Abstract
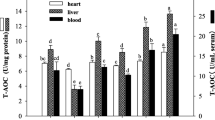
Imbalance in Th1/Th2 immune pathways and cellular antioxidant systems with progressive aging are among the leading causes of increased risk of morbidity and mortality in elderly. Although probiotics have been considered to boost immune system, there is a lack of comprehensive analysis of probiotic effects on aging physiology. The present study aimed at determining anti-immunosenescence potential of milk fermented with probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus (LR) in 16 months old mice by concurrent analysis of immunosenescence markers associated with Th1/Th2 profile of splenocytes, inflamm-aging in plasma, neutrophil functions and antibody response in intestine along with analysis of antioxidant enzymes in liver and red blood cells (RBCs) after feeding trials of 1 and 2 months, respectively. An enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (ATCC 14948)-based infection model in aging mice was also designed to validate protective attributes of LR. Splenocytes registered increased IFN-γ and decreased IL-4 and IL-10 production in LR-fed animals. Neutrophil respiratory burst enzymes and phagocytosis increased significantly while no aggravation in plasma levels of MCP-1 and TNF-α was observed. Further, owing to increased Th1 response, antibodies registered a decrease in IgG1/IgG2a ratio and IgE levels in LR groups. No significant variations were observed in secretory IgA and IgA + cells in the intestine. Antioxidant enzymes (superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione peroxidase) in LR-fed groups recorded increased activities which were more pronounced in the liver than in RBCs. LR supplementation significantly reduced E. coli translocation to organs (intestine, liver, spleen, peritoneal fluid) by enhancing E. coli-specific antibodies (IgA and IgG1) and inflammatory proteins. In conclusion, LR supplementation alleviated immunosenescence-associated Th1/Th2 imbalance, improved antioxidant capacity, and enhanced resistance of aged mice to E. coli infection thereby signifying its potential in augmenting healthy aging.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Aw D, Silva AB, Palmer DB (2007) Immunosenescence: emerging challenges for an ageing population. Immunology 120:435–446
Azcárate-Peril MA, Sikes M, Bruno-Bárcena JM (2011) The intestinal microbiota, gastrointestinal environment and colorectal cancer: a putative role for probiotics in prevention of colorectal cancer? Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 301:G401–G424
Bernet MF, Brassart D, Neeser JR, Servin AL (1993) Adhesion of human bifidobacterial strains to cultured human intestinal epithelial cells and inhibition of enteropathogen-cell interactions. Appl Environ Microbiol 59(12):4121–4128
Bradley PP, Priebat DA, Christensen RD, Rothstein G (1982) Measurement of cutaneous inflammation: estimation of neutrophil content with an enzyme marker. J Invest Dermatol 78:206–209
Braga PC, Sala MT, Dal Sasso M, Mancini L, Sandrini MC, Annoni G (1998) Influence of age on oxidative bursts (chemiluminescence) of polymorphonuclear neutrophil leukocytes. Gerontology 44:192–197
Bruunsgaard H, Pedersen BK (2003) Age-related inflammatory cytokines and disease. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am 23:15–39
Costa D, Marques AP, Reis RL, Lima JL, Fernandes E (2006) Inhibition of human neutrophil oxidative burst by pyrazolone derivatives. Free Radic Biol Med 40:632–640
Dorrington MG, Bowdish DM (2013) Immunosenescence and novel vaccination strategies for the elderly. Front Immunol 4:171
Effros RB (2005) Roy Walford and the immunologic theory of aging. Immun Ageing 2:7
Ellis TN, Beaman BL (2004) Interferon-γ activation of polymorphonuclear neutrophil function. Immunology 112:2–12
Engwall E, Perlmann P (1971) Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay, ELISA III. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme labeled antiimmunoglobin in antigen coated tubes. J Immunol 109:129–135
Feili-Hariri M, Falkner DH, Morel PA (2005) Polarization of naive T cells into Th1 or Th2 by distinct cytokine-driven murine dendritic cell populations: implications for immunotherapy. J Leukoc Biol 78:656–664
Ghosh S, van Heel D, Playford RJ (2004) Probiotics in inflammatory bowel disease: is it all gut flora modulation? Gut 53:620–622
Ginaldi L, De Martinis M, D'Ostilio A, Marini L, Loreto MF, Martorelli V, Quaglino D (1999) The immune system in the elderly: II. Specific cellular immunity. Immunol Res 20:109–115
Hawkley LC, Cacioppo JT (2004) Stress and the aging immune system. Brain Behav Immun 18:114–119
Hay FC, Westwood OMR (2002) Practical immunology, 4th edn. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 203–206
