Abstract
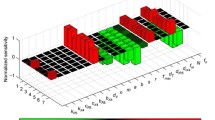
We use a mathematical model to determine the factors affecting the delayed or rare coreceptor switch in HIV-1 subtype C infected individuals. The model takes into account the two main target cells for the CXCR4-tropic and CCR5-tropic virus and includes the the lytic and non-lytic immune responses. Computer-based simulations and a sensitivity analysis of the model predict that a persistent immune response suppresses the CXCR4-tropic virus to low levels and hence preventing a phenotypic switch. However, not only should the immune response be persistent, but it should have an efficient lytic immune response rather that an efficient non-lytic response. In addition, we also find that the availability of macrophage cells and enhanced viral kinetics are also crucial for the dominance of the R5 strain. We suggest that an altered host environment probably as a result of immune activation may explain the difference in coreceptor switching kinetics between HIV-1 subtype B and subtype C individuals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ball, S.C., Abraha, A., Collins, K.R., Marozsan, A.J., Baird, H., Quinones-Mateu, M.E., Penn-Nicholson, A., Murray, M., Richard, N., Lobritz, M., Zimmerman, P.A., Kawamura, T., Blauvelt, A., Arts, E.J., 2003. Comparing the ex vivo fitness of CCR5 tropic human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates of subtypes B and C. J. Virol. 77, 1021–1038.
Beres, D.L., Hawkins, D., 2001. Plackett-Burman technique for sensitivity analysis of many parametered models. Ecol. Model. 141, 171–183.
Callaway, D.S., Ribeiro, R.M., Nowak, M.A., 1999. Virus phenotype switching and disease progression in HIV-1 infection. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 266, 2523–2530.
Cilliers, T., Nhlapo, J., Coetzer, M., Orlovic, D., Ketas, T., Olson, W.C., Moore, J.P., Trkola, A., Morris, L., 2003. The CCR5 and CXCR4 coreceptors are both used by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 primary isolates from subtype C. J. Virol. 77, 4449–4456.
Clerici, M., Butto, S., Lukwiya, M., Saresella, M., Declich, S., Trabattoni, D., et al., 2000. Immune activation in Africa is environmentally driven and is associated with upregulation of CCR5. AIDS 14, 2083–2092.
Clerici, M., Declich, S., Rizzardini., G., 2001. African enigma: Key player in human immunodeficiency virus pathogenesis in developing countries? Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 8, 864–866.
Collman, R., Balliet, J.W., Gregory, S.A., Friedman, H., Kolson, D.L., Nathanson, N., Srinivasan., A., 1992. An infectious molecular clone of an unusual macrophage tropic and highly cytopathic strain of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J. Virol. 66, 7517–7521.
Collman, R.G., 2003. HIV 1 env chemokine receptor interactions in primary human macrophages: Entry and beyond. Research Initiative Treatment Action. http://www.centerforaids.org/rita/0403/collman.pdf.
Connor, R.I., Mohri, H., Cao, Y., Ho, D.D., 1993. Increased viral burden and cytopathicity correlate temporally with CD4+ T lymphocyte decline and clinical progression in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infected individuals. J. Virol. 67, 1772–1777.
Connor, R.I., Sheridan, K.E., Ceradini, D., Choe, S., Landau, N.R., 1997. Change in coreceptor use coreceptor use correlates with disease progression in HIV 1 infected individuals. J. Exp. Med. 185, 621–628.
Dimitrov, D.S., Xiao, X., Chabot, D., Broder, C.C., 1998. HIV coreceptors. J. Membr. Biol. 166, 75–90.
Doms, R.W., Moore, J.P., 1997. HIV 1 coreceptor use: A molecular window into viral tropism. In: HIV Database Review Articles. HIV sequence database, http://www.hiv.lanl.gov/content/hiv-db/REVIEWS/reviews.html.
Douek, D.C., Picker, L.J., Koup, R.A., 2003. T cell dynamics in HIV 1 infection. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 21, 265–304.
Finnegan, A., Roebuck, K.A., Nakai, B.E., Gu, D.S., Rabbi, M.F., Song, S., Landay., A.L., 1996. IL-10 cooperates with TNF-alpha to activate HIV 1 from latently and acutely infected cells of monocyte/macrophage lineage. J. Immunol. 156, 841–851.
Fraziano, M., Cappelli, G., Santucci, M., Mariani, F., Amicosante, M., Casarini, M., Giosue, S., Bisetti, A., Colizzi, V., 1999. Expression of CCR5 is increased in human monocyte derived macrophages and alveolar macrophages in the course of in vivo and in vitro Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 15, 869.
Harouse, J.M., Buckner, C., Gettie, A., Fuller, R., Bohm, R., Blanchard, J., Cheng-Mayer, C., 2003. CD8+ T cell mediated CXC chemokine receptor 4 simian/human immunodeficiency virus suppression in dually infected rhesus macaques. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 10977–10982.
Johnston, E.R., Zijenah, L.S., Mutetwa, S., Kantor, R., Kittinunvorakoon, C., Katzenstein, D.A., 2003. High frequency of syncytium inducing and CXCR4 tropic viruses among human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtype C infected patients receiving antiretroviral treatment. J. Virol. 77, 7682–7688.
