Abstract
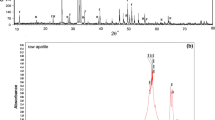
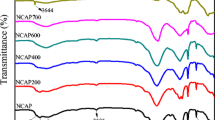
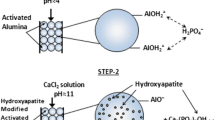
In many parts of the world, fluoride in drinking water is responsible for notable public health issues. The present study is aimed to prepare a new adsorbent magnesia-hydroxyapatite (Mg-HAP) that can serve as a valuable defluoridating agent. Characterization of the synthesized adsorbent was done by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Transmission electron microscope (TEM), and Scanning electron microscope (SEM)/Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) analysis to reveal the bonding patterns, phase characteristics, and microstructural and morphological details. The influences of pH, adsorbent dose, contact time, and initial fluoride concentration and the effect of interfering anions were studied. The defluoridation capacity was evaluated to be 1.4 mg/g, and the adsorbent showed very good capability to remove fluoride from contaminated water over a wide range of pH. Equilibrium modeling was done, and the experimental data was fitted into Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin, and Dubinin-Radushkevich isotherms. Study of the kinetic data for the adsorption process revealed that it follows pseudo-second-order reaction. It also indicated that the intraparticle diffusion contributes to the rate-determining step in the process. The quality of treated water was analyzed for total dissolved solids (TDS), turbidity, residual calcium, residual phosphorus content, electrical conductivity, hardness, and total alkalinity. The results obtained were very promising and confirmed the prospects of usage of Mg-HAP in defluoridation of drinking water.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- q e :
-
Amount of adsorption at equilibrium (mg/g)
- q t :
-
Amount of adsorption at time t (mg/g)
- C 0 :
-
Initial concentrations of fluoride (mg/L)
- C e :
-
Equilibrium concentrations of fluoride (mg/L)
- C t :
-
Concentration of fluoride at time t (mg/L)
- v :
-
Volume of the aqueous solution (L)
- m :
-
Adsorbent mass (g)
- Q 0 :
-
Maximum adsorption capacity reflecting complete monolayer (mg/g)
- R L :
-
Separation factor depicting favorability of the process
- b :
-
Langmuir constant related to energy
- K f :
-
Freundlich constants (mg/g)
- N :
-
Heterogeneity factor
- R :
-
Universal gas constant (8.314 J/mol K)
- T :
-
Temperature (K)
- A T :
-
Temkin isotherm equilibrium binding constant (L/g)
- B T :
-
Temkin isotherm constant
- b 1 :
-
Adsorption rate constant of first order reaction (min−1)
- b 2 :
-
Adsorption rate constant of first order reaction (g mg−1 min−1)
- k i :
-
Intraparticle diffusion rate constant (mg g−1 min−1/2)
- a :
-
Initial adsorption rate (mg g−1 min−1)
- α :
-
Desorption rate (g mg−1)
- B :
-
Dubinin-Radushkevich isotherm constant
- q d :
-
Theoretical isotherm saturation capacity (mg/g)
- ε :
-
Polanyi potential
- k p :
-
Particle diffusion coefficient (min−1)
References
APHA. (1995). Standard methods (19th ed.). Washington, DC: American Public Health Association.
Ayoob, S., & Gupta, A. K. (2006). Fluoride in drinking water: a review on the status and stress effects. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 36(6), 433–487.
Bhargava, D. S., & Killedar, D. J. (1992). Fluoride adsorption on fishbone charcoal through a moving media adsorber. Water Research, 26(6), 781–788.
Chen, Q. Z., Wong, C. T., Lu, W. W., Cheung, K. M. C., Leong, J. C. Y., & Luk, K. D. K. (2004). Strengthening mechanisms of bone bonding to crystalline hydroxyapatite in vivo. Biomaterials, 25(18), 4243-4254.
Choubisa, S. L., Choubisa, L., & Choubisa, D. (2009). Osteo-dental fluorosis in relation to nutritional status, living habits, and occupation in rural tribal areas of Rajasthan, India. Fluoride, 42, 210.
Daifullah, A. A. M., Yakout, S. M., & Elreefy, S. A. (2007). Adsorption of fluoride in aqueous solutions using KMnO4-modified activated carbon derived from steam pyrolysis of rice straw. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 147, 633–643.
