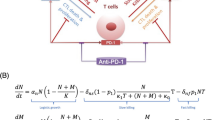
Abstract
The surface protein B7-H1, also called PD-L1 and CD274, is found on carcinomas of the lung, ovary, colon, and melanomas but not on most normal tissues. B7-H1 has been experimentally determined to be an antiapoptotic receptor on cancer cells, where B7-H1-positive cancer cells have been shown to be immune resistant, and in vitro experiments and mouse models have shown that B7-H1-negative tumor cells are significantly more susceptible to being repressed by the immune system. We derive a new mathematical model for studying the interaction between cytotoxic T cells and tumor cells as affected by B7-H1. By integrating experimental data into the model, we isolate the parameters that control the dynamics and obtain insights on the mechanisms that control apoptosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberts, B., Johnson, A., Lewis, J., Raff, M., Roberts, K., & Walter, P. (2008). Molecular biology of the cell (5th ed.). New York: Garland Science.
Azuma, T., Yao, S., Gefeng, Z., Flies, A. S., Flies, S. J., & Chen, L. (2008). B7-H1 is a ubiquitous antiapoptotic receptor on cancer cells. Blood, 111(7), 3635–3643.
Bellomo, N., Bellouquid, A., & DeAngelis, E. (2003). The modelling of the immune competition by generalized kinetic (Boltzmann) models: review and research perspectives. Math. Comput. Model., 37, 65–86.
Berger, R., Rotem-Yehudar, R., Slama, G., Landes, S., Kneller, A., Leiba, M., Koren-Michowitz, M., Shimoni, A., & Nagler, A. (2008). Phase I safety and pharmacokinetic study of CT-011, a humanized antibody interacting with PD-1, in patients with advances hematologic malignancies. Clin. Cancer Res., 14, 3044–3051.
Chen, L. (2004). Co-inhibitory molecules of the B7-CD28 family in the control of T-cell immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol., 4, 336–347.
de Pillis, L. G., Radunskaya, A. E., & Wiseman, C. L. (2005). A validated mathematical model of cell-mediated immune response to tumor growth. Cancer Res., 65(17), 7950–7958.
Dong, H., Strome, S. E., Salomao, D. R., Tamura, H., Hiaro, F., Flies, D. B., Roche, P. C., Lu, J., & Zhu, G. (2002). Tumor-associated B7-H1 promotes T-cell apoptosis: a potential mechanism of immune evasion. Nat. Med., 8(8), 793–800.
Ebelt, K., Babaryka, G., Frankenberger, B., Stief, C. G., Eisenmenger, W., Kirchner, T., Schendel, D. J., & Noessner, E. (2009). Prostate cancer lesions are surrounded by FOXP3+, PD-1+ and B7-H1+ lymphocyte clusters. Eur. J. Cancer, 45(9), 1664–1672.
Golovchenko, E. N., Hanin, L. G., Kaufmann, S. H., Tyurin, K. V., & Khanin, M. A. (2008). Dynamics of granzyme B-induced apoptosis: mathematical modeling. Math. Biosci., 212, 54–68.
Hirano, F., Katsumi, K., Tamura, H., Dong, H., Wang, S., Ichikawa, M., Rietz, C., Flies, D. B., Lau, J. S., Zhu, G., Tamada, K., & Chen, L. (2005). Blockade of B7-H1 and PD-1 by monoclonal antibodies potentiates cancer therapeutic immunity. Cancer Res., 65(3), 1089–1096.
Jeong, H. Y., Lee, Y. J., Seo, S. K., Lee, S. W., Park, S. J., Lee, J. N., Sohn, H. S., Yao, S., Chen, L., & Choi, I. (2008). Blocking of monocyte-associated B7-H1 (CD274) enhances HCV-specific T cell immunity in chronic hepatitis C infection. J. Leukoc. Biol., 83(3), 755–764.
Kirschner, D., & Panetta, J. C. (1998). Modeling immunotherapy of the tumor-immune interaction. J. Math. Biol., 37, 235–252.
Lai, R., & Jackson, T. L. (2004). A mathematical model of receptor-mediated apoptosis: dying to know why FasL is a trimer. Math. Biosci. Eng., 1(2), 325–338.
Russell, J. H., & Ley, T. J. (2002). Lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity. Annu. Rev. Immunol., 20, 323–370.
Thorn, R. M., & Henney, C. S. (1976). Kinetic analysis of target cell destruction by effector T cells: I. Delineation of parameters related to the frequency and lytic efficiency of killer cells. J. Immunol., 117, 2213–2219.
Webb, S., Sherratt, J. A., & Fish, R. G. (2002). Cells behaving badly: a theoretical model for the Fas/FasL system in tumour immunology. Math. Biosci., 179, 113–129.
Weinberg, R. A. (2007). The biology of cancer. New York: Garland Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Galante, A., Tamada, K. & Levy, D. B7-H1 and a Mathematical Model for Cytotoxic T Cell and Tumor Cell Interaction. Bull Math Biol 74, 91–102 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-011-9665-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-011-9665-1