Abstract
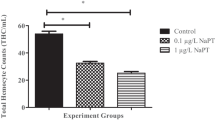
Pollutants via run-off into the ocean represent a potential threat to marine organisms, especially bivalves such as oysters living in coastal environments. These organisms filter large volumes of seawater and may accumulate contaminants within their tissues. Pesticide contamination in water could have a direct or indirect toxic action on tissues or cells and could induce alteration of immune system. Bivalve immunity is mainly supported by hemocytes and participates directly by phagocytosis to eliminate pathogens. Some studies have shown that pesticides can reduce immune defences and/or modify genomes in vertebrates and invertebrates. Metaldehyde is used to kill slugs, snails and other terrestrial gastropods. Although metaldehyde has been detected in surface waters, its effects on marine bivalves including the Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas, have never been studied. Given the mode of action of this molecule and its targets (molluscs), it could be potentially more toxic to oysters than other pesticides (herbicides, fungicides, insecticides, etc.). Effects of metaldehyde on oyster hemocyte parameters were thus monitored through in vivo experiments based on a short-term exposure. In this work, metaldehyde at 0.1 μg/L, which corresponds to an average concentration detected in the environment, modulated hemocyte activities of Pacific oysters after an in vivo short-term contact. Individuals belonging to two families showed different behaviours for some hemocyte activities after contamination by metaldehyde. These results suggested that effects of pollutants on oysters may differ from an individual to another in relation to genetic diversity. Finally, it appears essential to take an interest in the effects of metaldehyde on a wide variety of aquatic invertebrates including those that have a significant economic impact.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez MR, Friedl FE (1992) Effects of a fungicide on in vitro hemocyte viability, phagocytosis and attachment in the American oyster, Crassostrea virginica. Aquaculture 107(2–3):135–140
Anderson RS (1981) Effects of carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic environmental pollutants on immunological functions in marine invertebrates.Phyletic approaches to cancer. Japan Scientific Societies Press, Tokyo, pp 319–331
Bates NS, Sutton NM, Campbell A (2012) Suspected metaldehyde slug bait poisoning in dogs: a retrospective analysis of cases reported to the Veterinary Poisons Information Service. Vet Rec 171(13):324
Bilan 2010 du réseau Corpep (2011) Les pesticides dans les eaux superficielles bretonnes-Bretagne Environnement. http://www.bretagne-environnement.org/Media/Documentation/Bibliographies/Les-pesticides-dans-les-eaux-superficielles-bretonnes-bilan-2010-du-reseau-Corpep
Blakley B, Brousseau P, Fournier M, Voccia I (1999) Immunotoxicity of pesticides: a review. Toxicol Ind Health 15(1–2):119–132
Burgeot T, Gagnaire B, Renault C, Haure J, Moraga D, David D, Boutet I, Sauriau PG, Malet N, Bouchet V, Le Roux A, Lapègue S, Bouilly K, Le Moullac G, Arzul G, Knoery J, Bacher C, Soletchnick P (2008) Oyster summer mortality risks associated with environmental stress. Chapter 3 in Summer mortality of pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. The Morest project. Edited by J.F. Samain and H. Combie. Quae Editions.107–153
Campbell A (2008) Metaldehyde poisoning of dogs. Vet Rec 163(11):343
Canty MN, Hagger JA, Moore RTB, Cooper L, Galloway TS (2007) Sublethal impact of short term exposure to the organophosphate pesticide azamethiphos in the marine mollusc Mytilus edulis. Mar Pollut Bull 54(4):396–402
Cooper EL, Roch P (2003) Earthworm immunity: a model of immune competence. Pedobiologia 47(5–6):676–688
Dai L, Wang W, Dong X, Hu R, Nan X (2011) Molluscicidal activity of cardiac glycosides from Nerium indicum against Pomacea canaliculata and its implications for the mechanisms of toxicity. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 32(2):226–232
Dunier M, Siwicki AK (1993) Effects of pesticides and other organic pollutants in the aquatic environment on immunity of fish: a review. Fish Shellfish Immunol 3(6):423–438
Dunier M, Siwicki AK, Demaël A (1991) Effects of organophosphorus insecticides: effects of trichlorfon and dichlorvos on the immune response of carp (Cyprinus carpio). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 22(1):79–87
Gagnaire B, Renault T, Bouilly K, Lapegue S, Thomas-Guyon H (2003) Study of atrazine effects on Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas, haemocytes. Curr Pharm Des 9(2):193–199