Davila-Rodriguez, J. L., Escobar-Barrios, V. A., Shirai, K., & Rangel-Mendez, J. R. (2009). Synthesis of a chitin-based biocomposite for water treatment: optimization for fluoride removal. Journal of Fluorine Chemistry, 130(8), 718–726.
Essadki, A. H., Gourich, B., Vial, C., Delmas, H., & Bennajah, M. (2009). Defluoridation of drinking water by electrocoagulation/electroflotation in a stirred tank reactor with a comparative performance to an external-loop airlift reactor. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 168(2), 1325–1333.
Fan, X., Parker, D. J., & Smith, M. D. (2003). Adsorption kinetics of fluoride on low cost materials. Water Research, 37, 4929–4937.
Fawell, K., Bailey, J., Chilton, E., Dahi, L., Fewtrell, Y., Magara. (2006) Fluoride in drinking-water. World Health Organization.
Gao, S., Sun, R., Wei, Z., Zhao, H., Li, H., & Hu, F. (2009). Size-dependent defluoridation properties of synthetic hydroxyapatite. Journal of Fluorine Chemistry, 130(6), 550–556.
George, S., Pandit, P., & Gupta, A. B. (2010). Residual aluminium in water defluoridated using activated alumina adsorption—modeling and simulation studies. Water Research, 44(10), 3055–3064.
Gogoi, P. K., & Baruah, R. (2008). Fluoride removal from water by adsorption on acid activated kaolinite clay. Indian Journal of Chemical Technology, 15(5), 500–503.
Gogoi, S., Nath, S. K., Bordoloi, S., & Dutta, R. K. (2015). Fluoride removal from groundwater by limestone treatment in presence of phosphoric acid. Journal of Environmental Management, 152, 132–139.
He, G. L., & Cao, S. R. (1996). Assessment of fluoride removal from drinking water by calcium phosphate systems. Fluoride, 29(4), 212–216.
Ho, Y. S. (2004). Citation review of Lagergren kinetic rate equation on adsorption reactions. Scientometrics, 59(1), 171–177.
Ho, Y. S. (2006). Review of second-order models for adsorption systems. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 136(3), 681–689.
Hu, K., & Dickson, J. M. (2006). Nanofiltration membrane performance on fluoride removal from water. Journal of Membrane Science, 279(1), 529–538.
Hutson, N. D., & Yang, R. T. (1997). Theoretical basis for the Dubinin-Radushkevitch (DR) adsorption isotherm equation. Adsorption, 3(3), 189–195.
Indian Standard Drinking Water Specification. (2012). Bureau of Indian Standards. IS 10500.
Jain, S., & Jayaram, R. V. (2009). Removal of fluoride from contaminated drinking water using unmodified and aluminium hydroxide impregnated blue lime stone waste. Separation Science and Technology, 44(6), 1436–1451.
Jimenez-Reyes, M., & Solache-Rios, M. (2010). Sorption behavior of fluoride ions from aqueous solutions by hydroxyapatite. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 180(1), 297–302.
Lagergren, S. (1898). About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens. Handlingar, 24, 1–39.
Liu, H., Deng, S., Li, Z., Yu, G., & Huang, J. (2010). Preparation of Al–Ce hybrid adsorbent and its application for defluoridation of drinking water. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 179(1), 424–430.
Long, H., Jin, Y., Lin, M., Sun, Y., Zhang, L., & Clinch, C. (2009). Fluoride toxicity in the male reproductive system. Fluoride, 42, 260–276.
Maheshwari, R. C. (2006). Fluoride in drinking water and its removal. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 137(1), 456–463.
Maliyekkal, S. M., Shukla, S., Philip, L., & Nambi, I. M. (2008). Enhanced fluoride removal from drinking water by magnesia-amended activated alumina granules. Chemical Engineering Journal, 140(1), 183–192.
Mehta, D., George, S., & Mondal, P. (2014). Synthesis of hydroxyapatite by chemical precipitation technique and study of its biodegradability. International Journal of Research in Advent Technology, 2(4), 159–161.
Mondal, P., & George, S. (2014). A review on adsorbents used for defluoridation of drinking water. Reviews in Environmental Science and Biotechnology, 14(2), 195–210.
Mondal, P., George, S., & Mehta, D. (2014). Use of calcite for defluoridation of drinking water in acidic medium. Research Journal of Chemical Science, 4, 62–65.
