Abstract
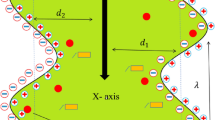
We consider the mathematical model of dynamic antimicrobial action against bacterial biofilms. A mixture model is used in which the biofilm consisting of live and dead bacteria is modeled as one fluid component, while the solvent containing biocide is modeled as the other, and each component is represented by its volume fraction. The whole system is assumed to be an incompressible fluid and the velocity is governed by the Navier–Stokes equation. Biocide kills the live bacteria and its transport is governed by an advection–reaction–diffusion equation. Certain biocide also weakens the mechanical cohesiveness of the biofilm and results in biofilm removal under the shear stress of the external flow. Spatial and temporal patterns of antimicrobial action of three different biocides are considered and numerical simulation results by finite difference method are presented.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anguige, K., King, J. R., & Ward, J. P. (2005). Modelling antibiotic- and anti-quorum sensing treatment of a spatially-structured pseudomonas aeruginosa population. J. Math. Biol., 51, 557–594.
Chambless, J. D., Hunt, S. M., & Stewart, P. S. (2006). A three-dimensional computer model of four hypothetical mechanisms protecting biofilms from antimicrobials. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 72, 2005–2013.
Characklis, W. G., & Marshall, K. C. (1990). Biofilms. New York: Wiley.
Cogan, N. G. (2008). Two-fluid model of biofilm disinfection. Bull. Math. Biol., 70, 800–819.
Cogan, N. G., Cortez, R., & Fauci, L. (2005). Modeling physiological resistance in bacterial biofilms. Bull. Math. Biol., 67, 831–853.
Costerton, J. W., Lewandowski, Z., Caldwell, D. E., Korber, D. R., & Lappin-Scott, H. M. (1995). Microbial biofilms. Annu. Rev. Microbiol., 49, 711–745.
Davison, W. M., Pitts, B., & Stewart, P. S. (2010). Spatial and temporal patterns of biocide action against staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 54, 2920–2927.
Demaret, L., Eberl, H. J., Efendiev, M. A., & Lasser, R. (2008). Analysis and simulation of a meso-scale model of diffusive resistance of bacterial biofilms to penetration of antibiotics. Adv. Math. Sci. Appl., 18, 269–304.
Dodds, M. G., Grobe, K. J., & Stewart, P. S. (2000). Modeling biofilm antimicrobial resistance. Biotechnol. Bioeng., 68, 456–465.
Doi, M. (1995). Introduction to polymer physics. Oxford: Oxford Science Publications.
Eberl, H. J., & Sudarsan, R. (2008). Exposure of biofilms to slow flow fields: The convective contribution to growth and disinfection. J. Theor. Biol., 253, 788–807.
Gibbons, R. J., & van Houte, J. (1980). Bacterial adherence and the formation of dental plaque. In E. M. Beachey (Ed.), Bacterial adherence (pp. 61–104). London: Chapman & Hall.
Guermond, J. L., Minev, P., & Shen, J. (2006). An overview of projection methods for incompressible flows. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng., 95, 6011–6045.
Hinson, R. K., & Kocher, W. M. (1996). Model for effective diffusivities in aerobic biofilms. J. Environ. Eng., 122(11), 1023–1030.
Jesaitis, A. J., Franklin, M. J., Berglund, D., Sasaki, M., Lord, C. I., Bleazard, J. B., Duffy, J. E., Beyenal, H., & Lewandowski, Z. (2003). Compromised host defense on pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms: characterization of neutrophil and biofilm interactions. J. Immunol., 171, 4329–4339.
Klapper, I., & Dockery, J. (2010). Mathematical description of microbial biofilms. SIAM Rev., 52, 221–265.
Lewis, K. (2001). Riddle of biofilm resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 45, 999–1007.
Lindley, B., Wang, Q., & Zhang, T. (2011). A multicomponent model for biofilm-drug interaction. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst., Ser. B, 15, 417–456.
Ol’shanskii, M. A., & Staroverov, V. M. (2000). On simulation of outflow boundary conditions in finite difference calculations for incompressible fluid. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids, 33, 499–534.
Passerini, L., Lam, K., Costerton, J. W., & King, E. G. (1992). Biofilms on indwelling vascular catheters. Clin. Crit. Care Med., 20, 665–673.
Saad, Y., & Schultz, M. H. (1986). Gmres: A generalized minimal residual algorithm for solving nonsymmetric linear systems. SIAM J. Sci. Stat. Comput., 7, 856–869.
Sanderson, S. S., & Stewart, P. S. (1997). Evidence of bacterial adaptation to monochloramine in pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms and evaluation of biocide action model. Biotechnol. Bioeng., 56, 201–209.
Schein, O. D., Glynn, R. J., Seddon, J. M., & Kenyon, K. R. (1989). The relative risk of ulcerative keratitis among users of daily-wear and extended-wear soft contact lenses. N. Engl. J. Med., 321, 773–778.
Shaw, T., Winston, M., Rupp, C. J., Klapper, I., & Stoodley, P. (2004). Commonality of elastic relaxation times in biofilms. Phys. Rev. Lett., 93, 098102.
Stewart, P.S. (1996). Theoretical aspects of antibiotic diffusion into microbial biofilms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 40, 2517–2522.
Stewart, P. S. (2002). Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in bacterial biofilms. Int. J. Med. Microbiol., 292, 107–113.
Stewart, P. S. (2003). Diffusion in biofilms. J. Bacteriol., 185, 1485–1491.
Stewart, P. S., & Costerton, J. W. (2001). Antibiotic resistance of bacteria in biofilms. Lancet, 358, 135–138.
Stickler, D., Ganderton, L., King, J., Nettleton, J., & Winters, C. (1993). Proteus mirabilis biofilms and the encrustation of urethral catheters. Urol. Res., 21(6), 407–411.
Szomolay, B., Klapper, I., Dockery, J., & Stewart, P. S. (2005). Adaptive responses to antimicrobial agents in biofilms. Environ. Microbiol., 7, 1186–1191.
Zhang, T., & Klapper, I. (2010). Mathematical model of biofilm induced calcite precipitation. Water Sci. Technol., 61, 2957–2964.
Zhang, T., Cogan, N., & Wang, Q. (2008a). Phase-field models for biofilms I. Theory and simulations. SIAM J. Appl. Math., 69, 641–669.
Zhang, T., Cogan, N., & Wang, Q. (2008b). Phase-field models for biofilms. II. 2-D numerical simulations of biofilm-flow interaction. Commun. Comput. Phys., 4, 72–101.
Acknowledgements
T. Zhang is supported by NSF through Grant DMS-0934696. The author thanks Philip Stewart for many helpful suggestions and comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, T. Modeling of Biocide Action Against Biofilm. Bull Math Biol 74, 1427–1447 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-012-9719-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-012-9719-z