Gagnaire B, Gay M, Huvet A, Daniel J-Y, Saulnier D, Renault T (2007) Combination of a pesticide exposure and a bacterial challenge: in vivo effects on immune response of Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas (Thunberg). Aquat Toxicol 84(1):92–102
His E, Heyvang I, Geffard O, De Montaudouin X (1999) A comparison between oyster (Crassostrea gigas) and sea urchin (Paracentrotus lividus) larval bioassays for toxicological studies
Jacquet R, Miège C, Bados P, Schiavone S, Coquery M (2012) Evaluating the polar organic chemical integrative sampler for the monitoring of beta-blockers and hormones in wastewater treatment plant effluents and receiving surface waters. Environ Toxicol Chem 31(2):279–288
Khakame SK, Wang X, Wu Y (2013) Baseline toxicity of metaflumizone and lack of cross resistance between indoxacarb and metaflumizone in diamondback moth (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). J Econ Entomol 106(3):1423–1429
Koner BC, Banerjee BD, Ray A (1998) Organochlorine pesticide-induced oxidative stress and immune suppression in rats. Indian J Exp Biol 36(4):395–398
Koutros S, Berndt SI, Hughes Barry K, Andreotti G, Hoppin JA, Sandler DP et al (2013) Genetic susceptibility loci, pesticide exposure and prostate cancer risk. PLoS ONE 8(4):e58195
Larson KG, Roberson BS, Hetrick FM (1989) Effect of environmental pollutants on the chemiluminescence of hemocytes from the American oyster Crassostrea virginica. Dis Aquat Org 6(2):131–136
Luna-Acosta A, Renault T, Thomas-Guyon H, Faury N, Saulnier D, Budzinski H et al (2012) Detection of early effects of a single herbicide (diuron) and a mix of herbicides and pharmaceuticals (diuron, isoproturon, ibuprofen) on immunological parameters of Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas) spat. Chemosphere 87(11):1335–1340
Mills NJ (2008) Metaldehyde poisoning of dogs. Vet Rec 163(10):310
Moreau P, Burgeot T, Renault T (2014) Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas) hemocyte are not affected by a mixture of pesticides in short-term in vitro assays. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(7):4940–4949
Nielsen JW (1988) "Method and composition for killing terrestrial molluscs." U.S. Patent No. 4,765,979. 23 Aug. 1988
Renault T (2011) Effects of pesticides on marine bivalves: what do we know and what do we need to know? In: Stoytcheva M, editor. Pesticides in the modern world—risks and benefits [Internet]. InTech; 2011 [cited 2014 May 19]. Available from: http://www.intechopen.com/books/pesticides-in-the-modern-world-risks-and-benefits/effects-of-pesticides-on-marine-bivalves-what-do-we-know-and-what-do-we-need-to-know-
Russo J, Lagadic L (2004) Effects of environmental concentrations of atrazine on hemocyte density and phagocytic activity in the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis (Gastropoda, Pulmonata). Environ Pollut 127(2):303–311
Segarra A, Pépin JF, Arzul I, Morga B, Faury N, Renault T (2010) Detection and description of a particular Ostreid herpesvirus 1 genotype associated with massive mortality outbreaks of Pacific oysters, Crassostrea gigas, in France in 2008. Virus Res 153(1):92–99
Snieszko SF (1974) The effects of environmental stress on outbreaks of infectious diseases of fishes*. J Fish Biol 6(2):197–208
Tawde SN, Puschner B, Albin T, Stump S, Poppenga RH (2012) Death by caffeine: presumptive malicious poisoning of a dog by incorporation in ground meat. J Med Toxicol 8(4):436–440
Triebskorn R, Henderson IF, Martin A, Kolher HR (1996) Slugs as target or non-target organisms for environmental chemicals. In: Henderson IF (ed) Slugs and Snail Pests in Agriculture. BCPC Monograph No 66: 65–72
Wong S, Fournier M, Coderre D, Banska W, Krzystyniak K (1992) Environmental immunotoxicology. Animal biomarkers as pollution indicators. Springer, Netherlands, pp 167–189
Zhang H, Wang C, Lu H, Guan W, Ma Y (2011) Residues and dissipation dynamics of molluscicide metaldehyde in cabbage and soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74(6):1653–1658
Acknowledgments
This work was partially funded through the EU project Bivalife (no. 266157) and the Poitou Charentes Region. The authors wish to thank the Ifremer hatchery team (LGPMM) in La Tremblade and the nursery team (LSPC) in Bouin for the production of Pacific oysters.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Henner Hollert
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moreau, P., Burgeot, T. & Renault, T. In vivo effects of metaldehyde on Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas: comparing hemocyte parameters in two oyster families. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 8003–8009 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3162-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3162-7