Murray, J. J. (Ed.). (1986). Appropriate use of fluorides for human health. Geneva: World Health Organization.
Orlovskii, V. P., Komlev, V. S., & Barinov, S. M. (2002). Hydroxyapatite and hydroxyapatite-based ceramics. Inorganic Materials, 38(10), 973–984.
Pekar, M. (2009). Fluoride anion binding by natural lignite (South Moravian Deposit of Vienna Basin). Water Air Soil Pollution, 197(1–4), 303–312.
Percival, M. (1999). Bone health & osteoporosis. Applied Nutritional Science Reports, 5, 1–5.
Rafique, A., Awan, M. A., Wasti, A., Qazi, I. A., & Arshad, M. (2012). Removal of fluoride from drinking water using modified immobilized activated alumina. Journal of Chemistry. doi:10.1155/2013/386476.
Ramanan, S. R., & Venkatesh, R. (2004). A study of hydroxyapatite fibers prepared via sol–gel route. Materials Letters, 58(26), 3320–3323.
Ravindra, K., & Garg, V. K. (2007). Hydro-chemical survey of groundwater of Hisar city and assessment of defluoridation methods used in India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 132(1-3), 33–43.
Russell, S. W., Luptak, K. A., Suchicital, C. T. A., Alford, T. L., & Pizziconi, V. B. (1996). Chemical and structural evolution of sol‐gel‐derived hydroxyapatite thin films under rapid thermal processing. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 79(4), 837–842.
Sakhare, N., Lunge, S., Rayalu, S., Bakardjiva, S., Subrt, J., Devotta, S., & Labhsetwar, N. (2012). Defluoridation of water using calcium aluminate material. Chemical Engineering Journal, 203, 406–414.
Sargin, Y., Kizilyalli, M., Telli, C., & Güler, H. (1997). A new method for the solid-state synthesis of tetracalcium phosphate, a dental cement: X-ray powder diffraction and IR studies. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 17(7), 963–970.
Sarkar, M., Banerjee, A., Pramanick, P. P., & Sarkar, A. R. (2006). Use of laterite for the removal of fluoride from contaminated drinking water. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 302(2), 432–441.
Sehn, P. (2007). Fluoride removal with extra low energy reverse osmosis membranes: three years of large scale field experience in Finland. Desalination, 223, 73–84.
Sharma, J. D., Sohu, D., & Jain, P. (2009). Prevalence of neurological manifestations in a human population exposed to fluoride in drinking water. Fluoride, 42, 127–132.
Spittle, B. (2008). Dyspepsia associated with fluoridated water. Fluoride, 41, 89.
Sundaram, C. S., Viswanathan, N., & Meenakshi, S. (2008). Defluoridation chemistry of synthetic hydroxyapatite at nano scale: equilibrium and kinetic studies. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 155(1), 206–215.
Sundaram, C. S., Viswanathan, N., & Meenakshi, S. (2009). Fluoride sorption by nano-hydroxyapatite/chitin composite. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 172(1), 147–151.
Tatawat, R. K., & Chandel, C. S. (2008). A hydrochemical profile for assessing the groundwater quality of Jaipur City. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 143(1-3), 337–343.
Tor, A. (2006). Removal of fluoride from an aqueous solution by using montmorillonite. Desalination, 201(1), 267–276.
Tripathy, S. S., & Raichur, A. M. (2008). Abatement of fluoride from water using manganese dioxide-coated activated alumina. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 153(3), 1043–1051.
Trivedi, M. H., Sangai, N. P., Patel, R. S., Payak, M., & Vyas, S. (2012). Assessment of groundwater quality with special reference to fluoride and its impact on IQ of schoolchildren in six villages of the Mundra region, Kachchh, Gujarat, India. Fluoride, 45, 377–383.
WHO. (2011). Guidelines for drinking-water quality, recommendations (4th ed.). Geneva: World Health Organization.
Wu, F. C., Tseng, R. L., & Juang, R. S. (2009). Initial behavior of intraparticle diffusion model used in the description of adsorption kinetics. Chemical Engineering Journal, 153(1), 1–8.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Materials Research Centre, Malaviya National Institute Jaipur for providing all the characterization facilities needed for this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mondal, P., George, S. Removal of Fluoride from Drinking Water Using Novel Adsorbent Magnesia-Hydroxyapatite. Water Air Soil Pollut 226, 241 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2515-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2515-2