Leaders Opportunity Grant and operated by SHARCNET, an SGI Altix UV and custom-built Intel Xeon workstation funded by NSERC through a Research Tool and Infrastructure Grant and operated by the Department of Mathematics and Statistics. The authors thank Kaizaad Bilimorya (SHARCNET) and Larry Banks (Dept. Math & Stats) for the technical support. The authors thank Greg Kepka (Lakehead University) for providing the CLSM images.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahman, K.A., Sudarsan, R. & Eberl, H.J. A Mixed-Culture Biofilm Model with Cross-Diffusion. Bull Math Biol 77, 2086–2124 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-015-0117-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-015-0117-1