Jain S, Yadav H, Sinha PR, Naito Y, Marotta F (2008) Dahi containing probiotic Lactobacillus acidophilus and Lactobacillus casei has a protective effect against Salmonella enteritidis infection in mice. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 21:1021–1029
Jain S, Yadav H, Sinha PR (2009) Probiotic dahi containing Lactobacillus casei protects against Salmonella enteritidis infection and modulates immune response in mice. J Med Food 12:576–583
Jijon H, Backer J, Diaz H, Yeung H, Thiel D, McKaigney C, De Simone C, Madsen K (2004) DNA from probiotic bacteria modulates murine and human epithelial and immune function. Gastroenterol 126:1358–1373
Kapila S, Sinha PR, Singh S (2007) Influence of feeding fermented milk and non-fermented milk containing Lactobacillus casei on immune response in mice. Food Agric Immunol 18:75–82
Kapila R, Kapila S, Kapasiya M, Pandey D, Dang A, Salingati V (2012) Comparative evaluation of oral administration of probiotic Lactobacilli fermented milks on macrophage function. Probiot Antimicrob Prot 4:173–179
Kapila R, Sebastian R, Verma DV, Sharma R, Kapasiya M, Salingati V, Kapila S, Dang A (2013) Comparative activation of innate immunity on prolonged feeding of Lactobacilli fermented milks. Microbiol and Immunol 57:778–784
Kaushal D, Kansal VK (2012) Probiotic Dahi containing Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium bifidum alleviates age-inflicted oxidative stress and improves expression of biomarkers of ageing in mice. Mol Biol Rep 39:1791–1799
Kekkonen RA, Lummela N, Karjalainen H, Latvala S, Tynkkynen S, Jarvenpaa S, Kautiainen H, Julkunen I, Vapaatalo H, Korpela R (2008) Probiotic intervention has strain-specific anti-inflammatory effects in healthy adults. World J Gastroenterol 14:2029–2036
Kiernan JA (2008) Histological & histochemical methods theory & practice, 4th edn. Bloxham, UK
Kovacs EJ, Duffner LA, Plackett TP (2004) Immunosuppression after injury in aged mice is associated with a TH1-TH2 shift, which can be restored by estrogen treatment. Mech Ageing Dev 125:121–123
Kullisar T, Zilmer M, Mikelsaar M, Vihalemm T, Annuk H, Kairanc C, Kilk A (2002) Two antioxidative lactobacilli strains as promising probiotics. Int J Food Microb 72:215–224
Le Bon A, Schiavoni G, D'Agostino G, Gresser I, Belardelli F, Tough DF (2001) Type I interferons potently enhance humoral immunity and can promote isotype switching by stimulating dendritic cells in vivo. Immunity 14:461–470
Lim TS, Messiha N, Watson RR (1981) Immune components of the intestinal mucosa of ageing and protein deficient mice. Immunology 43:401–407
Lin SP, Sun XF, Chen XM, Shi SZ, Hong Q, Lv Y (2010) Effect of aging on pulmonary ICAM-1 and MCP-1 expressions in rats with lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 30:584–587
Lord JM, Butcher S, Killampali V, Lascelles D, Salmon M (2001) Neutrophil ageing and immunosenescence. Mech Ageing Dev 122:1521–1535
Lutgendorff F, Nijmeijer RM, Sandström PA, Trulsson LM, Magnusson KE, Timmerman HM, van Minnen LP, Rijkers GT, Gooszen HG, Akkermans LM, Söderholm JD (2009) Probiotics prevent intestinal barrier dysfunction in acute pancreatitis in rats via induction of ileal mucosal glutathione biosynthesis. PLoS One 4:e4512
Marklund S, Marklund G (1974) Involvement of superoxide dismutase anion radical in autooxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase. Eur J Biochem 42:469–474
Martarelli D, Verdenelli MC, Scuri S, Cocchioni M, Silvi S, Cecchini C, Pompei P (2011) Effect of a probiotic intake on oxidant and antioxidant parameters in plasma of athletes during intense exercise training. Curr Microbiol 62:1689–1696
Matsumoto M, Kurihara S (2011) Probiotics-induced increase of large intestinal luminal polyamine concentration may promote longevity. Med Hypotheses 77:469–472
McElhaney JE (2003) Overcoming the challenges of immunosenescence in the prevention of acute respiratory illness in older people. Conn Med 67:469–474
Melton-Witt JA, Rafelski SM, Portnoy DA, Bakardjiev AI (2012) Oral infection with signature-tagged Listeria monocytogenes reveals organ-specific growth and dissemination routes in guinea pigs. Infect Immun 80:720–732
Mocchegiani E, Giacconi R, Cipriano C, Malavolta M (2009) NK and NKT cells in aging and longevity: role of zinc and metallothioneins. J Clin Immunol 29:416–425
Mohamadzadeh M, Klaenhammer TR (2008) Specific Lactobacillus species differentially activate Toll-like receptors and downstream signals in dendritic cells. Expert Rev Vaccines 8:1155–1164
Mohamadzadeh M, Olson S, Kalina WV, Ruthel G, Demmin GL, Warfield KL, Bavari S, Klaenhammer TR (2005) Lactobacilli activate human dendritic cells that skew T cells toward T helper 1 polarization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:2880–2885
Neish AS (2004) Bacterial inhibition of eukaryotic pro-inflammatory pathways. Immunol Res 29:175–186
Neish AS, Gewirtz AT, Zeng H, Young AN, Hobert ME, Karmali V, Rao AS, Madara JL (2000) Prokaryotic regulation of epithelial responses by inhibition of IkappaB-alpha ubiquitination. Science 289:1560–1563