Kesmir, C., Boer, R.J.D., 2003. Clonal exhaustion as a result of immune deviation. Bull. Math. Biol. 65, 359–374.
Koot, M., Wout, A.B.V., Kootstra, N.A., de Goede, R.E., Tersmette, M., Schuitemaker, H., 1996. Relation between changes in cellular load evolution of phenotype and the clonal composition of virus populations in the course HIV 1 infection. J. Infect. Dis. 173, 349–354.
Moore, J.P., Kitchen, S.G., Pugach, P., Zack, J.A., 2004. The CCR5 and CXCR4 coreceptors central to understanding the transmission and pathogenesis of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 20, 111–126.
Morris, L., Cilliers, T., Bredell, H., Phoswa, M., Martin, D., 2001. CCR5 is the major coreceptor used by hiv 1 subtype c isolates from patients with active tuberculosis. AIDS. Res. Hum. Retrovir. 17, 697–701.
Mosier, D.E., Picchio, G.R., Gulizia, R.J., Sabbe, R., Poignard, P., Picard, L., Offord, R.E., Thompson, D.A., Wilken, J., 1999. Highly potent RANTES analogues either prevent CCR5 using human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection in vivo or rapidly select for CXCR4 using variants. J. Virol. 73, 3544–3550.
Moskophidis, D., Lechner, F., Pircher, H., Zinkernagel, R.M., 1993. Virus persistence in acutely infected immunocompetent mice by exhaustion of antiviral cytotoxic effector T cells. Nature 362, 758–761.
Pastores, C., Ramos, A., Mosier, D.E., 2004. Intrinsic obstacles to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 coreceptor switching. J. Virol. 78, 7565–7574.
Perelson, A.S., Essunger, P., Cao, Y., Vesanen, M., Hurley, A., Saksela, K., Markowitz, M., Ho, D.D., 1997. Decay characteristics of HIV 1 infected compartments during combination therapy. Nature 387, 188–191.
Plackett, R.L., Burman, J.P., 1946. The design of optimum multifactorial experiments. Biometrika 33, 305–332.
Pollakis, G., Abebe, A., Kliphuis, A., Chalaby, M.I., Bakker, M., Mengistu, Y., Brouwer, M., Goudsmit, J., Schuitemaker, H., Paxton, W.A., 2004. Phenotypic and genotypic comparisons of CCR5 and CXCR4 tropic human immunodeficiency virus type 1 biological clones isolated from subtype C infected individuals. J. Virol. 78, 2841–2852.
Regoes, R.R., Bonhoeffer, S., 2002. HIV coreceptor usage and drug treatment. J. Theor. Biol. 217, 443–457.
Rizzardini, G., Trabattoni, D., Saresella, M., Piconi, S., Lukwiya, M., Declich, S., Ferrante, P., Clerici, M., 1998. Immune activation in HIV infected African individuals. AIDS 12, 2387–2396.
Schuitemaker, H., 1994. Macrophage tropic HIV 1 variants: initiators of infection and aids pathogenesis? J. Leukocyte Biol. 56, 218–224.
Schuitemaker, H., Koot, M., Kootstra, N.A., Dercksen, W.A., Lange, J.M., Schattenkerk, J.K., Miedema, F., Tersmette, M., 1992. Biological phenotype of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 clones at different stages of infection progression of disease is associated with a shift from monocytotropic to T cell tropic virus population. J. Virol. 66, 1354–1360.
Starfield, A.M., Bleloch, A.L., 1991. Building Models for Conservation and Wildlife Management, The Burgess Press, Edina, Minnesota.
Stevenson, M., 1996. Portals of entry: Uncovering HIV nuclear transport pathways. Trends Cell Biol. 6, 9–15.
Van’t Wout, A.B., Kootstra, N.A., Kampinga, G.A.M., van Lent, N.A., Scherpbier, H.J., Veenstra, J., Boer, K., Coutinho, R.K., Miedema, F., Schuitemaker, H., 1994. Macrophage tropic variants initiate human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection after sexual parenteral and vertical transmission. J. Clin. Invest. 94, 2060–2067.
WHO, February 2003. HIV vaccine trial results are an important step forward in developing an effective vaccine, say WHO and UNAIDS. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/news/releases/2003/pr19/en/.
Wodarz, D., Klenerman, P., Nowak, M.A., 1998. Dynamics of cytotoxic T lymphocyte exhaustion. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 265, 191–203.
Wodarz, D., Krakauer, D.C., 2000. Defining CTL induced pathology: Implications for HIV. Virology 274, 94–104.
Wodarz, D., Lloyd, A.L., Jansen, V.A.A., Nowak, M.A., 1999. Dynamics of macrophage and T cell infection by HIV. J. Theor. Biol. 196, 101–113.
Wodarz, D., Nowak, M., 1998. The effect of different immune responses on the evolution of virulent CXCR4 trophic HIV. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 265, 2149–2158.
Zinkernagel, R.M., Bachmann, M.F., Kundig, T.M., Oehen, S., Pirchet, H., Hengartner, H., 1996. On immunological memory. A. Rev. Immunol. 14, 333–367.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mugwagwa, T., Witten, G. Coreceptor Switching in HIV-1 Subtype B and Subtype C. Bull. Math. Biol. 69, 55–75 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-006-9137-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-006-9137-1