Abstract
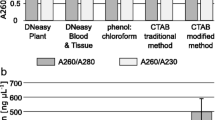
We present an improved method for genomic DNA extraction from cyanobacteria by updating the earlier method from our group (Sinha et al. 2001) that does not require lysozyme treatment or sonication to lyse the cells. This method use lysis buffer to lyse the cells and also skips the initial treatments to remove the exopolysaccharides or to break the clumps. To test the efficacy of the method DNA was extracted from the freshwater cyanobacteria Anabaena variabilis PCC 7937, Anabaena sp. PCC 7120, Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803, Synechococcus sp. PCC 6301 and Rivularia sp. HKAR-4 (Accession number: FJ939128). The spectrophotometric and gel electrophoresis analysis revealed high yield and high quality of genomic DNA extracted by this method. Furthermore, the RAPD resulted in the amplification of unidentified genomic regions of various lengths; however, rDNA amplification gave only one band of 1.5 kb in all studied cyanobacteria. Thymine dimer detection study revealed that thymine dimers are induced only by UV-B radiation in A. variabilis PCC 7937 and there is no effect of PAR and UV-A on its genome. Collectively, all these findings put forward the applicability of this method in different studies and purposes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abed RMM, Dobretsov S, Sudesh K (2009) Applications of cyanobacteria in biotechnology. J Appl Microbiol 106:1–12
Angermayr SA, Hellingwerf KJ, Lindblad P, de Mattos MJT (2009) Energy biotechnology with cyanobacteria. Curr Opin Biotechnol 20:257–263
Berrendero E, Perona E, Mateo P (2008) Genetic and morphological characterization of Rivularia and Calothrix (Nostocales, Cyanobacteria) from running water. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:447–460
Berry JP, Gantar M, Perez MH, Berry G, Noriega FG (2008) Cyanobacterial toxins as allelochemicals with potential applications as algaecides, herbicides and insecticides. Mar Drugs 6:117–146
Fiorea MF, Moona DH, Tsaia SM, Leeb H, Trevorsb JT (2000) Miniprep DNA isolation from unicellular and filamentous cyanobacteria. J Microbiol Meth 39:159–169
Kumar A, Tyagi MB, Jha PN (2004) Evidences showing ultraviolet-B radiation-induced damage of DNA in cyanobacteria and its detection by PCR assay. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 318:1025–1030
Leak LV (1967) Fine structure of the mucilaginous sheath of Anabaena sp. J Ultra Res 21:61–74
Margheri MC, Bosco M, Giovannetti L, Ventura S (1999) Assessment of the genetic diversity of halotolerant coccoid cyanobacteria using applied 16S rDNA restriction analysis. FEMS Microbiol Lett 173:9–16
Morin N, Vallaeys T, Hendrickx L, Natalie L, Wilmotte A (2010) An efficient DNA isolation protocol for filamentous cyanobacteria of the genus Arthrospira. J Microbiol Meth 80:148–154
Philippis RD, Vincenzini M (1998) Exocellular polysaccharides from cyanobacteria and their possible applications. FEMS Microbiol Rev 22:151–175
Rastogi RP, Sinha RP (2009) Biotechnological and industrial significance of cyanobacterial secondary metabolites. Biotechnol Adv 27:521–539
Rastogi RP, Richa, Sinha RP, Singh SP, Häder D-P (2010a) Photoprotective compounds from marine organisms. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 37:537–558
Rastogi RP, Richa, Singh SP, Häder D-P, Sinha RP (2010b) Mycosporine-like amino acids (MAAs) profile and their activity under PAR and UVR in a hot spring cyanobacterium Scytonema sp. HKAR-3. Aus J Bot 58:286–293
Saha SK, Uma SL, Subramanian G (2005) An improved method for marine cyanobacterial DNA isolation. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 21:877–881
Sinha RP, Dautz M, Häder D-P (2001) A simple and efficient method for the quantitative analysis of thymine dimers in cyanobacteria, phytoplankton and macroalgae. Acta Protozool 40:187–195
Srivastava AK, Ara A, Bhargava P, Mishra Y, Rai SP, Rai LC (2007) A rapid and cost-effective method of genomic DNA isolation from cyanobacterial culture, mat and soil suitable for genomic fingerprinting and community analysis. J Appl Phycol 19:373–382
Stanier RY, Kunisawa R, Mandel M, Cohen-Bazire G (1971) Purification and properties of unicellular blue-green algae (order Choococcales). Bact Rev 35:171–205
Tillett D, Neilan BA (2000) Xanthogenate nucleic acid isolation from cultured and environmental cyanobacteria. J Phycol 36:251–258
Wu X, Zarka A, Boussiba S (2000) A simplified protocol for preparing DNA from filamentous cyanobacteria. Plant Mol Biol Rep 18:385–392
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully thank M. Schuster for providing excellent technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, S.P., Rastogi, R.P., Häder, DP. et al. An improved method for genomic DNA extraction from cyanobacteria. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 27, 1225–1230 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-010-0571-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-010-0571-8