Ogawa K, Suzuki K, Okutsu M, Yamazaki K, Shinkai S (2008) The association of elevated reactive oxygen species levels from neutrophils with low-grade inflammation in the elderly. Immun Ageing 5:13
Otte JM, Podolsky DK (2004) Functional modulation of enterocytes by gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 286:G613–G626
Paglia DE, Valentine WN (1967) Studies on quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J Lab Clin Med 70:158–169
Rammelsberg M, Radler F (1990) Antibacterial polypeptides of Lactobacillus species. J Appl Bacteriol 69:177–184
Roessler A, Friedrich U, Vogelsang H, Bauer A, Kaatz M, Hipler UC, Schmidt I, Jahreis G (2008) The immune system in healthy adults and patients with atopic dermatitis seems to be affected differently by a probiotic intervention. Clin Exp Allergy 38:93–102
Ruiz PA, Hoffmann M, Szcesny S, Blaut M, Haller D (2005) Innate mechanisms for Bifidobacterium lactis to activate transient pro-inflammatory host responses in intestinal epithelial cells after the colonization of germfree rats. Immunol 115:441–450
Schiavi E, Barletta B, Butteroni C, Corinti S, Boirivant M, Di Felice G (2011) Oral therapeutic administration of a probiotic mixture suppresses established Th2 responses and systemic anaphylaxis in a murine model of food allergy. Allergy 66:499–508
Sharma R, Kapila R, Kapila S (2013a) Probiotics as anti-immunosenescence agents. Food Rev Int 29:201–216
Sharma R, Kapila R, Haq MR, Salingati V, Kapasiya M, Kapila S (2013b) Age-associated aberrations in mouse cellular and humoral immune responses. Aging Clin Exp Res. doi:10.1007/s40520-013-0190-y, In Press
Shearer GM (1997) Th1/Th2 changes in aging. Mech Ageing Dev 94:1–5
Sheil B, McCarthy J, O’Mahony L, Bennett MW, Ryan P, Fitzgibbon JJ, Kiely B, Collins JK, Shanahan F (2004) Is the mucosal route of administration essential for probiotic function? Subcutaneous administration is associated with attenuation of murine colitis and arthritis. Gut 53:694–700
Shih PH, Yen GC (2007) Differential expressions of antioxidant status in aging rats: the role of transcriptional factor Nrf2 and MAPK signaling pathway. Biogerontol 8:71–80
Shu Q, Gill HS (2002) Immune protection mediated by the probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001 (DR201) against Escherichia coli O157:H7 infection in mice. FEMS Immunol Med Micro 34:59–64
Snapper CM, Finkelman FD, Paul WE (1988) Differential regulation of IgG1 and IgE synthesis by interleukin 4. J Exp Med 167:183–196
Stadlbauer V, Mookerjee RP, Hodges S, Wright GA, Davies NA, Jalan R (2008) Effect of probiotic treatment on deranged neutrophil function and cytokine responses in patients with compensated alcoholic cirrhosis. J Hepatol 48:945–951
Tan M, Zhu JC, Du J, Zhang LM, Yin HH (2011) Effects of probiotics on serum levels of Th1/Th2 cytokine and clinical outcomes in severe traumatic brain-injured patients: a prospective randomized pilot study. Crit Care 15:R290
Tortorella C, Piazzolla G, Spaccavento F, Vella F, Pace L, Antonaci S (2000) Regulatory role of extracellular matrix proteins in neutrophil respiratory burst during aging. Mech Ageing Dev 119:69–82
Uciechowski P, Kahmann L, Plümäkers B, Malavolta M, Mocchegiani E, Dedoussis G, Herbein G, Jajte J, Fulop T, Rink L (2008) TH1 and TH2 cell polarization increases with aging and is modulated by zinc supplementation. Exp Gerontol 43:493–498
Yadav H, Jain S, Sinha PR (2008) Oral administration of dahi containing probiotic Lactobacillus acidophilus and Lactobacillus casei delayed the progression of streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats. J Dairy Res 75:189–195
Zhou X, Tian Z, Wang Y, Li W (2010) Effect of treatment with probiotics as water additives on tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) growth performance and immune response. Fish Physiol Biochem 36:501–509
Zommara M, Toubo H, Sakono M, Imaizumi K (1998) Prevention of peroxidative stress in rats fed on a low vitamin E containing diet by supplementing with a fermented bovine milk whey preparation: effect of lactic acid and b-lactoglobulin on the antiperoxidative action. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 62:710–717
Acknowledgments
The financial assistance provided by the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India, and laboratory facilities provided by National Dairy Research Institute are thankfully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, R., Kapila, R., Dass, G. et al. Improvement in Th1/Th2 immune homeostasis, antioxidative status and resistance to pathogenic E. coli on consumption of probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus fermented milk in aging mice. AGE 36, 9686 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-014-9686-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-014-9686-4